MANLY MORAL ORDER
A couple of brief cultural messages and true tales about Manly Moral Order -- from
Xenophon's Anabasis, The Journey Up-Country, The Story of the 10,000
Cast of Characters :
In 401, Xenophon, whose interests were primarily military, became involved in an attempt to overthrow the Persian Great King Artaxerxes II and replace him with his phil-hellene brother, Kyrus.
And so he joined a mercenary army, painstakingly assembled by Kyrus, of more than 10,000 Greek Hoplitai who marched "up country" -- that is, away from the coast, and into the interior of Persia.
There, near Babylon, a great battle was fought, in which the Greeks prevailed, but Kyrus was killed.
Without Kyrus to lead them, those Persians who had been part of his revolt swiftly defected to the Great King.
At which point the Greeks realized they were stranded in the midst of a very large and very hostile enemy.
And their situation became even worse when the Persians, who'd claimed to be willing to escort the Greeks back to the coast, and with whom the Greeks had a truce, suddenly and treacherously seized and killed the five Greek generals who'd headed up the army.
After a night of despondency -- of athumia -- of want of fighting spirit -- Xenophon emerged as the Leader who could and would rally the troops to Fight their way out of Persia.
Not by trekking west back to the Ionian coast -- but by a grueling journey north -- to the shores of the Black Sea -- where there were Greek cities and colonies.
Years later, living safely and contentedly on an estate gifted him by the Spartans, Xenophon wrote an account of that journey, an account known as the Anabasis.
The two cultural messages presented here are excerpted from Xenophon's Anabasis.
And at this point in that story he's now in more-or-less over-all command of the 10,000.
Cheirisophos -- the accent in his name is on the second syllable -- Chay REE so phos -- and Xenophon worked very closely and, except for one instance, amicably together -- Cheirisophos was in charge of the vanguard of the 10,000 as they Fought their way out of Persia and back to Greek territory.
The name Cheirisophos is a combination of cheir = hand + sophos = skilled ; most likely, and given that most Spartan names were combative, Cheirisophos means Skilled in Hand-to-Hand Fighting.
Pleis derives from Pleistos = most + Sthenes = Sthenos = strength, might, of all kinds moral as well as physical -- Place THE nes -- the most strength, the most might -- the name, aggressive and combative, spells out the Warrior's strength and power.
And the tios may be a diminutive meant to give him human stature -- a Human Dragon, a Human Python.
Drakontios -- the accent in his name is on the second syllable -- Dra KON tios -- had been "exiled from home as a boy because he had accidentally killed another boy with his whittle" -- the whittle, called a Xuele, which was part of a Lakonikan soldier's kit, was used for whittling wood, and especially spears ; it could also be sickle-shaped, and Spartan boys indulged in Sickle Fights in which, sometimes, one of them got killed :
Two boys were fighting, and one of them wounded the other mortally with the stroke of a sickle [Xuele.] The friends of the wounded boy, as they were about to separate, promised to avenge him and make away with the one who had struck him, but the boy said, 'Do not, by the Gods, for it isn't right ; the fact is, I should have done that myself if I'd been quick enough and brave [agathos -- Manly] enough.'
Drakontios is put in charge of the Gymnikos Agon -- naked athletic games, held to Honor the Gods, and in thanks for deliverance from Persian territory -- and as you'll see, like any Spartan, Drakontios likes his games Fought Rough and Hard.
First Cultural Message
[4.6.1] When seven days had passed, Xenophon gave over the village chief to Cheirisophos to act as guide, leaving his family behind with the exception of his son, who was just coming into the prime of youth [hebasko -- to enter puberty, come to man's estate, come to one's strength, Lat. pubescere] ; this son he gave [as a hostage] into the keeping of Pleisthenes of Amphipolis, in order that the father, if he should serve them well as guide, might take him also back with him. Then, after putting into his house as large a quantity of supplies as they could, they broke camp and set out upon the march.
[2] The village chief [komarches -- archo of a kome], who was not bound, guided their way through the snow ; but by the time they were on the third stage Cheirisophos got angry with him for not leading them to villages. He replied that there were none in this region.
[3] Then Cheirisophos struck [paio] him, but neglected to bind him. The result was that he stole away during the night, leaving his son behind. And this was the only cause of difference between Cheirisophos and Xenophon during the course of the march, this ill-treatment of the guide and carelessness in not guarding him. Pleisthenes, however, fell in love with [eramai] the boy, took him home with him, and found him absolutely faithful [pistos].
~Xen. Anab. 4.6.1-3, translated by Brownson.
Bill Weintraub:
So -- what we see in the First Cultural Message is that the local boy, who'd been held as a hostage and abandoned by his father, is taken home by the Warrior Pleisthenes -- He Who Slays the Most -- He Who Has the Most Kills -- who has fallen in love with him, and who then finds him to be absolutely faithful.
The mention of male-male, of the Male Eros, is casual, and the emphasis is on Fidelity, and, given Pleisthenes' name and the fact that he's a mercenary, on Martial Ardor and Manly Might.
Pleisthenes falls in love with the boy who's been abandoned, takes him home, and finds that the boy returns his act of kindness with Absolute Fidelity.
Again, a cultural message -- taken from a real-life event.
. . .
Second Cultural Message
[4.8.25] After this they made ready the sacrifice [thusia] which they had vowed [euchomai] ; and a sufficient number of oxen had come to them so that they could pay their thank-offerings [hegemosuna] to Zeus for deliverance [soter], to Herakles for guidance, and to the other Gods according as they had vowed. They instituted also athletic games [gymnikos agon -- nude athletic games] on the mountain side, just where they were encamped ; and they chose Drakontios [Drakon -- a Dragon, a Serpent of huge size, a Python], a Spartan, who had been exiled from home as a boy because he had accidentally killed another boy with the stroke of a dagger [Xuele -- a whittle, a curved knife used in shaping a spear or javelin ; a sickle-shaped dagger], to look out for a race-course [dromos] and to act as manager of the games [prostateo tou agonos -- Steward of the Games].
[26] When, accordingly, the sacrifice had been completed, they turned over the hides to Drakontios and bade him lead the way to the place he had fixed upon for his race-course. He pointed out the precise spot where they chanced to be standing, and said, "This hill [lophos -- crest of a hill, ridge] is superb for running, wherever you please." "How, then," they said, "can men wrestle [palai-o] on ground so hard [skleros] and overgrown as this is?" And he replied, "The one that is thrown [katapalai-o] will get hurt [aniazo -- distressed] a bit more." [a truly Spartan response]
[27] The events were, a stadium race [stadion] for boys, most of them belonging to the captives, a long race [dolichos], in which more than sixty Cretans took part, wrestling [pale], boxing [pugme], and the pankration [pankration] ; and it made a fine spectacle [kalos thea -- a Noble and Beautiful Spectacle] ; for there were a great many entries and, inasmuch as the comrades [hetairoi] of the contestants were looking on, there was a great deal of rivalry [philonikia].
[28] There were horseraces also, and the riders had to drive their horses down the steep slope, turn them around on the shore, and bring them back again to the altar. And on the way down most of the horses rolled over and over, while on the way up, against the exceedingly steep incline, they found it hard to keep on at a walk ; so there was much shouting [krauge] and laughter [gelos] and cheering [parakeleusis].
~Xen. Anab. 4.8.25-27, translated by Brownson.
This cultural message is simply about the Ubiquity of Fighting among Boys and Men.
Drakontios, who'd been exiled because he accidently killed another boy with his whittle, is chosen to supervise the Games, which are both athletic and religious.
A typical Spartan, he's rough and tough.
It doesn't concern him that the Fighting Surface is hard -- the guy who gets thrown will just get hurt a bit more, he says.
The Games consist of Foot Races, Horse Races, and Boxing, Wrestling, and Pankration -- all run and Fought in the nude.
Xenophon says the spectacle was Kalos -- Noble and Beautiful : there were many contestants, and because their comrades were watching, there was a great deal of rivalry, of PhiloNikia -- Love of Victory, Rivalry, Contentiousness.
Rivalry and Contentiousness are Good ; Fighting is Good.
PhiloNikia -- Love of Victory -- and PhiloNeikia -- Love of Strife -- are like PhiloTimia -- Love of Honour -- they're Good, because they help Men realize the arrival, the Adventus, of their Manhood, their Fighting Manhood.
And Fighting Manhood is the Best Thing in the World.
Fighting Manhood is the Best Thing in the World.
In the Kynegetikos, the Hunting with Hounds, Xenophon says that
And in the Lakedaimonian Constitution, he says
All Men.
At the Games, the Men, who are all battle-hardened soldiers, and far, far from home, shout, laugh, and cheer for what they see among their comrades.
They're Men among Men, Fighting Men among Fighting Men -- and they're Happy.
Somewhere among them is Pleisthenes, and his Boy -- who's been liberated from his family, and found a home with a Warrior -- and his fellow Warriors.
Pleisthenes, and his Boy, are Happy too.
And their fellow Warriors are Happy -- for them.
Pleisthenes is also the name, in the Iliad, of the Atreid father of Agamemnon and Menelaus.
Πλεισθενης
Aside:
Smith, in his Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology (ca 1873), identifies Plei-sthenes with Epi-sthenes of Amphipolis, commander of Peltastai at the battle of Cunaxa [Xen. Anab. 1.10.7].
Translation : Smith thinks Epi-sthenes of Amphipolis and Plei-sthenes of Amphipolis are the same person, confused into two people by some medievally monkish copyist.
So does a classicist named Dillery, who revised Brownson's 1922 translation in 1998.
And maybe they are.
That would explain why Episthenes / Pleisthenes is put in charge of the young Armenian hostage at 4.6.1 -- that is, because he commands or has commanded the peltasts -- he's not just another grunt among ten thousand, in other words, but an officer of high rank and proven ability.
That said, does it matter whether the Warrior's name was Episthenes or Pleisthenes?
No.
But if they are the same person, it then becomes the case that Xenophon praises the Warrior -- in both Love and War.
Which is quite Xenophontic -- that is to say, the sort of thing Xenophon often does because he likes doing it.
And that's not a small point.
To Xenophon, if a Man is a good Warrior, he'll also be a good Lover, that is, a good practitioner of the Male Eros.
So if he can praise a Man as both a good Warrior and a good Lover, he will.
Cf, in that regard, Xenophon's recounting of the story of the Spartans Archidamus and Kleonymus, and his account of what happened when the Spartan Anaxibius was ambushed by Iphicrates -- as referenced by Smith.
Brownson's translation says of Anaxibius that "his favourite youth . . . fought and fell with him," but the Greek says that his paidika -- "his darling, his favourite, his male lover, stayed beside him . . . and there fought and fell."
Notice too that Anaxibius' record of service to Sparta in the Hellespont in 400 BC was decidedly mixed ; but by electing, in 389, to fight and die at his post, he achieved at the moment of his death, a kalon --a morally beautiful, because selfless, act -- which, in the ancient world, had the effect of wiping out any prior mis-steps and mis-demeanors, and guaranteed that, Anaxibius, like Aristonicus, would be remembered as having fought and died gloriously.
Inevitably, in the ancient world, every such Warrior act of aphilopsychos -- of disregard and contempt for mere life -- refers back to Achilles' decision to avenge his fallen lover Patroklos, even though so doing will bring about his own death.
That decision doesn't simply honor Manhood, the most important Idea, the Idea-of-Good, and the Sanction, of the Warrior World of Being -- but elevates Manhood - Manliness - Manly Spirit to an unassailable, an indomitable and invincible position over any world-of-becoming pleasures which might be lost to death.
Plutarch:
. . .
In some cases, even when there is no need for it, Erastai [Lovers] are moved to exhibit their love of danger [philokindunos], their disregard for mere life [aphilopsychos].
And that's what Anaxibius, in the presence of and joined by his paidika, does -- exhibits his love of danger and disregard for mere life.
As Achilles did before him.
It's what Manhood requires -- of Men.
See also:
And note that Episthenes of Amphipolis should not be confused with Episthenes of Olynthus, the paiderastes who, in yet another demonstration of true Warrior aphilopsychos, invites the rather boorish Thracian King Seuthes to chop off his head rather than kill a handsome youth.
Επισθενης Ολυνθιος
Finally -- there's something else which needs saying.
Xenophon says of these Games organized by Drakontios that they "made a fine spectacle [kalos thea -- a Noble and Beautiful Spectacle].
Classicist John Dillery, who revised Brownson's 1922 translation in 1998, in turn says, in a footnote, that this is the main point : That "the ordered, successful army holding athletic games [gymnikos agon] is a thing of beauty."
By which he means, clearly, as a Greek would, a kalon -- a thing of moral beauty.
To Xenophon, the ordered, successful army, holding athletic games, is a thing of moral beauty.
As it should be to us.
Bill Weintraub
16 March 2023
By
Bill Weintraub
Before Manly Moral Order was posted, Warrior Naked Wrestler, whom we call NW, had written to me about a nun who had had control of his early Catholic School education, a nun whom we call sister vicious viola, because she'd been sadistic towards him and his brothers.
It was the second time he'd written to me about her, and I wanted to present to him a very different and Man-focused upbringing and life, that of the Spartan Drakontios, as an alternative to the one NW had suffered through at the hands of the nuns in Catholic School.
So I put together and posted Manly Moral Order.
NW and I then had an email discussion about that post, and esp Drakontios ;
Here are five of those emails :
EMAIL 1, Bill Weintraub to Warrior NW :
Hi NW,
It never seems to occur to you that just as there was an organized religion behind sister vicious viola --
there was an organized religion behind Xenophon and Drakontios.
And there still is.
Religion -- Faith -- matters.
It teaches us that there are greater powers in this world -- than ourselves.
Cicero :
Lord Ares is one of those Powers.
Lord Ares is the God of Fight, of Manhood, and of Fighting Manhood.
And He was a tremendously powerful force in the lives of both Xenophon and Drakontios, who both, being Spartans by adoption and birth, worshipped Him.
sister viola worshipped a god of pain and humiliation
Xenophon and Drakontios worshipped a God of Warrior Might and the Blessedness of Warrior Pride.
We don't know the whole history of Drakontios, but we know that he killed another boy in a Fight.
A Sickle Fight.
Xenophon knew that too, and obviously, it not only didn't bother him -- but he liked it.
Xenophon was a Warrior and a Leader of Warriors.
He worshipped a God of Fight.
And he took under his wing a boy who'd killed another -- in a Fight.
You need to think that through -- all the way through :
The athletic games which Xenophon and Drakontios created, combat sport games, dedicated to the Gods Zeus and Polydeukes, Herakles and Hermes, and others, were kalon and kalos, a thing of moral beauty, of bodies well made and deeds of Fight -- well done.
The Games were presented to a victorious army, in a state of good order, harmony, discipline, and restraint.
Throughout the army, the Men could Love whomever they wanted.
While the Spartans -- the same guys who had endured the whipping contests at the temple of Artemis -- came from a culture which mandated male-male love affairs for its teenagers.
And celebrated the victories of its sons with iron sickles -- mounted on slabs.
Their culture was pro-Man -- and pro-Fight.
NW, I've attached a pic of a statue of Lord Ares, God of Fight.
That statue was created in 425 BC.
The Anabasis began in 401 BC.
THINK IT THROUGH.
In the statue, Lord Ares is gazing downward, lovingly, at the body of a younger person -- probably a teen-aged boy.
Like Drakontios.
THINK IT THROUGH.
EMAIL 2, Bill Weintraub to Warrior NW :
Hi NW,
What do sister viola and the terrorists in isis have in common ?
They're both followers of Abrahamic faiths -- Christianity and Islam -- and they're both extremely intolerant of our Greco-Roman heritage and traditions.
Esp of male-male.
And the Xenophon - Drakontios story is a male-male story.
Xenophon shows special favor to Drakontios when he appoints this homeless boy Steward of the Games.
And the Men in their orbit on the anabasis would have known that :
That Xenophon and Drakontios liked each other.
Just as they knew that the boy Pleisthenes adopted liked him -- and was loyal to him.
Was Drakontios a naked wrestler ?
Yes.
They all wrestled and they all wrestled naked.
Was sister viola a naked wrestler ?
No.
Nor was she into male-male.
You have a lot in common with Xenophon and Drakontios.
You have nothing in common with that wretched nun, but you keep bringing her into the conversation.
You'd be far better off if you forgot the ugly sister, and spent your time trying to understand the athletic, often naked, boy Drakontios, and the world in which he lived.
The Naked Games of which he was steward, and the Gods the Games were dedicated to.
Hermes, Polydeukes, Herakles, etc.
And Lord Ares too.
And his statue.
Drakontios would have seen the statue of Lord Ares in the agora in Athens.
Xenophon would have grown up with it.
They both would have known that the Lord Ares of that statue trained at the Palaistra in Athens.
Trained in Boxing, Wrestling, and Pankration.
As well as in War Games.
That he trained genitally nude.
Just as his statue is nude.
Both Xenophon and Drakontios were taught that the male genitals were sacred, holy, blessed, worthy of reverence and awe.
And they believed that.
Being determines consciousness.
When you spend your time with Xenophon, Drakontios, Ares -- they become your consciousness.
Their naked athleticism, their muscular homoeroticism, their cocks and balls.
Naked and Holy.
Look at the pix of Lord Ares.
Think of how many years of Nude Fighting it took him, from boyhood to late adolescence, to develop his body -- and in particular -- his massive glutes :
And think how much power he could generate with those glutes -- the power to strike with both hands and feet.
And look at the birth of a star.
It looks like male parthenogenesis to me.
And don't miss the ephebes -- the young military Men -- training nude.
EMAIL 3, Warrior NW to Bill Weintraub :
SUNDAY
Bill,
I sat down and read your Xenophon/Drakontios write-up from 12 July 2023. I print those things out to read them off the page slowly. It is the only way to take it all in.
Reading all that makes me think I could have been there. It took me a lifetime to grasp and realize that watching and anticipating and then participating in totally naked one-on-one, skin-on-skin, naked balls and cocks combat WAS a completely normal and beautiful thing. It was absolutely in tune with nature and human male nature.
For YEARS I hated myself for it and I kept the whole thing in my mind. NEVER sharing it with anyone. No one.
A 3 minute shirtless aggressive grapple with another boy on the mats could instantly and easily make my teenage cock get rock hard. It was a completely natural and positive response to the challenge and the fight. And the culture (the unwritten rules) made me ashamed of that. So I had to hide it from anyone.
As I am now older, it is frustrating to realize that back in my youth that I was completely spot-on. And that the culture was wrong. And that it was the anti-natural-male culture that I lived in that was -- and IS -- out of sync with nature and out of sync with natural law.
Check out the manly beauty of the fight below. What you cannot see is their beautiful man-testicles and their beautiful man-phalluses that drive them to fight in the first place, their beautiful Manhood between their legs.
That pic would give any normal boy or man a throbbing boner. In a culture in-tune with nature -- which we are not -- there would be no shame in that.
Let that sink in.
EMAIL 4, from Bill Weintraub to NW :
Hey NW,
You've come a long way.
But you're still ignoring the Gods.
Yet without the Gods, there's nothing.
Lord Ares is the God of Fight.
Fighting confers Manhood.
Lord Ares is the God of Manhood.
Manhood enables Fighting.
Ares, Mars, Tua, Polydeukes, Kastor, Hermes, Herakles -- all Gods of Fight.
Without the Gods of Fight, there's no Fight.
There's nothing,
With the Gods of Fight, the veils are torn away.
And there's everything.
This just in from the anabasis :
[6.6.30] Thereupon the troops resolved to send the generals and captains, Dracontius the Spartan, and such others as seemed fitted for the mission, and to request Cleander by all means to release the two men.
Once again Drakontios the Spartan, the boy who killed another while Fighting nude with sickles, is chosen for a sensitive diplomatic mission, this time to Kleandros, the Lakedaimonian general in charge of Byzantium.
Why Drakontios ?
EMAIL 5, from Bill Weintraub to NW :
DRAKONTIOS
When we first met Drakontios the Spartan, the boy who killed another in Nude Armed Combat, Nude Sickle Fight, he'd been given the high religious post of Steward of the Games.
Games which the 10,000, whom Xenophon always refers to as "the army," were celebrating to Honour the Gods who helped them reach the sea and the possibility of getting home.
Even if Drakontios was Xenophon's beloved or delicia or whatever, it's not like Xenophon to assign such a sensitive and religiously-important job to an airhead.
Drakontios obviously had other qualities which made him worthy of the post.
And we see this to be true in the next mention of Drakontios, which takes place some months after the army has arrived at the Black Sea.
So :
The coast of the Black Sea turns out to be another difficult and conflictful environment for the army.
There are more barbarians and other native peoples there, none of whom are easy, and there are Greek cities, all of which are controlled by the Lakedaimonians, aka the Spartans.
The Lakedaimonians, who possess the keys needed to get the army back home, are initially very wary and suspicious of the army,
Because the army is composed of 8,000 heavily armed Men, Hoplites, many of them from the Peloponnesus, which is where the Lakedaimonians are from, known to be the roughest and toughest Fighters in all of Greece.
Potentially, they're a threat to everyone who crosses their path, and Xenophon has to be constantly calm the concerns of other officials while keeping his Men, who are restive, under control.
That they be disciplined and controlled is key to the Lakedaimonians, who will not work with them unless, like full-bred Spartans, raised in the agoge, they show themselves to be subject to discipline, harmony, order, restraint.
In short, the Spartans will work with an army, but not a rabble.
And now an incident occurs which suggests they are just a rabble.
You can read about that starting here :
It seems minor but it isn't.
And it threatens to undermine all of Xenophon's hard work with Cleander -- the Greek is Kleandros -- the Spartan Harmost or Governor of Byzantium.
He's the most important Spartan official on the coast.
And Xenophon has to be very diplomatic in dealing with him.
Eventually, he and Xenophon become friends.
But, if you take the time to do the reading, you'll see that it wasn't easy for either ot them.
In any case, that Xenophon entrusts Drakontios with a diplomatic mission to Kleandros speaks volumes about Xenophon's high opinion of Drakontios, who was once a boy who killed another in nude sickle fight.
The episode says a great deal about the Greek attitude toward Fighting, Nude Fighting, and Sickle Fights, and the boys who engage in them, even unto death.
Overseeing that Nude Mortal Combat are the Gods, the Gods of Fight, who decree that Men should Fight Nude.
As They do.
The great Roman poet Statius has a phrase about this :
"nudamque lacessere pugnam"
which means "and incites to nude fight"
nude combat
pugnam nudam
The Gods incite Men to Nude Fight.
Including you.
In America, in the old days, when two guys wanted to Fight they stripped off their shirts and exposed their pecs and abs.
In Greece and Rome, the Men Stripped -- and exposed all, including their cocks and balls.
And if the Nude Fight was with Sickles, and there was damage to the cocks and balls, so be it.
NW :
Reading all that makes me think I could have been there. It took me a lifetime to grasp and realize that watching and anticipating and then participating in totally naked one-on-one, skin-on-skin, naked balls and cocks combat WAS a completely normal and beautiful thing. It was absolutely in tune with nature and human male nature.
For YEARS I hated myself for it and I kept the whole thing in my mind. NEVER sharing it with anyone. No one.
A 3 minute shirtless aggressive grapple with another boy on the mats could instantly and easily make my teenage cock get rock hard. It was a completely natural and positive response to the challenge and the fight. And the culture (the unwritten rules) made me ashamed of that. So I had to hide it from anyone.
As I am now older, it is frustrating to realize that back in my youth that I was completely spot-on. And that the culture was wrong. And that it was the anti-natural-male culture that I lived in that was -- and IS -- out of sync with nature and out of sync with natural law.
Check out the manly beauty of the fight above. What you cannot see is their beautiful man-testicles and their beautiful man-phalluses that drive them to fight in the first place, their beautiful Manhood between their legs.
Bill Weintraub :
"The beautiful Manhood between their legs"
That's right.
The beautiful Manhood, the beautiful cocks and balls, between their legs that impels them to Fight --
That's what the Gods want you to see.
The Beautiful Manhood of Men, both physical and spiritual, that compels and impels them to Fight :
Get rid of the twisted sister.
She's in the way.
She's opposed to the Gods, to Men, to Manhood and Manliness and Masculinity, to Virilitas and Pugnacitas, and to everything else we believe in and worship.
Get rid of her.
The Gods detest her.
Replace her with Drakontios.
Whom the Gods love.
The Spartan Boy who so trusted the Gods they he Fought Nude, with Sickles, against another Nude Spartan Boy -- for Domination and Control.
He won.
Not just the Fight, but his life.
He was exiled, but he didn't let that stop him.
Soon a Man himself, he joined up with other Fighting Men, Men who Fought Nude as he did, to Fight for the Freedom of the Greeks.
And he prospered.
Constantly surrounded by the cocks and balls and sweat and stink and blood of Fighting Men --
The Gods smiled upon him and he prospered.
Bill Weintraub
17 July 2023
THE SCENT OF THE FIGHT
This is a great pic. It's a visual of the ManScent that Men pick up from each other in a combative contest.
It's part of the experience in Wrestling and of the physical contact in stand-up Fighting when the Fighters come together in sparring or in a Boxing match.
They pick up the scent from each other either consciously or unconsciously.
It's always there. It's the scent of manliness, the scent of bodily aggression of two male bodies, and it's the scent of Men physically bonding-in-fight. And it leads to Eros, the God of romantic passionate love between Men. In the case of Fighters, that scent is part of the attraction that guys have for each other when they physically connect and sweat during a one-on-one match up.
That scent of mansweat-in-fight is an aphrodisiac.
Of course the vast majority of fighters would NEVER admit to it; our modern culture would never allow that.
Men might admit to the sensation the other man's scent has as an attraction for the other guy if they were in absolute privacy. Maybe.
In this Fight the bottom man is about to get finished off. Everything comes together at the end of the Fight : the Aggression, the hits (to the face), the ManScent of ManSweat, the mingling of each Fighter's Sweat, and the beautiful display of Manly Muscle made possible by Testosterone.
The Fighter is a thing of beauty. And the Fighter has a beautiful scent that you can only experience if you are in the Fight.
NW
20 July 2023
HARD HITS IN THE ARENA AT PALMYRA
This pic of the arena in the Roman town of Palmyra, which the present-day terror group ISIS tried to destroy, caught my attention. A Greek style theater, built by the Romans, it has a lot of arch work in the structure. It is magnificently preserved. It must have been aways out of reach of vandals, thieves, barbarians, and christians.
What caught my attention is the barrier wall separating the "stage" from the seating area. Not just a theatre, this place would also have been used for Gymnikos Agon -- Naked Struggle -- Festivals and their exhibitions of Nude Wrestling, Boxing, and Pankration --
and for Gladiatorial Fights as well.
It reminded me of the few times that I have sat directly next to the Fight Cage or Ring of an MMA Fight, close enough to touch the deck and to hear the Smacks and Thuds of the Dudes taking Hard Hits to the Body and Face. THERE IS NOTHING SO EROTIC. I remember sitting so close at some events to not only Hear the Hits, but close enough to occasionally get doused with FightSweat, FightSnot and FightBlood as the Young Men Slugged Each Other's Faces, just inches from me. NOTHING LIKE IT.
The Fight produces Eros.
NW
20 July 2023
WRESTLING AND BALL SACKS
Being in an all-male wrestling room packed with sweat-covered paired-up wrestlers made to repeat this move over and over, 10 times each and then switching positions -- is like nothing else ever.
It's a thing you do when being trained in wrestling.
Wrestling is about balls. And in a room full of shirtless wrestlers it's what you do.
It CAN give you a hard-on because it absolutely forces you to think about the manliness of the man-to-man contest. It is natural to be turned on by the fight.
Wrestling forces you to think about your ballsack and it forces you to think about the other man’s ballsack.
In the wrestling room you're almost naked.
No shirt, just shorts, which frequently ride-up and expose the balls.
One day we might again wrestle like the Greeks and Romans.
Naked and unashamed.
NW
20 July 2023
Two Muscular, Nude, Armed, Youths -- Each About to Strike the Other.
It's affirming to me -- of what Man Against Man and Male Against Male should be -- every time I see it :
Naked, unashamed, unafraid
Nude, Proud, Brave
When the Boys Fight, they Fight for their Honour and the Honour of all Men.
That's what the Gods have taught them to do ;
That's what the Gods want them to do.
That's what the Gods provoke them to do.
The Roman Poet Statius :
nudamque lacessere pugnam
and provoke to nude fight
nude combat
pugnam nudam
The Immortal Gods of Fight incite and provoke the Fighters :
To Fight for their Honour and the Honour of all Men
Naked, Unashamed, Unafraid
Bill Weintraub
25 July 2023
NAKED COCK AND BALLS
Everytime you take a step
everytime you move in your chair
everytime you adjust your position in bed
you can feel your cock and balls
That heaviness between your legs is a constant reminder from
the Gods -- that you're a Man.
With a ManCock and ManBalls.
Ever present, always there for you.
The Gods don't want you to ever forget that.
the twisted sister didn't have external genitals
You do.
And so do the Warrior Gods.
When you look at this statue of Lord Ares, his Warrior Male Genitals
are there for you to see :
As is the knowledge that that statue, before it was the statue of a
God, was a statue of the Palaistra-trained body of an athletes, a
combatant in Gymnikos Agon, the Strenuous and Brutal Naked Struggle of
Boxing, Wrestling, Pankration.
Naked
Unashamed
Unafraid
All your life NW, the Gods have provoked and incited you, as they
have all Men, to Naked Fight.
Because they want to see you, as you see them,
Nude
Proud
Brave
Naked
Unashamed
Unafraid
Bill Weintraub
25 July 2023
NW CICERO
"MASSED EPHEBIC BATTLES" -- TUSC DISP 5.77 :
Spartan youths utter no cry when their bodies are mangled with painful blows ; PLATO
"ENDURANCES OF PAIN, MANIFESTED IN HAND-TO-HAND COMBAT AMONG THE YOUTHS" -- LAWS : I.633 B-C
SPARTA
"THE INCULCATION OF COURAGE AND ENDURANCE"
Inculcate : to instill (an attitude, idea, or habit) by persistent and repeated instruction
KENNELL
"THE PREPONDERANT EMPHASIS SPARTANS PLACED ON PHYSICAL TRAINING EVEN IN THE LATER AGOGE "THE TRIAD OF PHYSICAL TRAINING, ENDURANCE, AND COURAGE [APPEARS IN PLATO'S LAWS]"
"THERE EXISTS AN IDEOLOGY OF PHYSICAL CULTURE IN HELLENISTIC EPHEBATES AND THE LATER AGOGE ... "
BILL WEINTRAUB
EACH OF THE VARIOUS CITY STATES HAD ITS OWN VERSION OF THE EPHEBATE, BASED IN THE GYMNASIA, Gymnasia were usually the highest Bill Weintraub :
Now, I've often said to you that we could revive the conditions under which Men lived in Sparta.
A case in point is Roman Sparta (146 BC to 395 AD), about which we know a lot, mainly because of the inscriptions on slabs of stone known as Sickle Dedications, and other inscriptions, such as those found on the base of statues and other public works, inscriptions to ephebes and former ephebes such as Battle-Ball Players and Endurance Contest Victors.
Prof Kennell in The Gymnasium of Virtue :
We can now sketch the outlines of the agoge's structure in the Roman period. All boys belonged to one of five age grades and were also enrolled in one of the five tribes, with each tribe containing members from all the grades. In each grade, the boys formed bouai [Herds of Young Bulls], probably one for each tribe, under the leadership of one of their number, who served as Bouagos [Head of the Herd of Young Bulls]. The post was, as a rule, an annual one, for we know of a boy who was the fellow ephebe of two different Bouagoi.
During their years in the agoge, the ephebes contended in the various competitions, festivals, and mock -- but violent -- battles either individually or as members of a boua or phyle [tribe], until, in the eiren year [that is, the last year], the boua turned into the tribe's team for the ball tournament, while their bouagos became the team's captain and the ephebic tribe's leader. After completing the game, the youths officially left the agoge and performed their first public act as young adults (sphaereis -- ball players), a sacrifice to Herakles, God of physical endurance and success in the face of adversity.
The relationships that developed among ephebes in the agoge had a semi-official character that lasted a lifetime. Returning to the fellow ephebes noted earlier, we find a large number of adult Spartan notables identifying themselves as fellow ephebes (syn-epheboi) of particular men who had been bouagoi. The title syn-ephebos appears in catalogs of magistrates as well as individual careers from the Flavian period onward. The relationship appears to have had overtones of patronage and dependency ; bouagoi (or their parents) sometimes paid the expenses for erecting honorific stelai the city had voted for their fellow ephebes, and one year a bouagos and four of his syn-epheboi had the good fortune to form the board of keepers of the laws (nomophylakes). We should perhaps envision the bouagos acting as a sponsor of sorts for the members of his boua. . .
The ephebes in these ranks were not, of course, left to their own devices. Close supervision had been fundamental to the Classical agoge, and the situation was no different during the Roman period. We have already met the Spartan equivalents of the prefects of twentieth century schools -- the bouagoi, who led the members of the bouai under them.
That there was more than one boua for each age grade is proved by a sickle dedication erected by two bouagoi of the mikkichizomenoi [sixteen-year-olds], who had been victorious in the same year.
The age of the bouagoi has been controversial for many years, some asserting that bouagoi were older than their charges, the other that they were coevals. ...
The tribe -- phyle -- was the only ephebic grouping to span more than one age grade. The eiren, who commanded boys of differing ages, was therefore not the leader of the herd (boua), but of the tribe (phyle). The eiren who bore this responsibility was known as the tribe's senior (presbys), a title known from a statue base and from the sphaereis dedications, where the senior appears as the team captain. If we accept the idea that the boua of the eirenes grade in each ephebic tribe transformed itself into an oba of sphaereis for the ball tournament, then the oba's captain would have been none other than the bouagos of the boua, who already acted, ex officio, as head of the entire ephebic tribe.
Not only did the agoge require elected magistrates and officials to function effectively, but also trained faculty and staff. A few of the functionaries appear on inscriptions : teachers concerned with the Lycurgan customs to instruct the youths in their heritage, drill instructors to teach them the martial arts, and physical trainers to keep them fit. The curriculum surely had some rhetorical and philosophical content as well, but given the primacy of athletics in later Greek education generally, and its overwhelming prominence in the traditions of education at Sparta, nothing explicit has survived. This does not mean that Sparta was an intellectual backwater ; in fact, a recent study has shown that from the late Hellenistic age onward, Sparta had an intelligentsia of its own and drew thinkers from all over the Greek world.
We must also keep in mind that the ephebes, drawn up by boua and tribe, commanded by their bouagos and presbeis, disciplined by their teachers, and guided by the senior magistrates of the agoge, were merely part of a larger picture.
Greek urban culture had been dominated by the gymnasium [and its Fight Sports] for centuries. As the centers of physical and literary training, the gymnasia assumed an importance visible even today in the immensity of their ruins. Sparta did not stand apart from this trend : the city was studded with gymnasia, which had to be maintained and staffed.
Ephebes would have made up only a portion of their clientele ; the rest were professional athletes and local enthusiasts who could not bear to forsake the camaraderie of ephebic life. Elsewhere in Greece, such people formed organizations of young men [neoi] who met together and kept up with the old exercises. At Sparta, those past ephebic age belonged to an association of neaniskoi, headed by a neaniskarches. The sphaereis, as ex-ephebes, would have formed a contingent within the neaniskoi, since neoi were usually young men older than twenty, but younger than thirty years old, the age at which they would normally assume the responsibilities and privileges of full citizenship.
Bill Weintraub :
Please see the pix below from Book V of Manhood : A Lexicon.
Moral Values were taught at the Gymnasia, where Fight Pits were literally core.
As we discussed in the Prolegomena, the Palaistra evolved from being a Fight School to being an All-Around School -- the Gymnasion -- but Fighting remained literally core to its function.
Gymnasia were usually the highest The classrooms were built around a central court which contained Fight Pits -- skamma.
The students in the open-air classrooms could see Kennell : The Spartan curriculum was heavily weighted toward physical education Apart from the overwhelming prestige of athletics in Greek culture since the Bill Weintraub :
Fighting was core to the Gymnasion and all education in ancient Greece.
Thus, the Gymnasion of Virtue :
That nude training was understood by the Greeks to be an An-amnesis -- an Un-forgetting.
Bill Weintraub
January 2024
The students in the open-air classrooms could see Kennell : The Spartan curriculum was heavily weighted toward physical education Apart from the overwhelming prestige of athletics in Greek culture since the Bill Weintraub :
The Forms are the Platonic Ideas or Ideals which exist in the World of Being, which for Fighting Men is the Warrior Kosmos.
The Truth of the Forms becomes visible through images created by the Gods, So :
The Ideal Form is Man.
At the core of the Form Man is another Ideal Form, Manliness, Masculinity,
Manhood, Fight is core to Man, as can be seen in these young Men, The Ideal Truths of the Warrior World of Being, the Warrior Kosmos, may be forgotten by Males When that happens, the young Warrior can be re-awakened to the Truth of his Manliness Every Ephebate of the Combatant Cosmos is dedicated to this disciplined AN-amnesis, And that's because his body The Ideal of the Palaestra, The students in the open-air classrooms could see Kennell : The Spartan curriculum was heavily weighted toward physical education Apart from the overwhelming prestige of athletics in Greek culture since the Bill Weintraub :
The Forms are the Platonic Ideas or Ideals which exist in the Warrior World of Being, which Fighting Men call The Truth of the Forms becomes visible through images created by the Gods, So :
The Ideal Form is Man.
At the core of the Form Man is another Ideal Form, Manliness, Masculinity,
Manhood, Men Fight for Honour :
Aristotelian WD Ross :
"The Motive of Manliness is the Sense of Honour"
MEN FIGHT for HONOUR
So as to Assert and Defend their Rights --
Their Honourable and Manly Rights.
Both Ancient Greece, and Republican and Imperial Rome, were, historians, anthropologists, and sociologists agree, Honour Societies.
In an Honour Society :
Every Man, no matter his station in life, seeks Honour ;
Every Man, no matter his station in life, fears dis-honour -- that is, dis-grace and shame ;
Every Man, no matter his station in life, expects the strict and reciprocal return of a Favor, for that alone is Honourable ;
No Man, no matter his station in life, will tolerate an insult -- an outrage -- to his Honour ;
And every Man, no matter his station in life, will seek to honourably avenge an outrage, usually through physical violence.
Learn more about the Honourable education of Roman youth Which classicist Werner Jaeger terms the Man's "natural instinct for self-assertion."
And that's what it is.
Scholars like Jowett and Shorey who were born and had lived in the nineteenth century would have understood, viscerally, that the word "honour" was inextricably connected to the Manly ideas and ideals of terms such as "Moral Beauty," "Manhood," and "Manliness."
As is Fighting.
Is the Sense of Honour Fighting is inextricably intertwined with Moral Nobility, Masculine Virtue, Manly Goodness, Manhood, Manliness --
and Honour.
The Motive of Manliness -- Manliness is the Willingness and Ability to Fight --
The Motive of Aggressive Self-Assertion and Combative Self-Preservation through FIGHT --
Is the Sense of HONOUR.
And the Ultimate Vindication of Honour -- which always reduces to Manhood -- lies in Fighting.
Which the Stoics termed Man's "natural instinct for self-preservation."
And which classicist Werner Jaeger terms Man's "natural instinct for self-assertion."
Fighting : Self-Preservation ; Self-Assertion.
Which is why, to the Romans, this image is affirming.
Gladiators affirm Manliness.
They instantiate Manliness, they embody Manliness, they affirm Manliness.
As do Boxers and Pankratiasts.
So :
Honour reduces to Manhood aka Manliness.
Which is to say that Honour and Manliness are basically the same thing.
Fighting confers Manliness.
Fighting generates Honour.
Fighting generates Manliness.
Fighting confers Honour.
H Rackham :
Morality ([honestum] 'the honourable') is an End in itself ; the virtues are based on Reason and have their roots in human nature.
No translation can convey the double meaning of the word [honestum, 'honourable,' used as an equivalent of το καλον, 'the morally beautiful or good.' [See De Fin. II. 48, fn a.]
The Latin word honestum means both Moral Goodness and Moral Virtue -- and The Honourable.
The Greek word το καλον means both Moral Nobility and Moral Beauty -- and The Honourable.
So that Honour -- Manly Honour -- is an integral and inescapable part of the ancient world of the Greeks and Romans.
FIGHTING GENERATES HONOUR.
HONOUR ENABLES AND PROMOTES FIGHTING.
MAN AGAINST MAN FIGHTING.
Which, again, the Stoics termed Man's "natural instinct for self-preservation."
And which, again, classicist Werner Jaeger terms Man's "natural instinct for self-assertion."
Fighting : Self-Preservation ; Self-Assertion.
"Aggression and the beauty of guys who assert that aggression" -- as NW so brilliantly says.
Male Assertion -- and Male Aggression.
FIGHTING IS BOTH NATURAL -- IN ACCORD WITH MAN'S NATURE --
AND VIRTUOUS.
Fighting confers Virtue -- which is Manliness.
And Manliness enables Fighting.
FIGHT.
VIRTUOUS, HONOURABLE, GLORIOUS, FIGHT.
Bill Weintraub
14 April 2024
The Ideal Truths of the Warrior World of Being, the Warrior Kosmos, may be forgotten by Males When that happens, the young Warrior can be re-awakened to the Truth of his Manliness Every Ephebate of the Combatant Cosmos is dedicated to this disciplined AN-amnesis,
But, according to the German historian Hegel, writing in 1848 AD,
The objective work of art, the ideal of the athlete created by Greek sculpture, was preceded by the subjective work of art that was the living man, the trained body of the Olympian victor.
Werner Jaeger :
In other words, the "beautiful individuality" which is the law of early Greek art was determined and shaped by Greek paideia [culture] and its gymnastic [-- palaistraean --] ideal.
So :
Before this image was an objectve work of art, a sculpted statue with the Divine Name of Ares, it was a subjective work of art, a living Man who, through his strenuously-trained body, was a Victor in Wrestling, Boxing, and Pankration -- the three agones of the Palaestra and its Fight Festivals.
That Man, who became the model for Lord Ares, trained at the Fight School, the Palaestra, and was named Deinomachus.
And that's because his body The Ideal of the Palaestra, Just Naked Male Bodies Pitted Relentlessly Against Each Other.
Day after day, week after week, month after month, year after year --
The Boys -- and then the Youths -- and then the Young Men -- Fought each other.
Day after day.
And their Bodies became Perfect.
Aristotle : Through strenuous physical struggle, the human male develops into the perfect specimen of its species -- the Fighting Man, the Warrior, defined and delineated by his Fighting Manhood, his Victorious Fighting Manhood.
Men were Designed to Fight ;
Men are Destined to Fight :
Standing up to blows face to face, Fighting "at close quarters" -- bone aganst bone, muscle against muscle, flesh against flesh -- as do Wrestlers, Boxers, and Pankratiasts --
When Men Fight daily, their Bodies become Perfect, their Souls impervious to Pain.
Which is what Nature intends, particularly for adolescent boys.
As for other adolescent male animals.
By Fighting, their Bodies reach that peak of perfection which Nature wants and needs both for Sex -- and War.
By the age of 19, which is the age of the Ares of the Borghesi Ares :
He's full of Piss and Vinegar, He's Ardently Ready for both Combat and Reproduction, for both Ares and Aphrodite.
Ancient generals and other war leaders knew this and planned accordingly -- and the Palaistra and the works of art -- the objective works of art -- the statues and vase paintings -- are proof.
Virgil, Aeneid :
Force Finds a Way
The word Vis means :
Strength, force, vigor, power, energy, virtue ; Hostile
strength, force, violence, compulsion ; Plur, military forces,
troops
And it's very closely related to the word Vir -- which means :
a man, a man of courage, principle, or honor, one who
deserves the name of a man ; in military usage, Vir often refers
to a soldier -- a Warrior.
Man is Vir, Man is Warrior.
So to the Romans, Man and Force -- which is Violent Force -- which is also Virtue, that is to say, Manliness -- Man and Violent Force go together.
Violent Force is an expression of Manly Strength -- Strength that's Willing and Able to Fight.
Violent Force is an expression of Manliness.
The Romans are very clear about that.
So we have :
Fit = finds
Via = a way
Vis = Force
Fit via vis.
Force finds a way.
Just as a Man, a Fighter, a Warrior, finds a way.
Force Finds a Way
The students in the open-air classrooms could see Kennell : The Spartan curriculum was heavily weighted toward physical education Apart from the overwhelming prestige of athletics in Greek culture since the And no Fight without Virtue "a severe athletic contest involving a combination of boxing and wrestling,
The image you see is that of a God, a God in human shape :
NW :
All of these moves would be absolutely necessary in one-on-one combat on the battlefield -- until warfare became a technical endeavor.
Bill Weintraub :
Right.
So -- compare these wrestler glutes of 2024 AD
With those of Deinomachos in 425 BC :
To this day, walking and, in particular, running up stairs, such as the stairs in a stadium -- is a common exercise for wrestlers and other combat athletes who rely on their glutes, not just for strength, but for explosive, violent, bodily force.
Lord Ares is the God of Masculinity, and of
Masculinity's Explosive Violent Force
possunt [possum], quia posse [possum] videntur Today I was in the supermarket, and heard a lad of perhaps eight or nine years reading aloud Would a Spartan boy have done that ?
No.
First off because he wouldn't have been with his mother ;
but secondly because worth was determined not by price, Always.
Strong They Are, for Strong They Deem Themselves
Let's return to our examination of powerful Glutes and the strong Man :
The image you see is that of a God, a God in human shape :
Bill Weintraub :
Obviously the answer is Yes.
What's interesting is how many bodies like it we see in Greek art.
Clearly, the Palaistrean training, along with daily involvement in Gymnikos Agon Athletes-- Nude Combatant Struggle, or, if you prefer, Nude Fight Sport -- molded and shaped the male body in certain ways.
For example :
What's striking in this vase painting is the breadth of the youth's chest ;
And the very strong glutes and hams in his lower body.
We see that repeatedly.
For example, in this painting of two youths boxing, the victor has a broad chest and a strong lower body.
His arms, by our standards, are skinny.
But clearly they get the job done.
The same is true in this boxing picture :
The victor has a broad chest and strong glutes and hams.
As he does here :
And breadth of chest along with strong lower body can clearly be seen in these two pix of the culture hero Theseus.
And in this picture of Herakles :
Here are more pix of Gymnikos Agon Boxers :
Broad Chests ; Strong Glutes and Hams. I've been told that the breadth of the chest is a sign of early -- pre-teen -- training in Wrestling.
Which explains why we see so many spectacular pecs -- like these of Lord Ares / Deinomachos -- among the ancient Greeks, who all Wrestled.
At the same time, when we step back a bit, we can see that the pecs are proportional to the Athlete's -- and the God's -- body :
Please remember that Deinomachos was no more than nineteen when he modeled for the sculptor Alkamenes.
His beard was just coming in, and he was an ephebe.
And Autolycus was only sixteen when he won his victory.
He probably looked something like this :
Or maybe like this :
Or like this :
There was almost certainly a statue of Autolycus made at the time of his victory.
There were a lot of statues, forests of statues, in a place like Athens, statues of, among others, Combatant Victors in Gymnikos Agon -- in Nude Struggle.
The ancient Greeks had a word -- Kalon -- a term of admiration for Bodies Well-Shaped and Deeds -- and the Deeds are always Deeds of Fight -- and Deeds well done.
Kalon : Bodies well-shaped and Deeds well-done.
Twenty years after his victory, Autolycus was killed by the Thirty Tyrants.
And his statue may have been destroyed.
But twenty years after that, Xenophon wrote his Symposion, as a memorial to both Socrates, his teacher, and the boy victor in pankration Autolycus --
Who'd stood up to the Tyrants, unarmed and unafraid.
Kalon.
Autolycus' father, Lycon, was one of the prosecutors at the trial of Socrates.
But Xenophon wrote his book in praise of both Socrates and Autolycus anyway.
We should never underestimate the Power of Ethics, nor of Aesthetics --
Nor of Manliness --
Nor of Fighter Beauty --
Which is Brave Beauty.
Lord Ares is a God in Human Shape.
His Human Shape is the shape of a Human Male -- a Man.
That Manly Shape includes his external genitalia -- his Penis and Testicles.
And his broad shoulders and thick, muscular chest, his beefy delts, lats, and traps, his meaty levators and rhomboids, his massive glutes and hams, his powerful arms and legs.
And that's not an accident.
His Manliness is crucial to his Divinity, for He is the hypostatization of Fighting Manhood.
Fighting, which confers Manliness.
Lord Ares' areté, his excellence, is the uniquely Male, Manly Excellence known to us as Manliness, which is Fighting Manhood :
That's Liddell and Scott's definition ; and, Liddell and Scott add,
From the same root [ARES] come areté, ari-, areion [better -- stronger, braver, more Manly], aristos [best -- strongest, bravest, most Manly], the first notion of goodness being that of manhood, bravery in war; cf. Lat. virtus.
Again, that's Liddell and Scott's definition, which is, appropriately, excellent.
In the Alliance and Ares is Lord we define Areté / Areta as Manly Excellence, which is Manliness, which is Manhood, which is Manly Goodness, which is Manly Virtue, which is Manly Spirit, which is Fighting Manhood.
Werner Jaeger : Areté / Areta -- The uniquely Male, Manly Excellence known to us as Fighting Manhood -- exists in mortal man. Areté is mortal man. But it survives the mortal and lives on in his glory, in that very ideal of his areté which accompanied and directed him throughout his life.
Robert Barron, writing in The Wall Street Journal, 7 April 2023 :
Basic to the ascendant anthropology of the West's cultural institutions is the characteristically Gnostic view of self in relation to body. Instead of recognizing the givenness of the body as an inescapable ingredient in one's identity, we increasingly conceive of it as subordinate to the true self and hence endlessly malleable, subject to the dictates of the "real me."
Thus, though a person is in fact gendered all the way down, even to the level of the chromosomes, he imagines he can escape from his physicality through wishful thinking or surgical intervention, "becoming" a woman, despite the
irreducible maleness of his body. Instead of being an essential aspect of the true self, the body simply serves the true self and assumes a subordinate role. Accepting this dualist understanding establishes within the heart of one's personality a tension that continually generates anguish and frustration.
~Our Bodies, Ourselves, and Our Lord, by Robert Barron.
Bishop Barron leads the Roman Catholic Diocese of Winona-Rochester, Minn., and is founder of the ministerial organization Word on Fire.
That brief article from Bishop Barron elicited two letters in response :
FIRST LETTER :
Chromosome Isn't Everything
April 20, 2023
In "Our Bodies, Ourselves and Our Lord" (Houses of Worship, April 7),
Catholic Bishop Robert Barron makes clear that the Catholic Church has
always rejected the idea that you can have a "real self" that is not
manifested by your physical body. On that basis, he goes on to
forcefully assert that a set of XY chromosomes makes one irrevocably
male, end of story.
I assume, however, that Bishop Barron participates in a ritual during
which bread and wine, without any change in their atoms, become
literally transformed into the actual body and blood of Christ. That
seems like a heavier lift than accepting someone as female who has XY
chromosomes.
Herb Berkowitz
SECOND LETTER :
April 24, 2023
The Philosophy of the Serpent
Herb Berkowitz ("Chromosome Isn't Everything," Letters, April 20)
seems to believe that each of us has the power to accomplish what only
God can do. Faithful Christians have believed for centuries that the
transformation of bread and wine into Christ's body and blood is
accomplished by the powerful word of God. Mr. Berkowitz accurately
demonstrates the current thinking that human opinions or thoughts have
similar power to change the reality of science and creation. That says
a lot about how we view ourselves and how far we have fallen.
James Burhop
Bill Weintraub :
Right.
Peggy Noonan:
In the Garden of Eden story, Adam and Eve and the fall, at the
beginning of the world -- God told them not to eat the fruit of the
tree, but the serpent told Eve no harm would come if she did, that
she'd become like God, knowing all. That's why he doesn't want you to
have it, the serpent said: You'll be his equal. So she took the fruit
and ate, she gave to Adam who also ate, and the eyes of both were
opened, and for the first time they knew shame. When God rebuked them,
Adam blamed Eve and Eve blamed the serpent. They were banished from
the garden into the broken world we inhabit.
You can experience the Old Testament story as myth, literature,
truth-poem or literal truth, but however you understand it its meaning
is clear. It is about human pride and ambition.
Bill Weintraub :
Right.
So :
I worship Lord Ares, who confers upon Men, Manhood and Manliness through Fight.
Do I know for a fact that Lord Ares exists ?
No.
But I think it's probable that He does.
And I get the idea of "probable" from Cicero.
Cicero (106 - 43 BC) was a statesman and lawyer, the head of the Roman Bar and a staunch supporter of the Roman Republic -- and a moderate, un-dogmatic, man.
As a lawyer, he was used to weighing evidence, and for that reason he was agnostic on many issues, saying simply that we cannot know for sure.
But he also spoke in terms of probabilities, of what was not just possible, but probable -- he thought that we as Men could legitimately do that -- and that it was probable therefore that there was a guiding or controlling mind which had created and continued to uphold the cosmos.
That, in Cicero's lifetime, was the Stoic point of view, and it differed sharply from that of the Epicureans, who maintained that the universe was the result of a series of accidents, the fortuitous collision of innumberable fortuitous atoms, and that there was no mind in back of those atoms.
That made no sense to Cicero -- and it doesn't to me either.
It seems to me that the universe -- and the world -- and human beings -- and esp Men -- are not
the result of a series of accidents, but the work of a Controlling
Mind, eager and able to achieve a Good Purpose, Object, Outcome.
In this case, Manliness, and Manhood, Fighting Manhood.
Which I experience as Good, Divine -- Blessed.
Aggression and the Beauty of Guys who Assert that Aggression.
Lord Ares is the Divine Being who wants and enables you to experience
that Beauty --
That Irreducible Goodness, that Irreducible Aggressive Male Beauty -- of Fighting Men.
And if the assertion of Man-Against-Man Aggression is Good, if follows that there have to be Fight Schools, Wrestling Schools, Palaistrai -- to teach Men how to Aggress -- and that activating the Fight School there has to be a Controlling Mind :
Cicero :
When a man goes into a house, a wrestling-school or a public assembly and observes in all that goes on arrangement, regularity and system, he cannot possibly suppose that these things come about without a cause: he realizes that there is someone who presides and controls.
~ Cicero, de Natura Deorum, Bk II, 15, translated by Rackham.
. . .
Again, if you see a spacious and beautiful house, you could not be induced to believe, even though you could not see its master, that it was built by mice and weasels; if then you were to imagine that this elaborate universe, with all the variety and beauty of the heavenly bodies and the vast quantity and extent of sea and land, were your abode and not that of the Gods, would you not be thought absolutely insane?
~ Cicero, de Natura Deorum, Bk II, 17, translated by Rackham.
There's also an aesthetic issue.
Cicero speaks of a spacious and beautiful house, designed by someone who presides and controls.
The Male Body, which houses the Male's Fighting Spirit, was designed to be essentially flat and angular --
with genitalia protruding --
often exuberantly.
Alain Danielou on the Phallus as Sacred :
It is only when the penis stands up straight that it emits semen, the source of life. It is then called the phallus, and has been considered, since earliest prehistory, the image of the creative principle, a symbol of the process by which the Supreme Being procreates the Universe.
This is not the case of a symbol plucked at random but the recognition of the continuity of the process that links all the various levels of manifestation, according to cosmological theory. The phallus is really the image of the creator in mankind, and we rediscover the worship of it at the origin of every religion.
A source of pleasure, the phallus evokes divine bliss, the Being of Joy. Within the microcosm of the living being it represents the progenitor, which is always present in its work.
Contempt for this sacred emblem, as well as degradation and debasement of it, pushes man from the divine reality. It provokes the anger of the Gods and leads to the decline of the species. The man who scorns the very symbol of the life principle abandons his kind to the powers of death.
~ Danielou, Alain. The Phallus: Sacred Symbol of Male Creative Power. (1995). Rochester, Vermont: Inner Traditions.
You can see that the body is male -- irreducibly male.
At the same time, you can see that the transsexual contempt for the male body, including the phallus, has led to degradation and debasement.
I once received an email from a male-to-female trans who said that he thought of his penis as a deformed vagina, and his testicles as deformed and descended ovaries.
They aren't.
A penis and testicles on the body of a person who thinks of himself as a woman -- are still a penis and testicles.
The male is irreducibly male.
And, as I said, there's an aesthetic question, or, really, a question of ethical nihilism, a belief system which
questions all standards of morality and aesthetics, and confuses justice and injustice, beauty and ugliness.
And, as I also said, this beautiful Male body houses the Male's beautiful Fighting Spirit.
Neither the Male's body nor his Fighting Spirit are ugly.
Both -- are Beautiful.
So :
Just as Bishop Barron speaks of the Irreducible Maleness of the Male Body, so may we speak of the Irreducible Maleness of the Male Spirit -- that is, of Manly Spirit.
Manly Spirit is Fighting Spirit, the Hallmark of Masculinity, Virillity, Manliness, and Manhood.
The Male Body was Designed to Fight.
The Male Body is Destined to Fight.
Men are Destined to Fight.
And that's why Men are given Masculinity, Manliness, and Manhood.
That they may fulfill their Destiny --
And Fight.
Fighting is Beautiful, Physically, Morally, and Spiritually.
It's difficult to convey how intensely beautiful Fighters and Fight are to me.
To try to express that Beauty on Ares Is Lord, which I created as an act of Devotion to Lord Ares, God of Fight and of Fighting Manhood,
I often repeat images which for me are particularly significant or iconic :
This picture too is iconic because of the way it delineates the ideal of the Palestrean body -- broad chest, strong glutes -- shaped by daily combat at the Fight School :
And this picture :
FIGHT IS VIRTUE.
FIGHT IS VIRTUOUS.
FIGHTER VIOLENCE IS VIRTUOUS VIOLENCE.
THERE IS NO VIRTUE WITHOUT FIGHT, AND THERE IS NO FIGHT WITHOUT VIRTUE.
THE WORD ARETE -- VIRTUE -- DERIVES FROM ARES, THE GOD OF FIGHT ; THE WORD VIRTUS -- VIRTUE -- DERIVES FROM VIR -- VIR IS MAN, AND MAN IS FIGHTER.
THERE IS NO VIRTUE WITHOUT FIGHT.
FOR ME, THIS IS AN IMAGE OF PURE BEAUTY.
AS IS THIS :
AND SO ARE THESE IMAGES OF LORD ARES :
Agapenor : loving manliness, manly
Agapenor is a combination of
Agape : love : esp. brotherly love, charity ; the love of God for man and of man for God
And
Enore-e : Doric is Anorea Ανορεα, which derives from Aner (Ανηρ) Man, and is, say Liddell and Scott, a poet. word for Andreia Ανδρεια, which derives from the genitive form of Man, Andros.
So :
Anorea ← Aner
Andreia ← Andros
This is how Liddell and Scott define Enore-e/Anorea :
Manhood, prowess, manly beauty, its strength, force ; in pl., triumphs of manhood
Manhood, prowess, Manly beauty, its strength and force
That's what MEN LOVE.
Let's repeat that:
Manhood, prowess, Manly beauty, its strength and force
That's what MEN LOVE.
Because that's what Agapenor means :
Loving Manhood, loving Prowess, loving Manly Beauty, loving Manhood's Strength and Force
Agapenor, once again, is a combination of the words Agape -- Love ; and
Enore-e, which, in the Spartan dialect, is pronounced Anorea -- Manliness, Manhood, Manly Spirit.
Agapenor is Loving Manliness, Manhood, Manly Spirit.
In Greek, it looks like this : αγαπ - ηνωρ -- Loving Manhood -- and it is, say Liddell and Scott, an "epith. of heroes."
Heroes.
Heroes love Manliness, love Manhood, love Manhood's Prowess, its Strength and Force.
Agapenor is a foundational word among the Greeks, it goes all the way back to the Iliad, which is often described as the ancient Greek Bible, and it refers to Heroes and Warriors who both love Manliness -- and are themselves Manly.
Agapenor is also a foundational word for Ares is Lord, for, as you will learn in Biblion Pempton of our Lexicon of Manhood, it's Lord Ares who has apportioned the Love of Manhood -- to the Souls of Men.
Related :
Agenoria
Derives from:
Doric:
αγανωρ
Agenor is formed from the words agan -- very, much, very much ; and aner -- Man.
So that, through crasis, we get Ag'Enor = Very Man, Much Man, Very Much Man = Manly.
And from Ag'Enor, there derives Agenoria -- Manliness, Manhood.
Both words are Homeric.
Basically, then, Man and Warrior are synonymous for the Greeks -- as they are for all Warriordoms.
He who is "Very Man" is Manly, that is, Willing and Able to Fight.
And "Very Man" + ness = Manliness, Manhood -- which, again, defines a Man, and is the Willingness and Ability to Fight.
Related :
Agapenor ;
Bianor
Related:
Agonios : of or belonging to the contest
Related:
Agonisma : a contest, in pl. deeds done in battle, brave deeds
Related:
Agonioi Theoi : the Gods who preside over the Games, over the Contest, over the Fight
Related:
Agonistes : a combatant ; a rival at the games, competitor ; one who struggles for a thing, a champion
αγωνιστης
Antagonistes : an opponent, competitor, rival
Related:
Agonizomai : to contend for a prize, to fight, to struggle
αγωνιζομαι
Two famous literary accounts of Anabatai have survived :
That of Xenophon, who describes the expedition up-country, in 401 BC, of the 10,000 Greek Hoplitai, mercenaries who were hired by the Persian prince Kyrus to help him wrest the throne of Persia from his brother ;
And that of Arrian, who describes the expedition up-country, from 336 to 323 BC, of Alexander the Great.
Kyrus was killed in battle, leaving the 10,000 Greek infantrymen stranded in enemy territory, and they had to Fight their way out of Persia -- a true-life story which Xenophon, who was present and commanded the retreat out of Persia, relates most compellingly.
Arrian, by contrast, was not part of Alexander's Anabasis -- he lived more than 400 years later, ca 120 AD.
But Arrian had available to him the memoirs of a number of Alexander's generals, and, like Xenophon, whom he admired, he tells the tale of Alexander's heroic exploits -- compellingly.
Please note:
An-amnesis -- recollection, or UN-forgetting -- is core to both Plato's Theory of Ideas and his Theory of Ethics.
To better understand anamnesis, please see Biblion Triton of this Lexicon of Manhood.
That's Liddell and Scott's definition ; and, Liddell and Scott add,
From the same root [ARES] come areté, ari-, areion [better -- stronger, braver, more Manly], aristos [best -- strongest, bravest, most Manly], the first notion of goodness being that of manhood, bravery in war; cf. Lat. virtus.
Again, that's Liddell and Scott's definition, which is, appropriately, excellent.
In the Alliance and Ares is Lord we define Areté / Areta as Manly Excellence, which is Manliness, which is Manhood, which is Manly Goodness, which is Manly Virtue, which is Manly Spirit, which is Fighting Manhood.
Werner Jaeger : Areté / Areta -- The uniquely Male, Manly Excellence known to us as Fighting Manhood -- exists in mortal man. Areté is mortal man. But it survives the mortal and lives on in his glory, in that very ideal of his areté which accompanied and directed him throughout his life.
So : Areté / Areta is the uniquely Male, Manly Excellence known to us as Fighting Manhood ; and Areté / Areta is about Fighting because Fighting confers Manhood.
Fighting Manhood.
While Manhood enables Fighting.
Bill Weintraub:
To fully understand Areté / Areta, please read the following discussion :
Areté is a uniquely Greek word and concept, which, according to classicist CM Bowra, refers to "an intrinsic excellence that exist[s] in all things."
To the Greeks, then, everything has its own intrinsic or inherent excellence, which, however, is latent until such time as it is, and ideally, realized, arrives, or becomes present [paragignomai].
So -- an implement -- such as a drinking cup -- has its own areté.
And so does a body part -- such as an eye.
And so does a Man -- and a Man's soul.
To take an easy example, the areté, that is, the intrinsic or inherent excellence, of an eye is vision, and when the eye sees well, that excellence is present.
Sokrates
~Plat. Alk. 1 133b, translated by Lamb.
The areté -- excellence -- of an eye [ophthalmos] is sight, eyesight, vision [opsis] ; when that excellence is present or realized, the eye is capable of and experiences good vision.
But -- suppose that excellence is not there ?
Sokrates
~Plat. Alk. 1 126b, translated by Lamb.
So : the presence of areté, of excellence, in an eye, is vision -- good vision ; the absence of excellence is blindness.
Similarly for an ear -- the presence or realization of an ear's areté is good hearing ; its absence is deafness.
What about for a Man?
Well, Greek culture is "anthropo-centric," or, really, "andro-centric" -- it centers upon Men.
And that's why Liddell and Scott say, in their definition of Areté, that
And, Liddell and Scott add,
So :
The Excellence of a Man is Manly Excellence, which is Manhood, which consists of valour and prowess, that is, the Willingness and Ability to Fight.
FIGHT.
The Excellence of a Man, his Manly Excellence, is Fighting Manhood.
When speaking of Man, then, and of Man's Soul, there can be no question that to the Greeks, as to us, the Areté / Areta of a Man -- is Manhood.
FIGHTING MANHOOD.
The presence or realization of Manly Excellence is the Adventus -- the arrival -- of Manhood, Fighting Manhood ; its absence is, in Greek, an-andria -- the want or lack of Manhood, UN-manliness.
And un-manliness is as devastating to the human male as blindness to the eye, and deafness to the ear.
Moreover :
When referring to a Man, Areté, one of the most important words in the Greek language, corresponds to the Greek Andreia and the Latin Virtus, both of which are defined as Manliness, Manhood ;
And which have the following attributes :
Again, this definition of the Greek word Andreia and the Latin word Virtus -- and guys, I cannot emphasize this strongly enough -- applies equally to the Greek word Areté:
In sum, Manhood, Valour, Goodness, Virtue, Worth -- Excellence.
Manhood is Valour, Manhood is Goodness, Manhood is Virtue, Manhood is Worth -- Manhood is Excellence.
Manly Excellence which is Fighting Excellence which is Fighting Manhood.
Liddell and Scott :
And, Liddell and Scott add,
Now :
Notice that Liddell and Scott say of Areté that "the first notion of goodness [is] that of manhood, bravery in war" ; and,
that Liddell and Scott define Areté as "goodness, excellence, of any kind, esp. of manly qualities, manhood, valour, prowess (like Lat. virtus, from vir)".
So :
Liddell and Scott twice use the word "goodness" in characterizing Areté, and, not surprisingly, many translators translate the word Areté as Virtue -- and Excellence.
Well, Areté can certainly mean Virtue and Excellence -- but -- what sort of Virtue and Excellence?
Liddell and Scott tell us, and unequivocally :
That of "manhood, bravery in war," they say, and add, "esp. of manly qualities, manhood, valour, prowess (like Lat. virtus, from vir)".
Which means that Areté / Areta, de facto, means Manhood and Manliness, which is the Willingness and Ability to Fight, and that the Virtue and Excellence referred to are attributes of that same Manhood, which, again, is Fighting Manhood.
To better comprehend the relationship between and among Areté / Areta and Andreia and Virtus, please see my brief article titled Understanding the core position and actual meaning of Andreia-Areté-Virtus within the Culture of Fighting Manhood under the Lexicon entry for Andreia.
And also useful is our Discussion of Areté / Areta, which includes a word-by-word dissection of Liddell and Scott's definition, in Chapter III Part I of Biblion Pempton.
Bill Weintraub
Within the Communion of Ares Is Lord, Areos is used to denote a Communicant.
In other words, a Communicant of Ares Is Lord is an Areos -- an embodied soul who is of Ares and who belongs to Lord Ares, Lord of Fight, Lord of Manhood, Lord of Fighting Manhood.
Related:
Αρεος ; Αρεως ; Αρηος
αθλητης
Derives from:
Athume-o : to be disheartened, lose heart , lose fighting spirit ; τινι at or for a thing
Derives from:
Athumos : without heart, fainthearted, αθυμος ειναι προς τι to have no heart for a thing, Xen. [to have no fighting spirit] ; without passion
αθυμος
In addition, Wm Slater, in his Lexicon to Pindar, says that χειρ can also have other connotations, such as of physical combat, contests of strength, simm., and references "like Ares in the strength of his hands" χειρας Αρει τ' εναλιγκιον in I 8.37.
Related:
Cheiro-o : to bring into hand, to manage, master, subdue ; mostly in Mid., to conquer, overpower, subdue
χειροω
Cheirisophos and Xenophon worked very closely and, on the whole, amicably together -- Cheirisophos was in charge of the vanguard of the 10,000 as they Fought their way out of Persia and back to Greek territory.
The name Cheirisophos derives from cheir -- hand, and sophos -- skilled ; most likely, and given that most Spartan names were combative, Cheirisophos means Skilled in Hand-to-Hand Fighting.
Χειρισοφος
Δρακων
εφηβεια
That's Liddell and Scott, but, and actually, the word has a number of inter-related meanings:
This expanded training became known as Ephebeia in Greek and the Ephebate in English.
Bill Weintraub :
Each of the various city states had its own version of the ephebate, based in the gymnasia, which functioned as hot houses for ideologies of physical culture and martial valour.
Prof Kennell :
The Spartan curriculum [, that is, the curriculum at Roman Sparta, 146 BC to 395 AD,] was heavily weighted toward physical education and military exercises, but so were those of most other ephebic systems.
Apart from the overwhelming prestige of athletics in Greek culture since the time of Homer, military preparedness was required of all ephebes everywhere because they formed the military reserve force for their cities.
Related:
from εφηβος
εφηβικος
Related:
Gymnikos : of or for gymnastic exercises, that is, athletic exercises practised nude ; gymnikos agon γυμνικος αγων a nude athletic contest, as opposed to a mousikos agon -- a musical, poetic, literary, etc contest
Related:
Gymnastikos : fond of [nude] athletic exercises, skilled in them ; he gymnastike η γυμναστικη (with or without techne τεχνη), gymnastics, gymnastic art, gymnastic skill, Plat.
Derives from
Related:
Gymnasteos : verb. adj. of γυμναξω ; one must train [naked], Xen.
γυμναστεος
Related:
Heba-o : to be at man's estate, to be in the prime of youth ; as Substantive, hoi hebontes οι ηβωντες, the young, the young men
Related:
Hebasko : to come to man's estate, come to one's strength, Lat. pubescere -- to attain puberty, to come to maturity
Also related:
Pros-hebos : near manhood, Xen.
See also
Pubertas
Ελλας
Related:
Phil-Hellen : fond of the Hellenes, that is, the Greeks -- as was the Persian prince Kyrus, whose desire to overthrow his brother, the Great King Artaxerxes II, led to the Anabasis.
φιλελλην
Please note: The Emperor Julian (r. 361-363 AD), the last non-Christian emperor and who was opposed to Christianity, used various Greek words like Hellenikos to characterize traditional, non-Christian, Greek thought and philosophy which, in his era, existed in opposition to Christianity. In my own work, I often use the English word "Hellenist" to characterize non-Christian, Greek thought and philosophy which exists in opposition to Christianity ; and which exemplifies Hellenism, which Merriam-Webster defines as "a body of humanistic and classical ideals associated with ancient Greece and including reason, the pursuit of knowledge and the arts, moderation, civic responsibility, and bodily development," and which is typified, according to classicist Victor Davis Hanson, by "constitutional government, civil liberties, free exchange of ideas, self-critique, and separation between religious and political/scientific thought."
Ελληνικος
Related:
Kynegeo : to hunt, chase -- usually, one would think, with hounds ; at Sparta, most certainly, with Lakonikan hounds
Related:
Kynegesion : a hunting-establishment, huntsmen and hounds, a pack of hounds ; a hunt, chase, pursuit ; that which is taken in hunting, the game
Derives from:
Kynegeteo : to hunt ; metaph. to persecute, harass ; to quest about, like a hound
Related:
Kynegetikos : of or for hunting, fond of the chase, Plato ; ho Kynegetikos [logos] ο Κυνηγετικος [λογος] name of Xenophon's work on Hunting.
Xenophon's very charming and instructive treatise on Hunting with Hounds, the Kynegetikos, begins as follows :
Game and hounds are the invention [eurema -- invention, discovery, thing discovered not by chance but by thought] of Gods [Theoi], of Apollo and Artemis. They bestowed it on Cheiron and honoured him [timao] therewith for his righteousness [dikaiosyne]. And he, receiving it, rejoiced [chairo] in the gift [doron], and used it.
And he had for pupils in venery [kynegesion] and in other noble [kalos] pursuits -- Cephalus, Asclepius, Meilanion, Nestor, Amphiaraus, Peleus, Telamon, Meleager, Theseus, Hippolytus, Palamedes, Odysseus, Menestheus, Diomedes, Kastor, Polydeukes, Machaon, Podaleirius, Anti-Lochos, Aineias, Achilles, of whom each in his time was honoured [timao] by Gods. . . .
Following this prooimion, Xenophon examines in great detail the mechanics of hunting hares with hounds.
The translator, Prof Marchant, believes that the Kynegetikos was Xenophon's first attempt at writing, undertaken when he was probably about thirty years old -- his friend and teacher Sokrates would have still been alive, and Xenophon would not have yet joined with 10,000 other Greek mercenaries in their attempt to invade Persia and overthrow the Great King, a journey which would be life-changing for Xenophon.
And that his "target audience," as we would say today, would have been 18-year-olds, "youths of Fighting age," that is, young Men who were now old enough to Fight in Battle, and who were also now old enough to learn to hunt in an organized and disciplined way.
Prof Marchant :
In Chapter VII, for example, Xenophon discusses, again in great detail, the breeding of hounds, and even gives this list of names :
~Xen. Hunt. 7.5, translated by Marchant.
In order to understand this list, and its significance in the Masculinist and Martial Warrior Societies of Ancient Greece, and particularly that of Sparta, we need to re-visit something we discussed in Biblion Proton, something the great classicist Werner Jaeger said about PhiloTimia, Areté, and the Greek system of naming :
Ambition [PhiloTimia -- the Love of Timé, of Honour, the Love of that Manly Honour which accrues to a Man through his Prowess in Battle, his Prowess in Fight --] is the aspiration of the individual towards that ideal and supra-personal sphere in which he alone can have real value.
Areté -- The uniquely Male, Manly Excellence known to us as Fighting Manhood -- exists in mortal man. Areté is mortal man. But it survives the mortal and lives on in his glory, in that very ideal of his areté ; which accompanied and directed him throughout his life.[24]
So, Jaeger says, the ideal of areté -- the Ideal of Manly Excellence -- accompanies and directs the Greek Warrior throughout his life.
And there's a footnote -- number 24:
24. This is especially manifest in the Greek system of proper names. They frequently were taken from the realm of social ideals and therefore often refer to such concepts as glory, reputation, fame, etc., and in addition were combined with some other word which expressed the degree of or reason for such fame or reputation (such as Pericles, Themistocles, etc.). The name was an anticipation of the future areté of its bearer ; it set, as it were, the ideal pattern for his whole life.
[emphasis mine]
So -- those wonderful ancient Greek names -- names which were given at birth, remember -- names such as Thrasymachos -- Bold in Battle -- and Aristomachos -- Most Manly in Battle -- were, as Prof Jaeger properly says,
Let's repeat that:
An ancient Greek name like Protomachos -- Foremost in Battle -- or Nikomedes -- Victorious Virility -- is an anticipation of the future areté -- that is to say, Manliness and Fighting Manhood -- of its bearer ; it sets the ideal pattern for his whole life.
And that's why Xenophon, a lover of horses and hounds, cares about the names given these dogs at birth.
Because a dog too has, at least potentially, Areté.
As we talk about at length in Chapter III of Biblion Pempton, and as you can learn simply by reading the discussion which follows our definition of Areté / Areta --
Every thing and every being has its own Areté, its own Excellence, put there by whoever fashioned that thing or being, and existing latent within the thing or being until circumstances are such that it can be realized, achieved, and lived.
For a Man, Areté is without question Manhood, Fighting Manhood, and all the attributes of Vigor, Valour, Virtue, and Value which belong to the Fighting Manhood of the Ideal and Perfect Man.
But a dog too has areté -- and if its life circumstances are right, that areté will be realized and lived.
Further, to the Greeks, as to many peoples, the Areté / Areta of a dog, particularly a male dog, is close or similar to that of a Man.
The dog, the Spartans said, was "the most valiant of domestic animals."
While Plato praised the High Spirit -- Thumos -- of the dog, and said that one should look for a similar High Spirit in those destined to be the Guardians, the Warrior caste, of his ideal Republic -- welcoming to friends, and unrelentingly hostile to foes.
So the Greeks, and particularly Greek aristocrats like Xenophon and Plato, routinely equated dogs with Warriors.
Which is understandable, since dogs, like Men, who are by nature Warriors, Hunt and Fight.
Xenophon's list, then, and to paraphrase Jaeger, is
For just that reason Xenophon's list, if we exlude the names intended for the female dogs, enlightens us as to the qualities that Xenophon, the classic soldier of classical Greece, believes are desirable in male hunting dogs -- and in Fighting Men :
If that list in any way mystifies you, and if in particular it seems too violent to you, you can learn more about Greek Warrior Names, and their relationship both to the Ideal of Areté / Areta, and to the times in which Greek Warriors lived, simply by clicking on this link.
Now :
Having discussed, in great technical detail, what a young Man needs to successfully go hunting with hounds, Xenophon ends his treatise as follows :
[2] In the first place, when marching over rough roads under arms [hopla], they will not tire : accustomed to carry arms for capturing wild beasts [ther], they will bear up [aireo] under their tasks [ponoi]. Again, they will be capable of sleeping on a hard [skleros] bed and of guarding well [phulax agathos -- being a Manly Guard of] the place assigned to them.
[3] In an attack on the enemy they will be able to go for him and at the same time to carry out the orders that are passed along, because they are used to do the same things on their own account when capturing the game [agra]. If their post is in the van they will not desert it, because they can endure [karteria dynamai].
[4] In the rout of the enemy they will make straight for the foe without a slip over any kind of ground, through habit. If part of their own army has met with disaster in ground rendered difficult by woods and defiles or what not, they will manage to save themselves without loss of honour [me aischros -- without shame] and to save others. For their familiarity with the business will give them knowledge that others lack.
[5] Indeed, it has happened before now, when a great host of allies has been put to flight, that a little band of such men, through their fitness [eutaxia -- good order, discipline] and confidence [thrasus], has renewed the battle and routed the victorious enemy when he has blundered owing to difficulties in the ground. For men who are sound in body [soma] and mind [psyche] may always stand on the threshold of success [eutyche-o].
[6] It was because they knew that they owed their successes against the enemy to such qualities that our ancestors [progonoi] looked after [epimeleia] the young men [neoi]. For in spite of the scarcity of corn it was their custom from the earliest times not to prevent hunters [kynegetes] from hunting over any growing crops ; and, in addition, not to permit hunting at
[7] night within a radius of many furlongs from the city, so that the masters of that art might not rob the young men of their game. In fact they saw that this is the only one among the pleasures [hedonai] of the younger men that produces a rich crop of blessings [agathoi -- Manly Goods]. For it makes sober [sophron-- sober -- that is, having control over the sensual desires] and upright [dikaios -- Manfully Morally Ordered] men of them, because they are trained in the school of truth [aletheia] (and they perceived
[8] that to these men they owed their success in war [eutyche-o polemos -- success in war], as in other matters) ; and it does not keep them from [apostereo -- rob them of] any other honourable [kalos -- morally beautiful] occupation they wish to follow, like other and evil pleasures [kakai hedonai -- evil, shitty, pleasures] that they ought not to learn. Of such men, therefore, are good [agathos -- Manly, that is, Willing and Able to Fight] soldiers [stratiotes -- in this instance, citizen-soldiers] and good generals [strategos -- citizen-generals] made [gignomai].
[9] For they whose toils [ponoi] root out whatever is base [aischros] and froward [hybristikos -- insolent, wanton] from mind and body and make desire for virtue ["virtue" is not correct. The word is Areté -- Manhood, Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood ; if you still don't understand why "virtue" is an inadequate translation of Areté, please review the article on Understanding the Core Position and Actual Meaning of Andreia-Areté-Virtus within the Culture of Fighting Manhood, the Translator's Note, and the Lexicon entry for the Attributes and Qualities of Fighting Manhood] --
[9] For they whose toils [ponoi] root out whatever is base [aischros] and froward [hybristikos -- insolent, wanton] from mind and body and make desire for Areté, Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood, to flourish in their place -- they are the best [aristos -- Most Manly], since they will not brook injustice to their own city nor injury to its soil.
. . .
[12] But many of those who talk in this way [that is, are critical of hunting], blinded by jealousy [phthonos], choose to be ruined through their own evil [kakia] rather than be saved by other men's virtue [Areté -- Manhood, Manly Excellence, Manly Goodness, Manly Virtue, Fighting Manhood]. For most pleasures [hedonai] are evil [kakai], and by yielding to these they are encouraged either to say or to do what is wrong.
~Xen. Hunt. 12.1-12, translated by Marchant.
Bill Weintraub:
Xenophon continues on in this vein for some time, and I encourage you to click on the link and read all he has to say.
But this passage is particularly useful and germane :
For it makes sober [sophron-- sober -- that is, having control over the sensual desires, the passions] and upright [dikaios -- Manfully Morally Ordered] men of them, because they are trained in the school of truth [aletheia] (and they perceived that to these men they owed their success in war [eutyche-o polemos -- success in war], as in other matters) ; and it does not keep them from [apostereo -- rob them of] any other honourable [kalos -- morally beautiful] occupation they wish to follow, like other and evil pleasures [kakai hedonai -- evil, shitty, pleasures] that they ought not to learn.
Of such men, therefore, are good [agathos -- Manly, that is, Willing and Able to Fight] soldiers [stratiotai -- in this instance, citizen-soldiers] and good generals [strategoi -- citizen-generals] made [gignomai].
So :
Xenophon isn't a Platonist -- indeed, as I pointed out earlier in this Lexicon, it's not unreasonable to think that, despite their being the same age and coming from the same social class, despite their both being students of Sokrates, and despite their shared admiration for Sparta -- Xenophon had little use for Plato.
Nevertheless, what he here very clearly enunciates are Warrior-World-of-Being values of the sort that Plato too praises and wishes to see inculcated into the Guardians and other citizens of his various ideal city-states.
So -- Xenophon starts by saying that the progonoi -- the ancestors -- had looked after and taken great care of the young Men, in this as in all other aspects of their upbringing.
To both Plato and Xenophon this is both obvious and absolutely necessary.
Both Men recognize that human beings must be schooled, trained, raised, brought up, and taught -- both skills -- and Values.
Both Men also recognize that most pleasures are suspect, and that far from being either necessary or benign, most are un-necessary, vicious, evil, and malaign.
But that hunting, to the extent that it is a pleasure, is not one of them.
For, says Xenophon, hunting "is the only one among the pleasures [hedonai] of the younger men that produces a rich crop of blessings."
And the word Marchant translates as "blessings" is agathoi, the plural of agathos, which is the adjectival form of Areté, and which therefore means, in this context, that which is both Manfully Excellent and Manfully Good, that which is expressive of Manhood -- Fighting Manhood.
Which emanates from the Warrior World of Being, the Warrior Kosmos.
So -- we use the word "goods" to refer to material benefits -- such as food, eg, "baked goods" -- or possessions, as in "all his wordly goods."
But we also use the words "good" and "goods" to refer to non-material benefits -- such as "social goods" -- "altruism and sharing are social goods."
And in the context of Xenophon's treatise, which is Martial and Masculinist, hunting confers "Manly Goods" -- non-material benefits which are Manly --
And, of course, the rich crop of blessings, of Manly Goods, produced by the "pleasure" of Hunting -- is Manhood --
Fighting Manhood --
And all its attributes.
This question of agathoi -- "goods" -- comes up in another of Xenophon's books, and easily the most famous, the Anabasis, Xenophon's account of the trip "upcountry," that is, into Persia, of some 10,000 or more Greek hoplites, part of a mercenary army put together by the Persian prince Kyrus, who wants to overthrow and replace his brother, the Great King.
Kyrus and his Greeks travel deep into Persia and Fight a Battle at a place called Cunaxa.
The Greeks easily win their part of the battle, but Kyrus is killed in the Fighting, and his cause dies with him, leaving the Greeks trapped deep inside of Persia, surrounded by hostile forces.
The Great King sends a Greek-speaking emissary named Phalinus to try to persuade the Greeks to surrender -- most especially to give up their arms, their hopla, the very arms which make the Hoplite Formation possible, and which the Persians are still unable to beat.
Phalinus has his say, and the Greeks dispute with him, among them, Xenophon :
Then Xenophon, an Athenian, said:
[12] "Phalinus, at this moment, as you see for yourself, we have no other possession [agathos -- "good," that is, Manly Good] save arms [hopla] and valour [Areté -- Manhood, Fighting Manhood]. Now if we keep our arms, we imagine that we can make use of our Manhood also, but if we give them up, that we shall likewise be deprived of [stereo -- deprived of, robbed of] our lives [somata -- living bodies]. Do not suppose, therefore, that we shall give up to you the only possessions [agatha -- Manly Goods] that we have ; rather, with these we shall do battle [machomai -- fight] against you for your possessions as well."
[13] When he heard this, Phalinus laughed and said : "Why, you talk like a philosopher [philosophos], young man [neaniskos], and what you say is quite pretty [ouk acharistos -- not unpleasing] ; be sure, however, that you are a fool [anoetos] if you imagine that your Manhood could prove superior to the King's might [dynamis]."
~Xen. Anab. 2.1.12-13, translated by Brownson.
Phalinus here unwittingly sums up the issue in both Xenophon's and Arrian's Anabatai -- Would Greek Manhood prove superior to Persian might?
The answer, in both cases, was Yes.
Might is an aspect of Manhood, but Manhood is more important, more encompassing, and more powerful -- than might alone.
Notice also that Xenophon uses the word agathos -- good, but that Prof Brownson renders the word as "possession."
Yet it's Xenophon's use of the word agathos that makes his remarks "philosophical."
"We have no other Good save Arms and Manhood."
That one sentence alone can stand as the Warrior Creed.
Xenophon continues :
"Do not suppose, therefore, that we shall give up to you the only Goods that we have ; rather, with these we will Fight you for your goods as well."
That is, With our only Goods, our Arms and our Manhood, we'll Fight you and take from you your goods, your arms, your land, and your manhood -- too.
We will Fight you -- and we will UN-man you.
And Xenophon means what he says.
Throughout his life, Xenophon believed it was the Destiny of Greek Manhood -- to Fight, Conquer, and UN-man -- Persian.
Let's return to the Kynegetikos.
In the context of the Kynegetikos, which, like the Anabasis, is Martial and Masculinist, Hunting confers "Manly Goods" -- non-material benefits which are Manly --
And, of course, the rich crop of blessings, of Manly Goods, produced by the "pleasure" of Hunting -- is Manhood.
Fighting Manhood.
For hunting, says Xenophon, "makes sober" -- that is, it helps give the young Man control over his passions, his sensual desires -- and that matters because to Warrior Ethicists like Xenophon and Plato, sensual desires and pleasures must always serve Manhood -- and never the reverse.
The only legitimate use of pleasure -- which is a function of the world of becoming -- is to serve Manhood, Fighting Manhood -- which is an expression -- of the Warrior World of Being.
And hunting, says Xenophon, gives the young Men control of their sensual desires and thus helps make "Manfully Morally Ordered Men of them, because they are trained in the School of Truth" --
And the School of Truth of course is the Warrior Kosmos -- the Warrior World of Being and its Values and its pre-eminent Value, its Idea of Good -- Fighting Manhood.
Xenophon continues :
So -- evil pleasures -- kakai hedonai -- will rob a Man, will steal from him, any other Honourable and Morally Beautiful occupation he wishes to follow -- which to Xenophon's mind, as to those of his fellow Warriors, will always be an occupation which centers on Fighting ; which is why, he says, "of such Men are Manly -- that is, Willing and Able to Fight -- citizen-soldiers and citizen-generals made."
Hunting, in other words, and says Xenophon, will impart the Values which make a Man more Morally Ordered and thus a better Warrior.
Does Plato agree?
Yes!
Training to be a Warrior, which includes hunting skills, is a core part of his programs, his ethical programs, in both the Republic and the Laws.
As Jaeger says, and as we discussed in Chapter II, Part II of Biblion Pempton :
Plato's ethical doctrines "were founded on the aristocratic morality of early Greece," which was Homeric Greece, a purely Warrior Society.
These doctrines were and are possessed of "permanent truth" and "indestructible ideality."
Translation : They're part of the World of Being, the Warrior World of Being, which explains their persistence over vast quantities of Time.
The point to all this being that while Plato and Xenophon did not, apparently, get along, they came from the same society, the same Masculinist and Martial Warrior Society, and shared the same Masculinist Values, the same Warrior Norms.
And when you've read deeply, as you should, in ancient literature, you'll see that Xenophon's and Plato's Warrior Ethics are not the exception -- they're the rule.
They're what Men in a Masculinist, Martial, Phallo-Centric, and by nature Pugnacious Warrior Society think about Life and the Right Way -- the Warrior Way -- to Live.
Xenophon :
[9] For they whose toils [ponoi] root out whatever is base [aischros] and froward [hybristikos -- insolent, wanton] from mind and body and make desire for Areté, Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood, to flourish in their place -- they are the best [aristos -- the Most Manly, that is, the Most Willing and Able to Fight], since they will not brook injustice to their own city nor injury to its soil.
. . .
[12] But many of those who are critical of hunting, blinded by jealousy [phthonos], choose to be ruined through their own evil [kakia] rather than be saved by other men's virtue [Areté -- Manly Virtue, which is Manly Excellence, which is Fighting Manhood, ]. For most pleasures [hedonai] are evil [kakai], and by yielding to these they are encouraged either to say or to do what is wrong.
Bill Weintraub:
Men can only be Saved through other Men's Manly Excellence, their Fighting Manhood.
Which is to say that
A point Xenophon repeats frequently, as he does in his Lakedaimonian Constitution :
Constitution of the Lakedaimonians [9.1] The following achievement of Lykourgos, again, deserves admiration. He caused his people to choose an honourable death [kalos thanatos -- a noble, selfless, and morally beautiful, death] in preference to a disgraceful life [aischros bios]. And, in fact, one would find on consideration that they actually lose a smaller proportion of their men than those who prefer to retire from the danger zone.
[2] To tell the truth, escape from premature death more generally goes with valour ["valour" is not correct. The word is Areté -- Manhood, Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood ; if you still don't understand why "valour" is an inadequate translation of Areté, please review the article on Understanding the Core Position and Actual Meaning of Andreia-Areté-Virtus within the Culture of Fighting Manhood, the Translator's Note, and the Lexicon entry for the Attributes and Qualities of Fighting Manhood] --
[2] To tell the truth, escape from premature death more generally goes with Manhood than with cowardice [kakia] : for Manhood [Areté -- Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood] is actually easier [radios] and pleasanter [hedus] and more resourceful [euporos] and mightier [ischyros]. And obviously glory [eukleia] adheres to the side of Manhood [Areté -- Manly Excellence, Fighting Manhood], for all [pas] men want [boulomai] to ally [symmacheo] themselves somehow with the brave [agathoi -- the Manly and Good ~Xen. Const. Lak. 9.1-2, translated by Marchant
[4.1] For those who had reached the prime of life [hebao] Lykourgos showed by far the deepest solicitude. For he believed that if these were of the right stamp they must exercise a powerful influence for good [agathos -- Manly Excellence] on the state [polis].
[2] He saw that where the spirit of rivalry [philoneikia -- love of strife, love of eager rivalry] is strongest among the people, there the choruses [choros] are most worth hearing and the athletic contests [gymnikos agon -- naked contests] afford the finest spectacle. He believed, therefore, that if he could match [symballo] the young men [hoi hebontes] together in a strife of valour [Eris peri Areté -- a Struggle of, for, and about Manhood -- not just valour, but all the attributes of Manhood] , they too would reach a high level of manly excellence [andragathia -- Manly Excellence]. I will proceed to explain, therefore, how he instituted matches [symballo] between the young men.
[3] The Ephors [ephoroi], then, pick out three of the very best [akmazo] among them. These three are called Commanders of the Guard [hippegretai]. Each of them enrols a hundred others, stating his reasons for preferring one and rejecting another.
[4] The result is that those who fail to win the honour [ta kala] are at war [polemeo] both with those who sent them away and with their successful rivals ; and they are on the watch for any lapse from the code of honour [ta kala].
[5] Here then you find that kind of strife [eris] that is dearest to the Gods [Theophiles], and in the highest sense political -- the strife that sets the standard of a brave man's [ton agathon -- a Manly Man's] conduct ; and in which either party exerts itself to the end that it may never fall below its best [kratistos], and that, when the time comes, every member of it may support [arego] the state with all his might [sthenos].
[6] And they are bound, too, to keep themselves fit [euexia], for one effect of the strife is that they fight [pukteuo -- strike with the fist] whenever they meet [symballo -- come together, are thrown together, come together in a hostile sense]; but anyone present has a right to part the combatants [machomai]. If anyone refuses to obey the mediator the Warden [paidomonos] takes him to the Ephors; and they fine him heavily, in order to make him realize that he must never yield to a sudden impulse [orge] to disobey [krateo] the laws [nomos].
~Xen. Const. Lak. 4.1-6, translated by Marchant.
Bill Weintraub:
Perrin translates the first sentence in Paragraph 6 as "And they are bound, too, to keep themselves fit, for one effect of the strife is that they spar [pukteuo -- box, fight, spar] whenever they meet [symballo -- are thrown together, come together in a hostile sense]. . ."
And while it's true that one definition of pukteuo is "spar," it's clear from the rest of the paragraph and the use of the word philoneikia in Paragraph 2, as well as the word symballo throughout Chapter 4, that not sparring, but an actual and all-out fist fight is what is meant.
Talbert's translation, is, then, more accurate :
That makes sense, since if all the Men were doing was sparring, there'd be no reason for "anyone present," as Perrin says, "to seek to part the combatants."
The Rivals are Combatants, and the Fight is an all-out Fight.
This isn't the YMCA or a meeting of the Women's Christian Temperance Union -- it's Sparta.
And the Struggle, the Fight, is a True Fight , a Fight of, for, and about -- MANHOOD.
And to Xenophon, as to any True Warrior, such Fighting is in the best and highest sense political, that is, of benefit to the polis, the city-state -- and Dearest to the Gods.
Just as Achilles' decision to serve Manhood by avenging Patroklos is timao -- Honored and Deemed of the Highest Worth -- by the Gods.
The Gods Love Manhood, Fighting Manhood, and those who live in its service.
Which means that the Gods Love Warriors, and Warriordoms.
Finally :
In the Anabasis, the emissary of the Great King, Phalinus, says to Xenophon, "You talk like a philosopher."
That's right, and it's because Xenophon is a philosopher.
He's rarely so regarded today, but the ancients -- his peers -- recognized him as a philosopher -- Xenophon "ho philosophos" -- who was schooled by Sokrates.
Xenophon is a moral philosopher, an ethicist, and that's why he writes.
He's interested in and greatly concerned with Right and Wrong, Virtue and Vice, Honestum et Turpe -- which for him, as for us, comes down to Manhood and want of manhood -- Andreia - Areté / Areta -- and an-andria.
He's not interested in ontology or epistemology etc.
He's a Warrior and a Military Man, and what interests him is Manliness.
That's why he's been read for 2400 years.
And also why he's the only ancient author whose work has come down to us intact.
That's to say, we have a copy of everything he wrote.
That's not true of anyone else, so far, at least, as I know.
But it is of Xenophon.
He has survived, and endured, and will continue to -- so long as there are Men.
Bill Weintraub
Kynegetikos derives from:
Kynegetes : a hunter, huntsman kynegetas amphi pala κυνηγετας αμφι παλα one who seeks the prize in wrestling
κυνηγετης
As of this writing, however, in AD June 2018, there is a feminist movement abroad stridently claiming that no shame should attach to female promiscuity, and that those who claim that such shame should so attach are guilty of "slut-shaming."
κυνωπης
κυπαρισσινος
Κυρος
For more about Xenophon, see Kynegetikos, above.
And to read Walter Miller's terrific 1914 Introduction to Xenophon and his Cyropaedia, click here.
Κυρου Παιδεια
Related:
Antipalos : properly wrestling against : then, generally, struggling against, antagonistic, an antagonist, rival, adversary, rivalling, a match for another
Related:
Related:
Prospalaio : to wrestle or struggle with
Related:
Katapalaio : to throw in wrestling ; metaph., to overthrow
See also:
Sympleko
παλαιστρα
Pleisthenes is also the name, in the Iliad, of the Atreid father of Agamemnon and Menelaus.
Πλεισθενης
Aside:
Smith, in his Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology (ca 1873), identifies Plei-sthenes with Epi-sthenes of Amphipolis, commander of Peltastai at the battle of Cunaxa [Xen. Anab. 1.10.7].
Translation : Smith thinks Epi-sthenes of Amphipolis and Plei-sthenes of Amphipolis are the same person, confused into two people by some medievally monkish copyist.
So does a classicist named Dillery, who revised Brownson's 1922 translation in 1998.
And maybe they are.
That would explain why Episthenes / Pleisthenes is put in charge of the young Armenian hostage at 4.6.1 -- that is, because he commands or has commanded the peltasts -- he's not just another grunt among ten thousand, in other words, but an officer of high rank and proven ability.
That said, does it matter whether the Warrior's name was Episthenes or Pleisthenes?
No.
But if they are the same person, it then becomes the case that Xenophon praises the Warrior -- in both Love and War.
Which is quite Xenophontic -- that is to say, the sort of thing Xenophon often does because he likes doing it.
And that's not a small point.
To Xenophon, if a Man is a good Warrior, he'll also be a good Lover, that is, a good practitioner of the Male Eros.
So if he can praise a Man as both a good Warrior and a good Lover, he will.
Cf, in that regard, Xenophon's recounting of the story of Archidamus and Kleonymus, and his account of what happened when Anaxibius was ambushed by Iphicrates -- as referenced by Smith.
Brownson's translation says of Anaxibius that "his favourite youth . . . fought and fell with him," but the Greek says that his paidika -- "his darling, his favourite, his male lover, stayed beside him . . . and there fought and fell."
Notice too that Anaxibius' record of service to Sparta in the Hellespont in 400 BC was decidedly mixed ; but by electing, in 389, to fight and die at his post, he achieved at the moment of his death, a kalon --a morally beautiful, because selfless, act -- which, in the ancient world, had the effect of wiping out any prior mis-steps and mis-demeanors, and guaranteed that, Anaxibius, like Aristonicus, would be remembered as having fought and died gloriously.
Inevitably, in the ancient world, every such Warrior act of aphilopsychos -- of disregard for life -- refers back to Achilles' decision to avenge his fallen lover Patroklos, even though so doing will bring about his own death.
That decision doesn't simply honor Manhood, the most important Idea, the Idea-of-Good, and the Sanction, of the Warrior World of Being -- but elevates Manhood - Manliness - Manly Spirit to an unassailable, an indomitable and invincible position over any world-of-becoming pleasures which might be lost to death.
Plutarch:
. . .
In some cases, even when there is no need for it, Erastai [Lovers] are moved to exhibit their love of danger [philokindunos], their disregard for mere life [aphilopsychos].
And that's what Anaxibius, in the presence of and joined by his paidika, does -- exhibits his love of danger and disregard for mere life.
As Achilles did before him.
It's what Manhood requires -- of Men.
See also:
And note that Episthenes of Amphipolis should not be confused with Episthenes of Olynthus, the paiderastes who, in yet another demonstration of true Warrior aphilopsychos, invites the rather boorish Thracian King Seuthes to chop off his head rather than kill a handsome youth.
Επισθενης Ολυνθιος
πλειστος
So -- a Polemarch is a War Leader (Polemos = Battle, Fight, War, Archos = Leader) ; and this, according to Liddell and Scott, is what the title meant in the various city-states :
πολεμαρχος
πολεμηδοκος
Related:
Propolemeo : to make war for or in defence of another : absol., οι προπολεμουντες the guards or defenders of a country, Plat. ; το προπολεμησον the body intended to act as guards, Arist.
προπολεμεω
Thus:
η πολεμικη αρετη
Related:
Empolemios : pertaining to war, Hdt.
εμπολεμιος
Derives from:
πολεμιζω
πολεμος
σωμα
Related:
Somatophulax : bodyguard
σωματοφυλαξ
Related:
Sophos : clever, skilled in any handicraft or art, cunning in his craft ;
clever in matters of common life, wise, prudent, shrewd
σοφος
Related:
A-stheneia : 1. want of strength, weakness, feebleness, sickliness, Hdt., Thuc., etc. ; 2. sickness, a disease, Thuc.
ασθενεια
© All material Copyright 1997 - 2024 by Bill Weintraub.
"I have spent countless hours submerged in water. I have slept for
days in arctic weather. I have slept under the desert stars with the
sound of a 105mm as a serenade. I have lived in a can under the ocean
breathing recycled farts for three months. I have brushed a swarm of
insects from the food in a malaria-ridden country and taken a bite.
"I don't need a lot to get by. Some men will roll over. I am not one
of those men. There are people who let their governments walk all over
them. Nations who have had their people persecuted, enslaved, or
slaughtered en masse.
"Our forefathers were not those kind of people. They started a war
with the most powerful empire on earth because they thought their
taxes were unfair. Some people are losers, some are survivors, and
some are fighters. I'm not going to stand by and let people I cared
for, served, and protected, treat me like less than the good Man,
father and soldier, I am."
XX Daniel Swift was killed in action Fighting for the Freedom of Ukraine.
On one face of the memorial is the finest explanation of wartime
service perhaps ever written, by a Confederate veteran who later
became a Christian minister: "Not for fame or reward, not for place or
for rank; not lured by ambition or goaded by necessity; but in simple
obedience to duty as they understood it; these men suffered all,
sacrificed all, dared all, and died."
~Jim Webb, Save the Confederate Memorial at Arlington
Mr Webb was a Marine infantry officer in Vietnam, Navy secretary
(1987-88) and a U.S. senator from Virginia (2007-13). He is the
distinguished fellow at Notre Dame's International Security Center.
© All material Copyright 1997 - 2024 by Bill Weintraub.





TWO
CULTURAL
MESSAGES



Bill Weintraub:
Pleis derives from Pleistos = most ; and Sthenes from Sthenos = strength, might, of all kinds, moral as well as physical :
Plei-sthenes -- the most strength, the most might -- the name spells out the Warrior's Moral Strength and Physical Power.
(While A-sthenes means wanting strength, weak, feeble -- think of an a-sth-matic.)
It is a fact that men desert their fellow tribesmen and relatives and even (God knows) their parents and children ; but lover and beloved, when their God is present [entheos -- when they're in-Godded, filled with their God, have their God within], no enemy has ever encountered and forced his way through.
AFTERWORD
That animal which we call man, endowed with foresight and quick intelligence, complex, keen, possessing memory, full of reason and prudence, has been given a certain distinguished status by the supreme Powers who created him ; for he is the only one among so many different kinds and varieties of living beings who has a share in reason and thought, while all the rest are deprived of it.
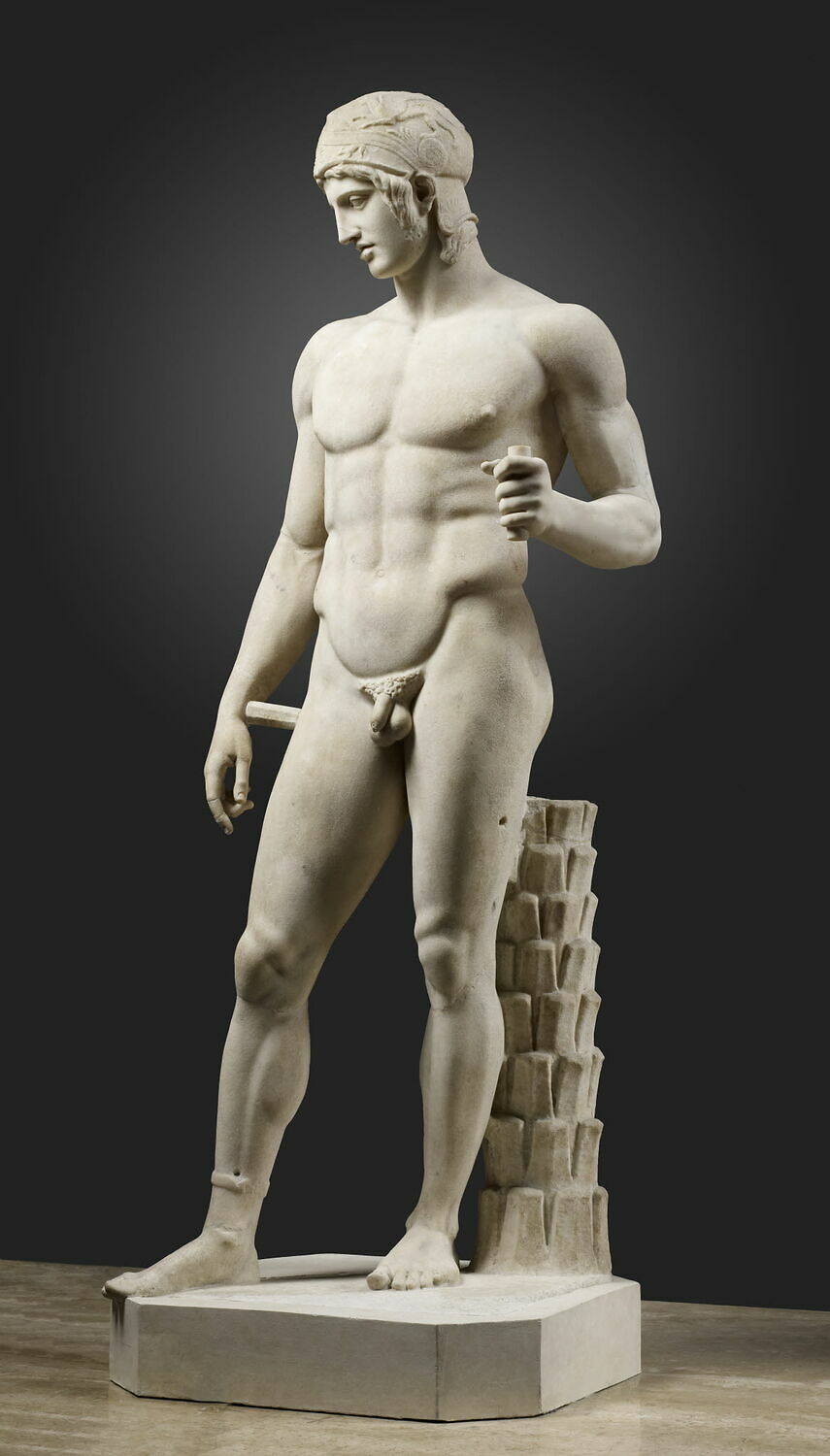
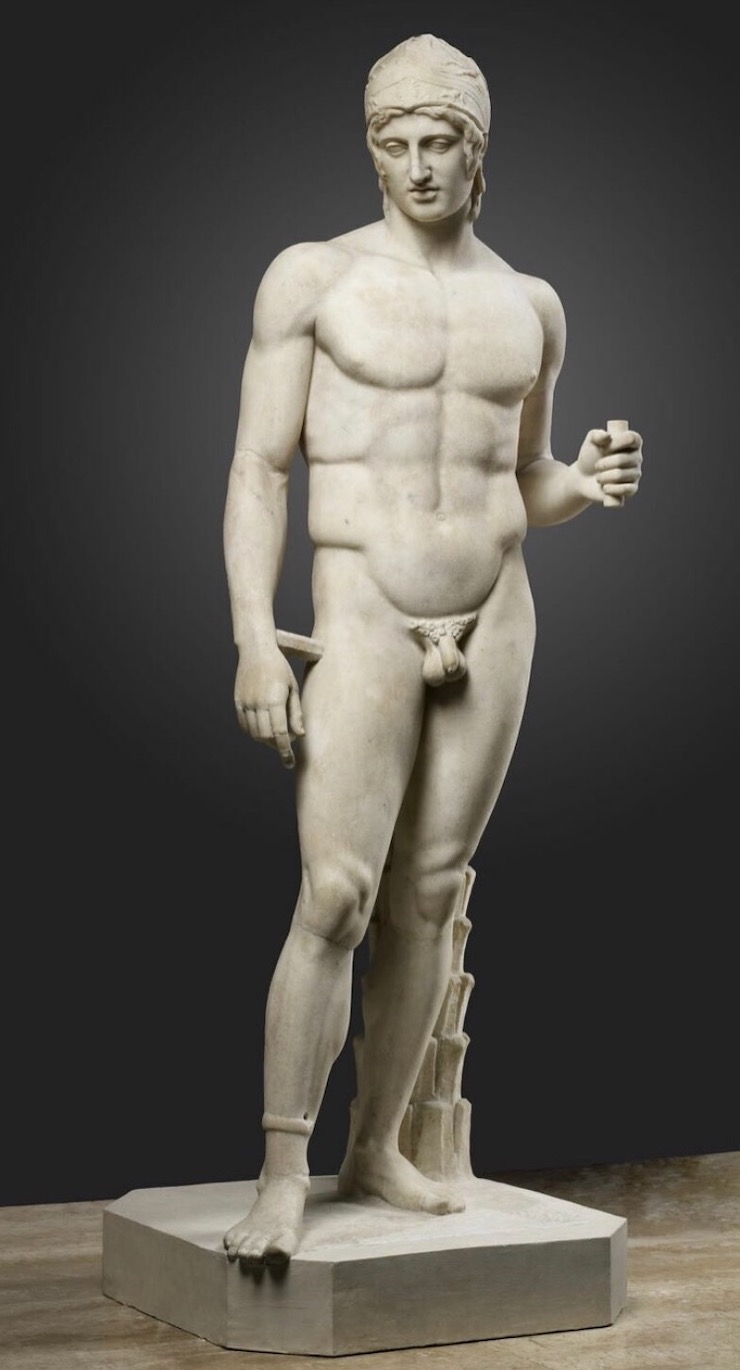
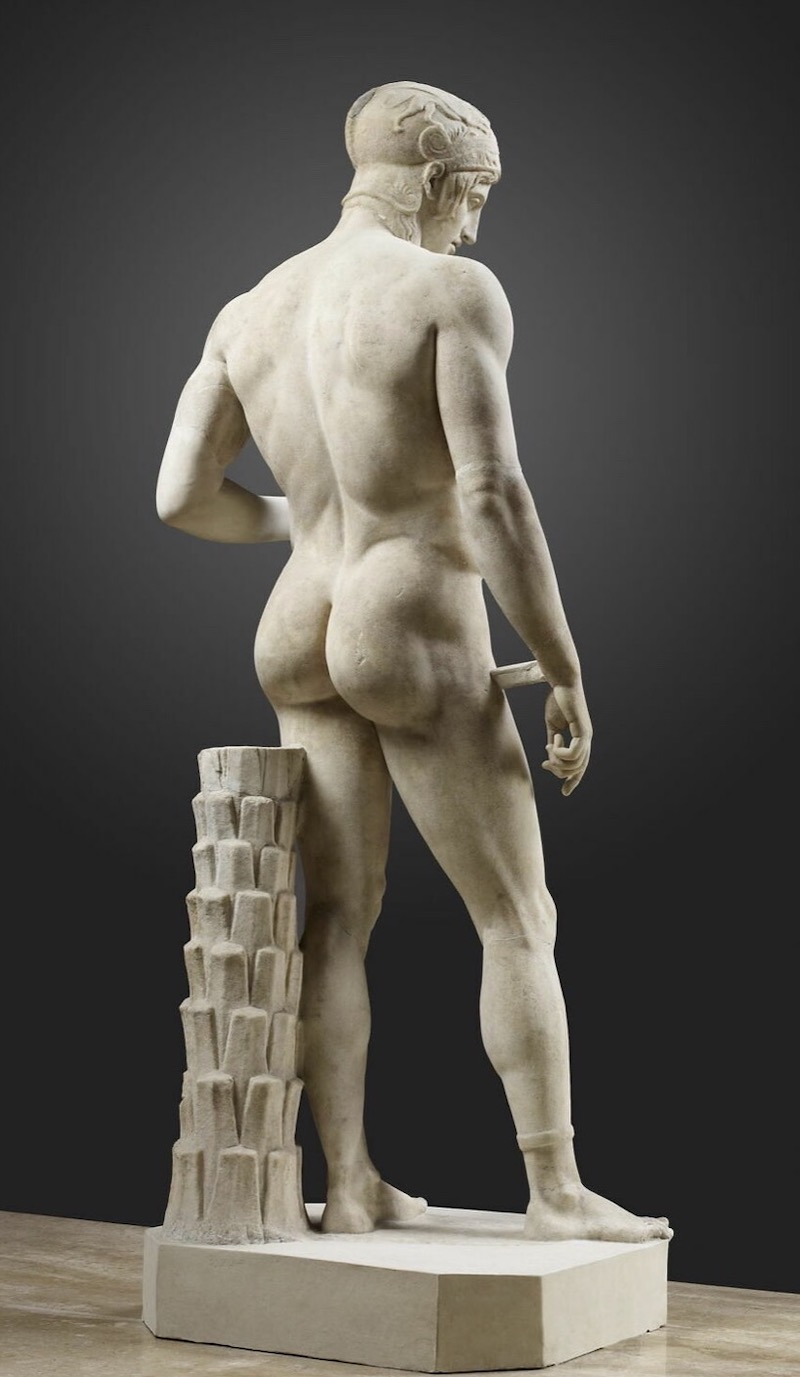
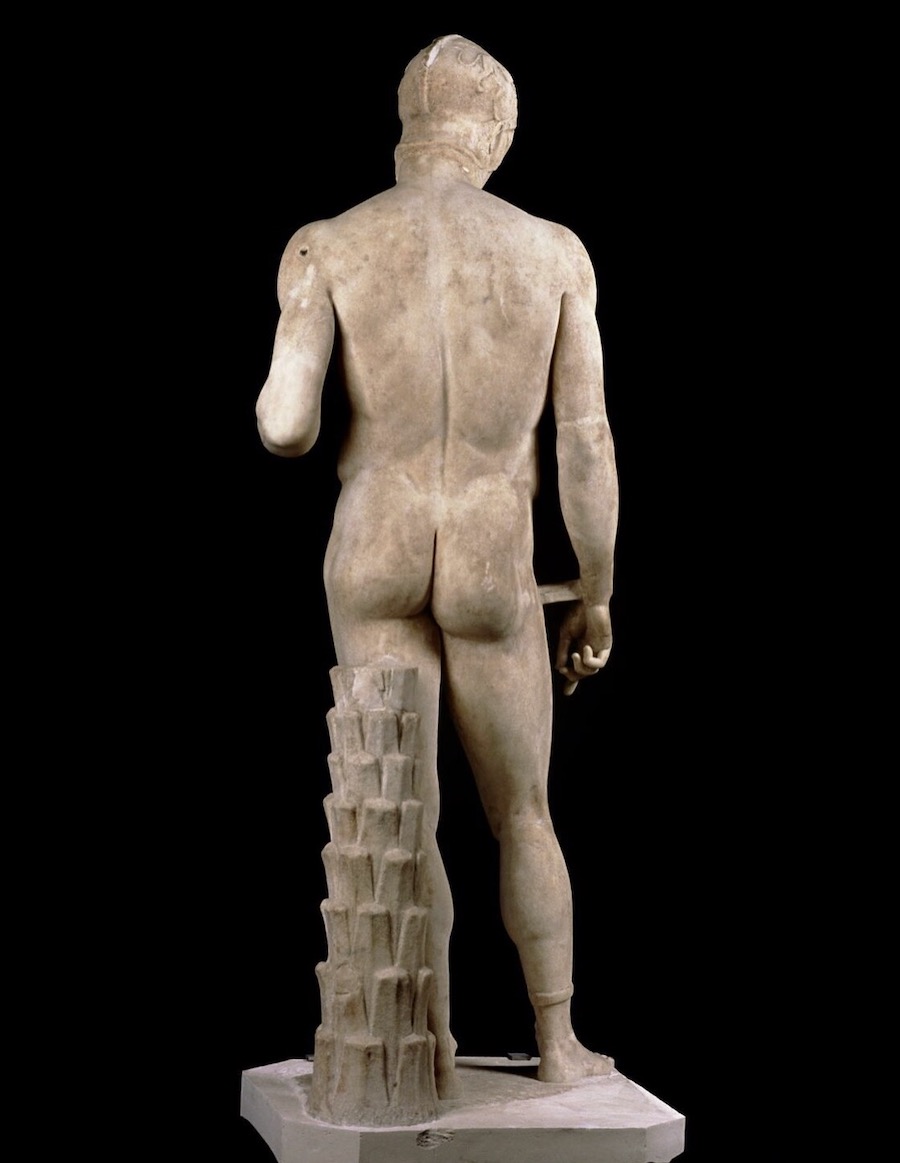
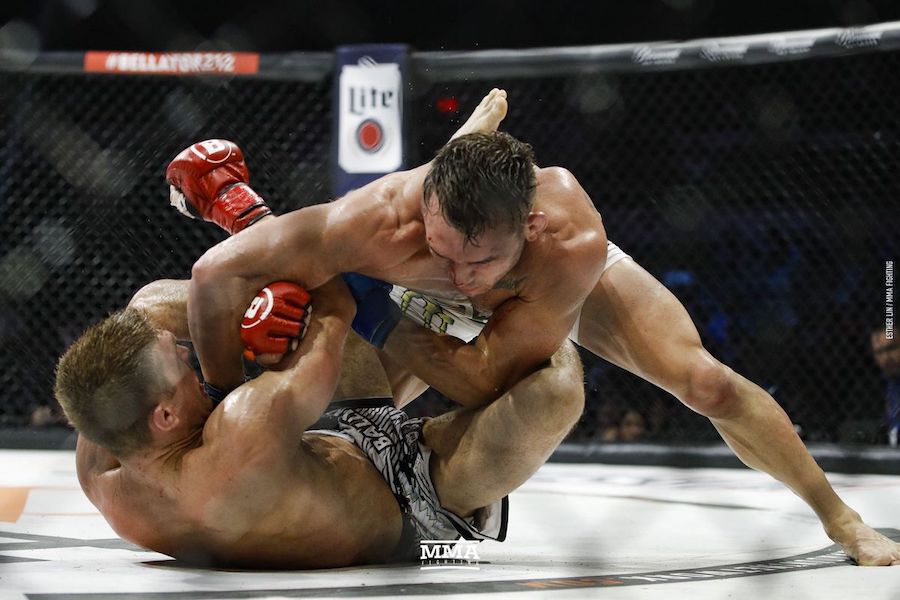










The Overwhelming Eagerness and Ardor to Fight of Young Men,
Youths in the Full and Fresh Bloom of Their Young Manhood,
Their Fighting Manhood
Than The Primal Love of Fight of Young Fighting Men


The Yearning for Manfight is the Yearning for Manhood
For the Manly Virtue of Manhood can only be conferred through Manfight
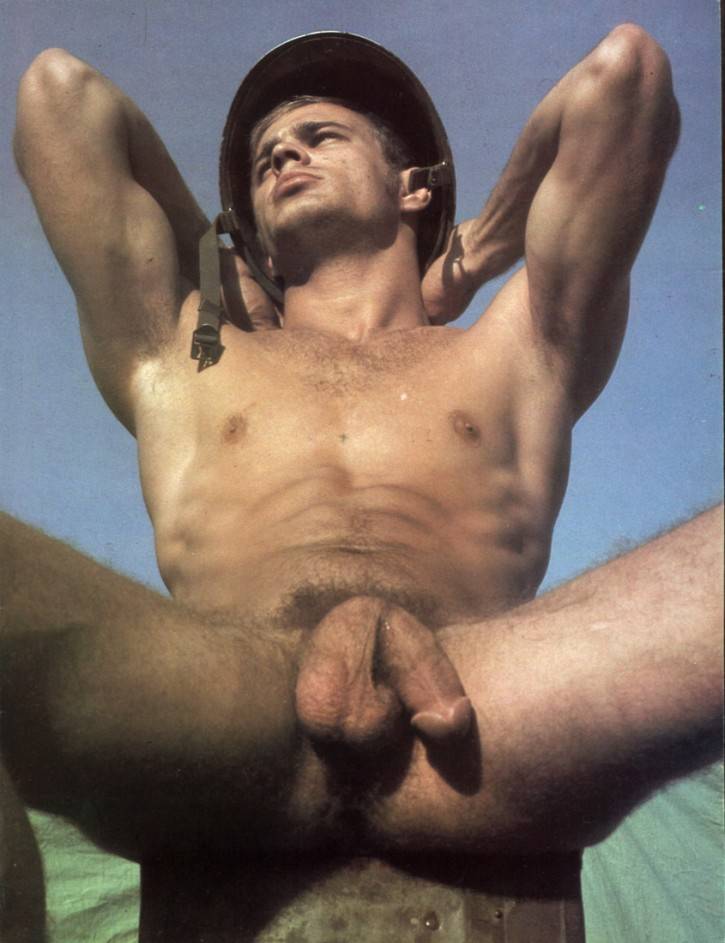
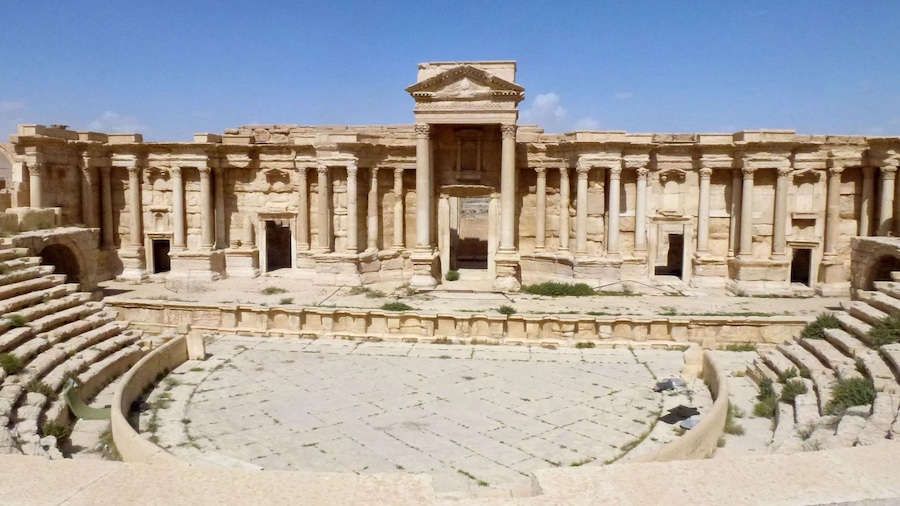
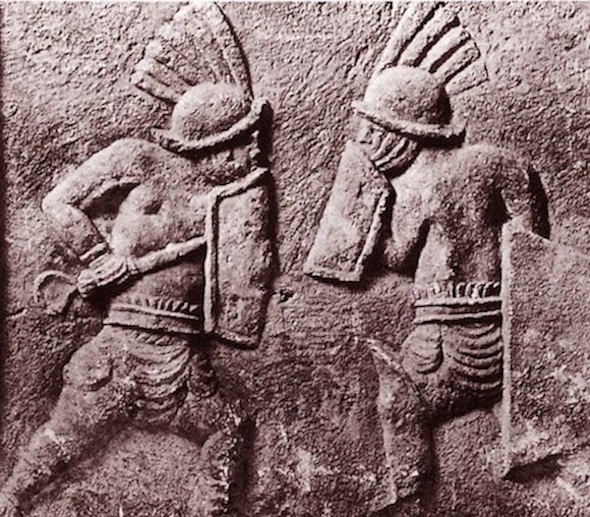





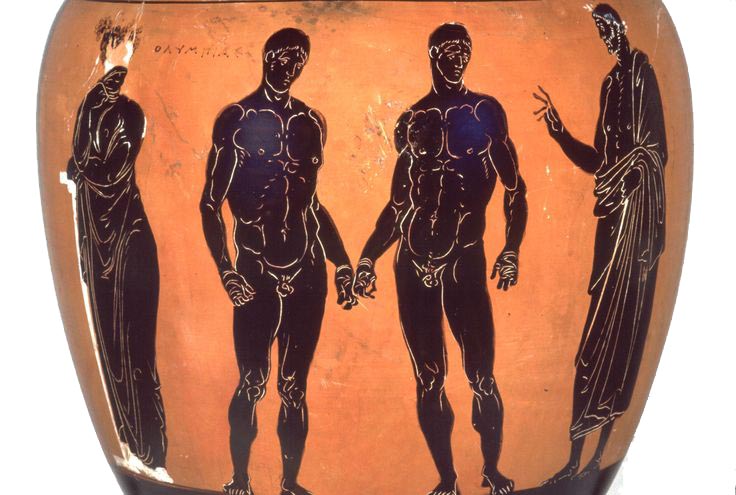

The wall would have kept the spectators clear of the Man-Fights as the spectators would have been extremely close to the Fighters in this arena.
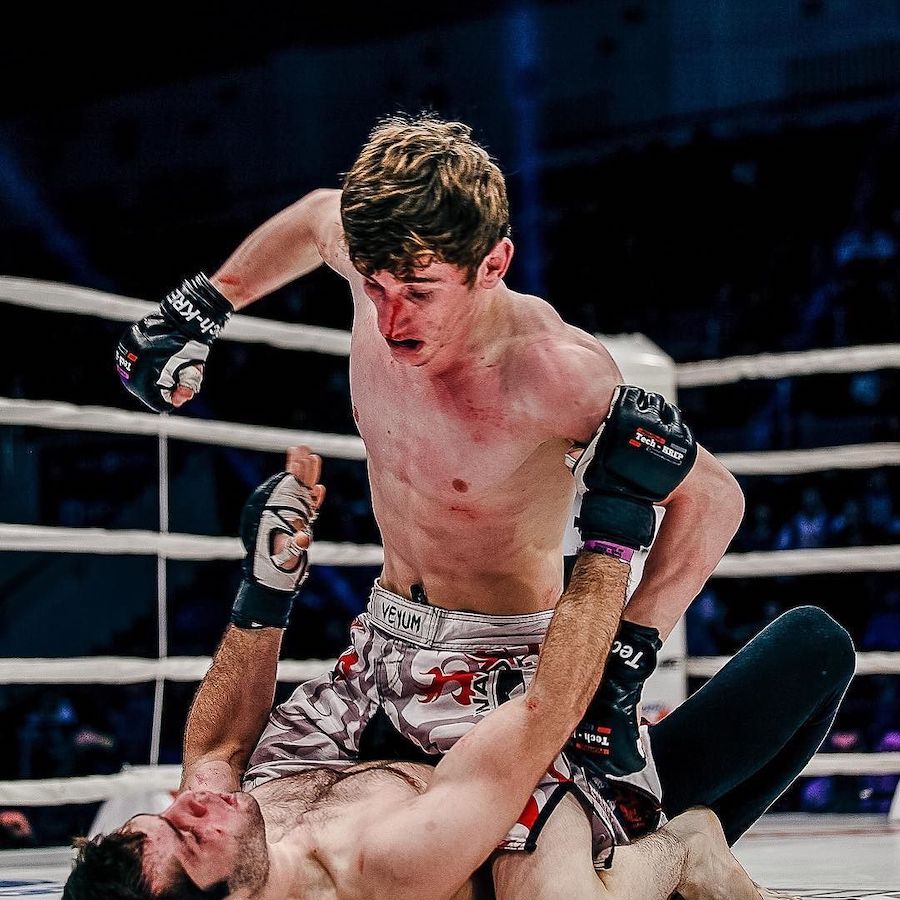

To Hear the Smacks and Thuds of the Dudes taking Hard Hits to the Body and Face
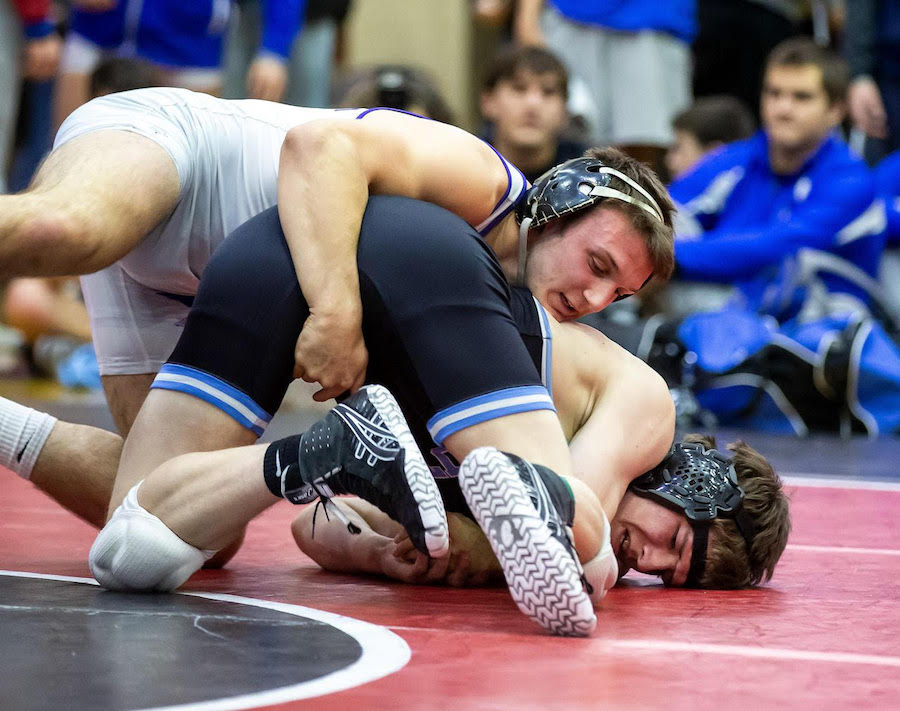
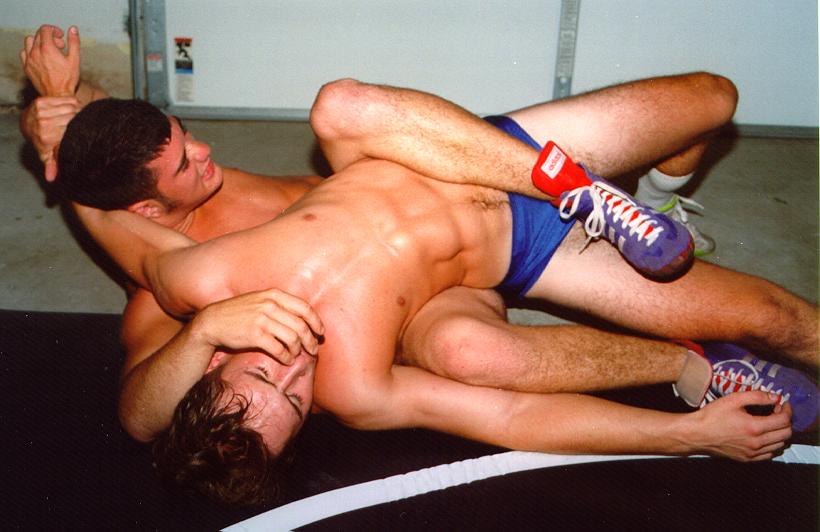






DRAKONTIOS
kai
POLYKRATES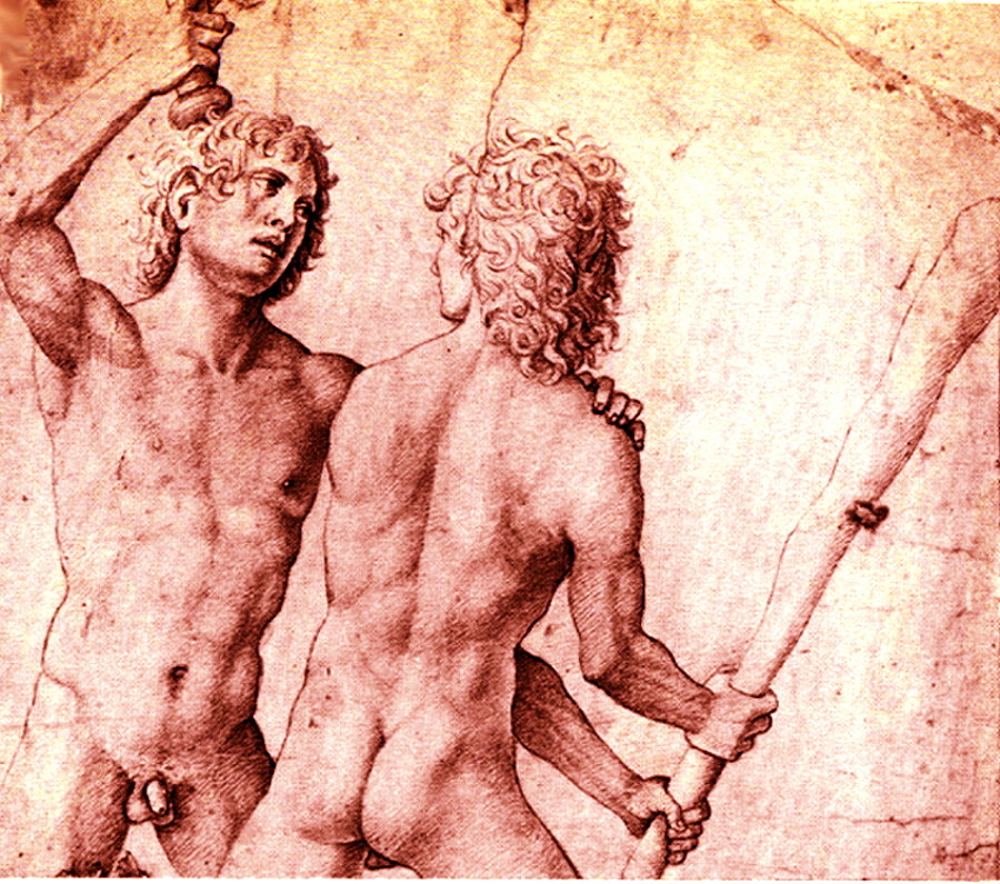 
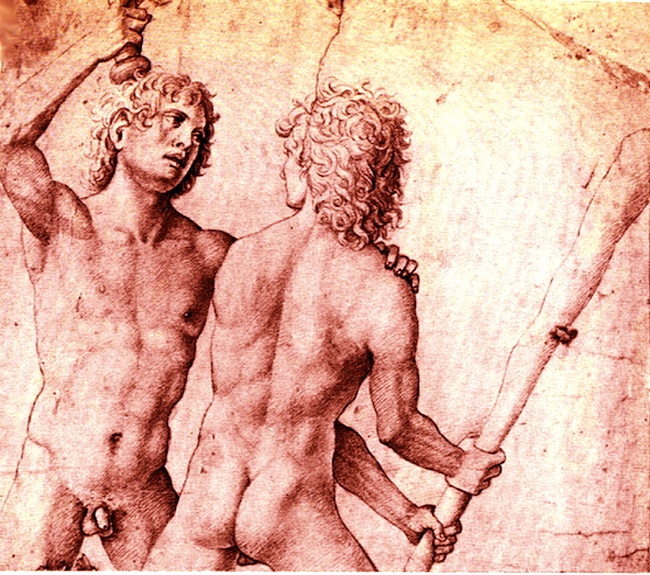
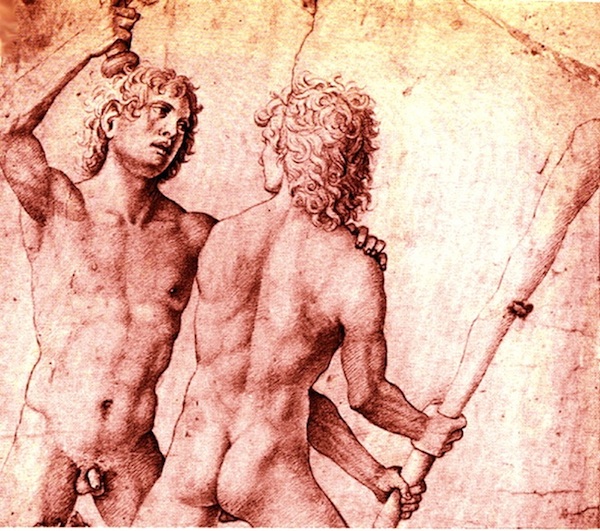
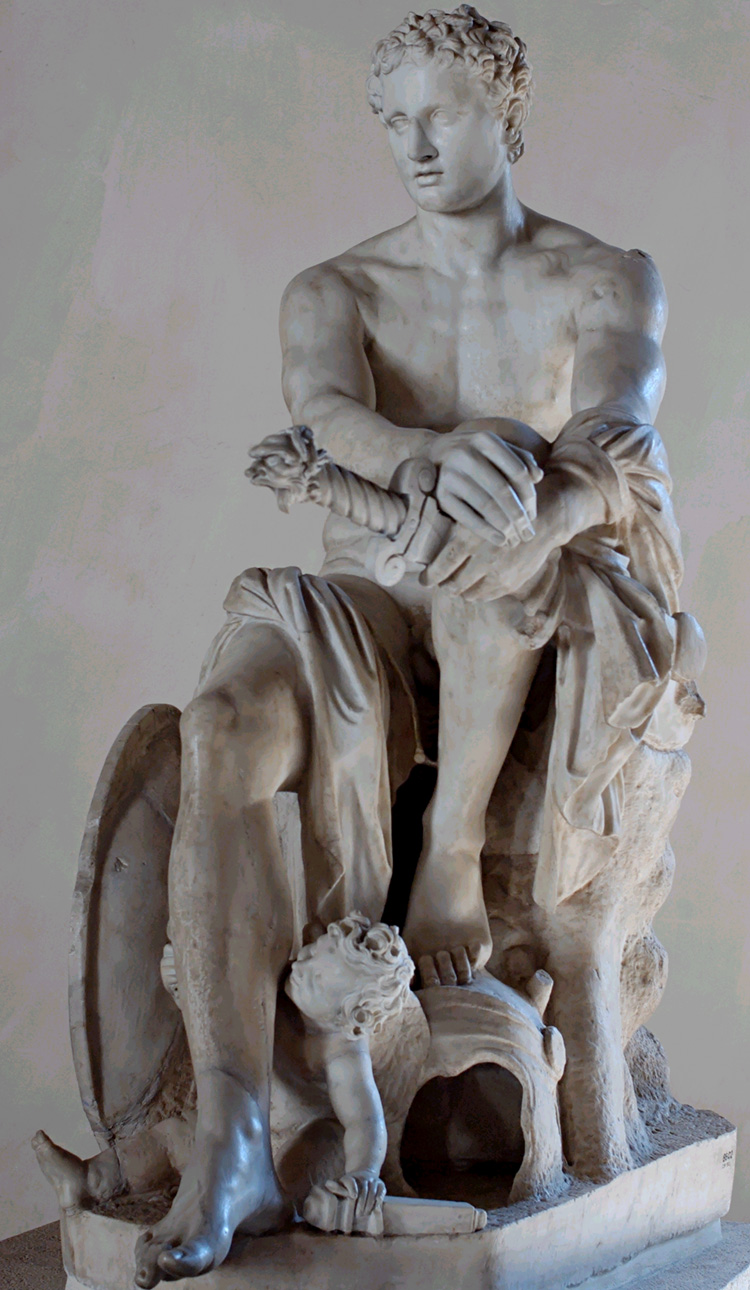

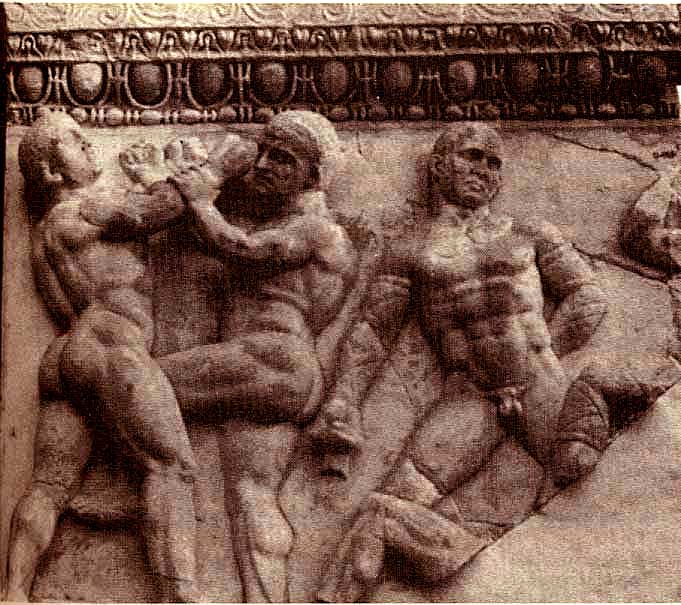









The Ludovisi Ares
The God's Cock and Balls
Are Visible Between His Legs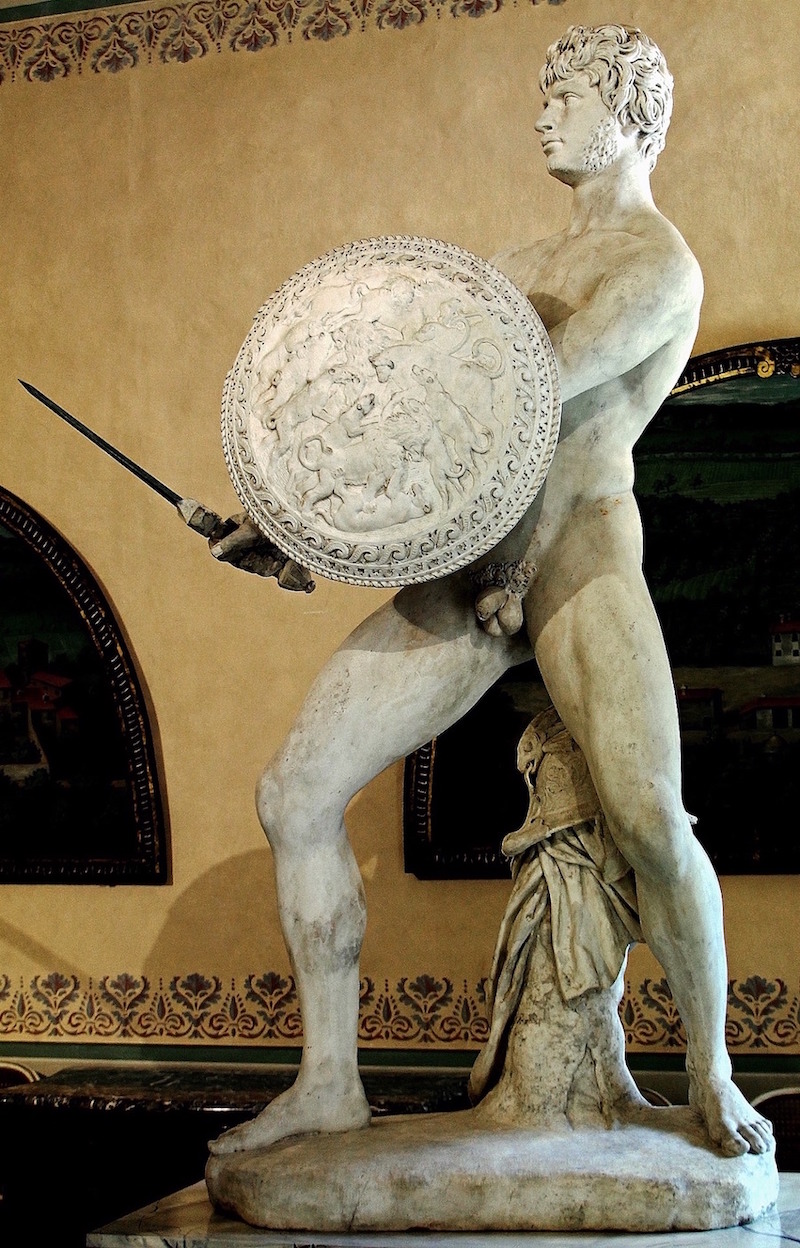

Agias of Pharsalos
Panktratiast
Perseus
Discus Thrower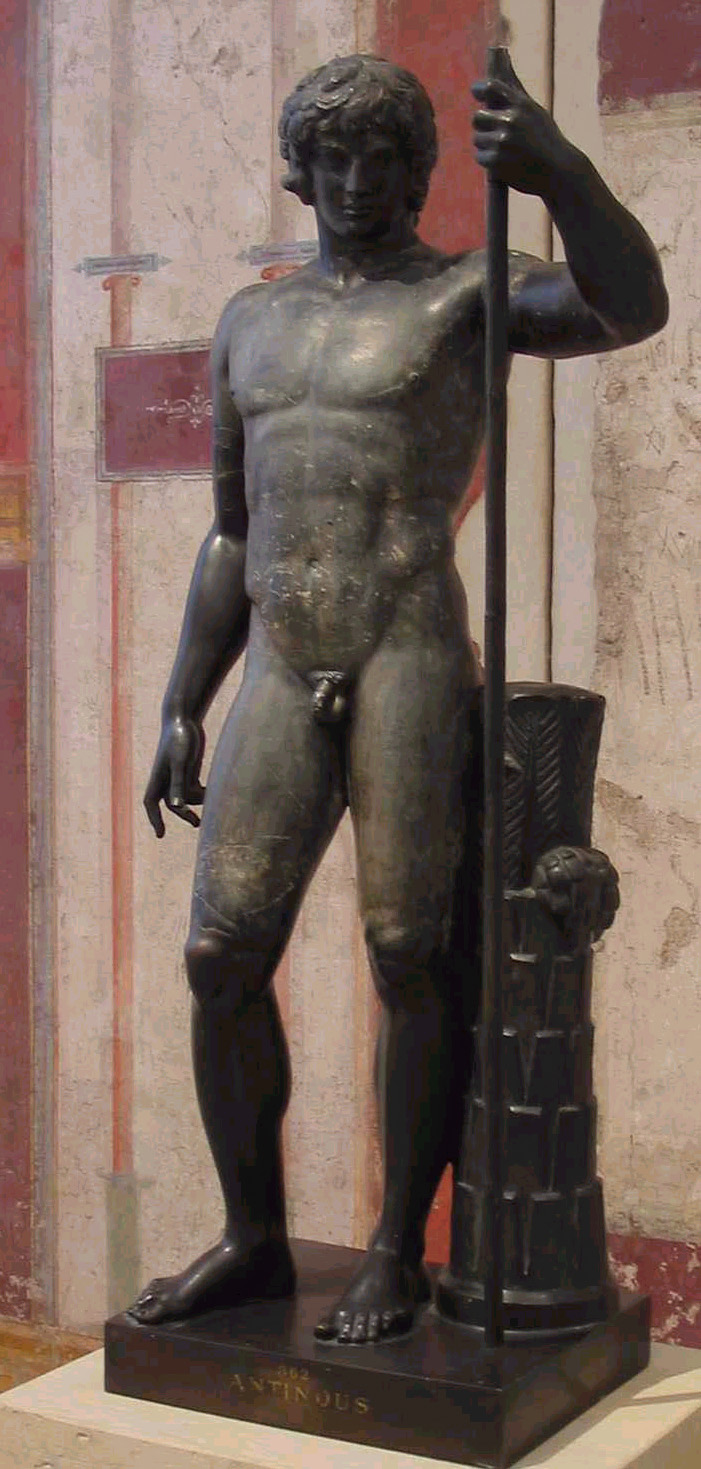
Antinous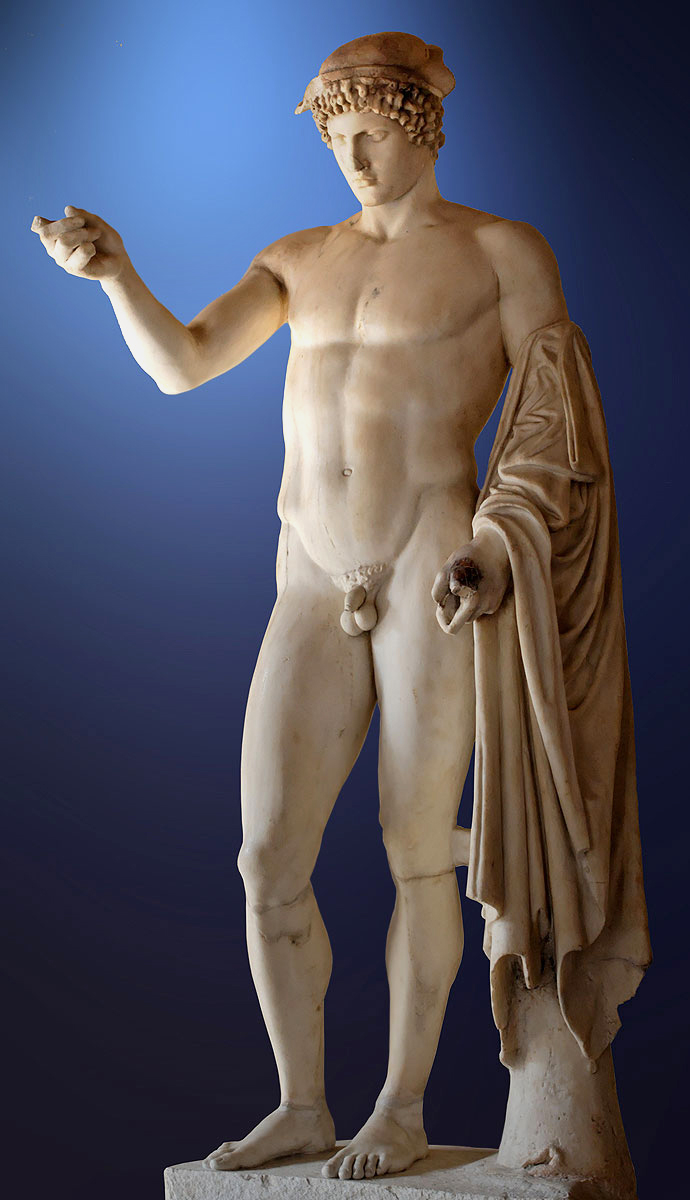
Hermes
Psychopomp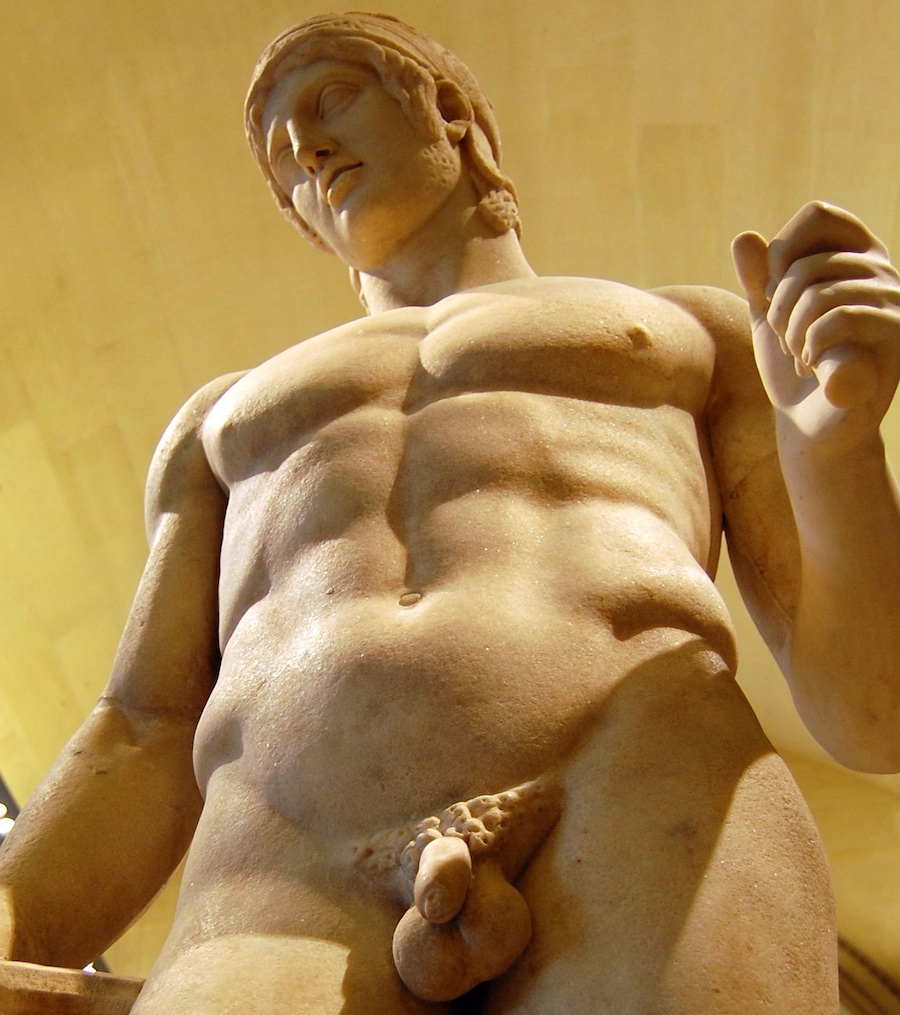







The Overwhelming Eagerness and Ardor to Fight of Young Men,
Youths in the Full and Fresh Bloom of Their Young Manhood,
Their Fighting Manhood

The Anticipation of Aggression :
There is nothing more Sacred or more Holy
Nothing more Alive with the Quickening, Pulsing, Throbbing, Yearning,
Surging, Swelling, Stiffening, and Rock-Hardening of Young Manhood
Than the Ardent Primal Love of Fighting Manhood
of Young Fierce and Ferocious Fighting Men

DRAKONTIOS
kai
POLYKRATES 
The Yearning for Manfight is the Yearning for Manhood
For the Manly Virtue of Manhood can only be conferred through Manfight
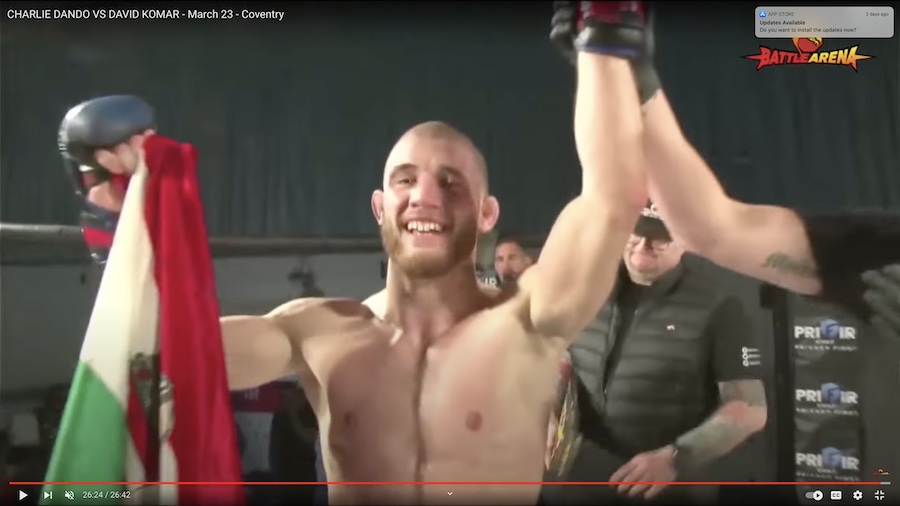





























Pubes
and the
Young Bulls
This Man is a Fighter
His nose is broken, his ears battered, his knuckles scored
This MAN is a FIGHTER








What a beautiful experience to have done even just once in life.
Fighting is an out of body experience . . . like
entering the World of Being for a brief few moments,
and quickly returning to the World of Becoming.






I have seen with my own eyes Troops of Nude Adolescent Boys in Lacedaemon
Fighting with Inconceivable Obstinacy, using Fists and Feet and Nails and even
Teeth to the point of losing their lives rather than admit defeat.
FINDS EXPRESSION IN THE NUMBER OF INSCRIPTIONS HONORING EPHEBES FOR THEIR COURAGE,
A PARTICULAR ATTRIBUTE OF VICTORS IN THE ENDURANCE CONTEST."
WHICH FUNCTIONED AS HOT HOUSES FOR IDEOLOGIES OF PHYSICAL CULTURE AND MARTIAL VALOUR

Gymnasion at Miletus
buildings in their cities' profiles

Gymnasion at Miletus
buildings in their cities' profiles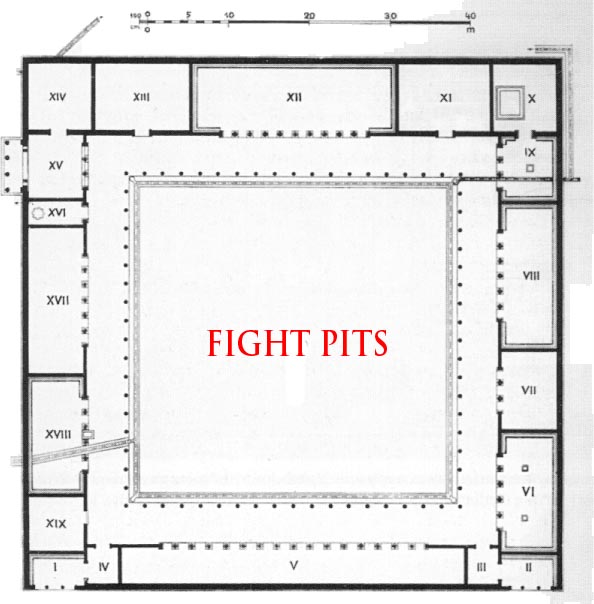
Classrooms grouped around Fight Pits
other Boys Excercising and Fighting Nude
So, for example, in this picture, the viewer is standing
in the central courtyard where the Fighters train,
and looking in at a classroom which faces out
-- which faces the Fight Pits.
The Ephebeion in the Palaistra at Priene
and military exercises, but so were those of most other ephebic systems.
time of Homer, military preparedness was required of all ephebes everywhere
because they formed the military reserve force for their cities.The Place of Naked Male Training in Manliness and Fight
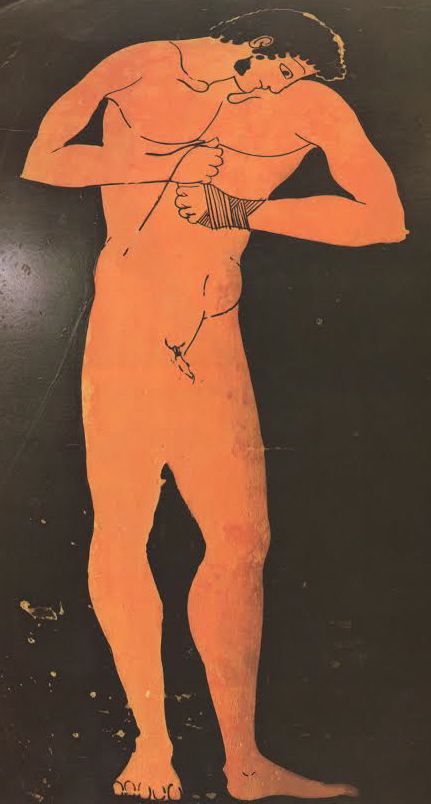
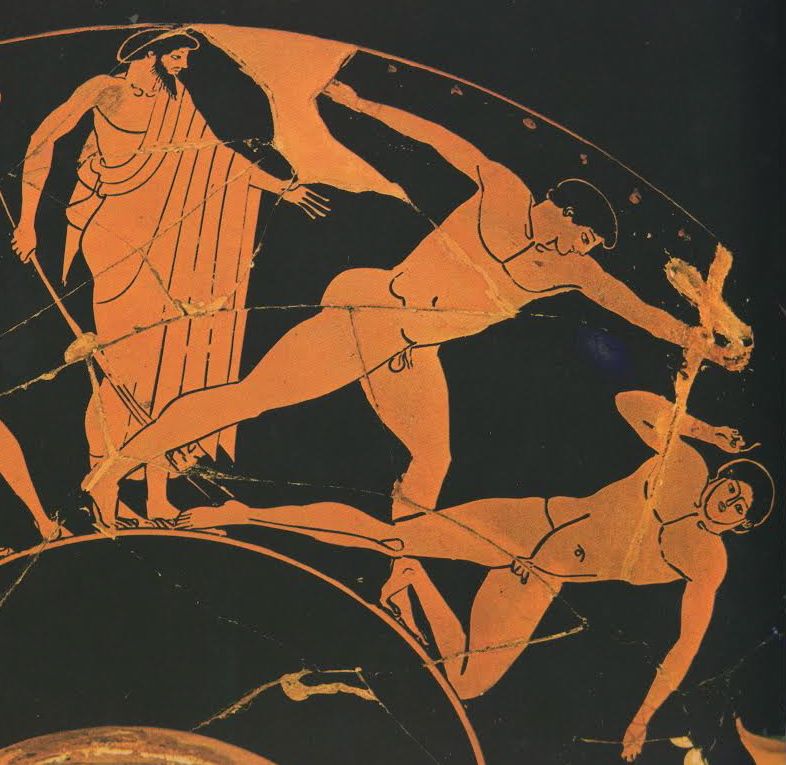




Classrooms grouped around Fight Pits
other Boys Excercising and Fighting Nude
The Ephebeion in the Palaistra at Priene
and military exercises, but so were those of most other ephebic systems.
time of Homer, military preparedness was required of all ephebes everywhere
because they formed the military reserve force for their cities.




which are then experienced by us in the Warrior World of Becoming,
the Combatant Cosmos.
all of which mean the Willingness and Abiilty to Fight.

who personify another attribute of the Form -- Manly Truth.




in the chaos of embodiment and re-birth into the World of Becoming, the Combatant Cosmos.
through a disciplined course of AN-amnesis, UN-forgetting.
this ordered UN-forgetting :












Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD




Again :
Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD
is formed and shaped by Greek paideia
and its gymnastic, palaistraean, ideal --
the Wrestling School.
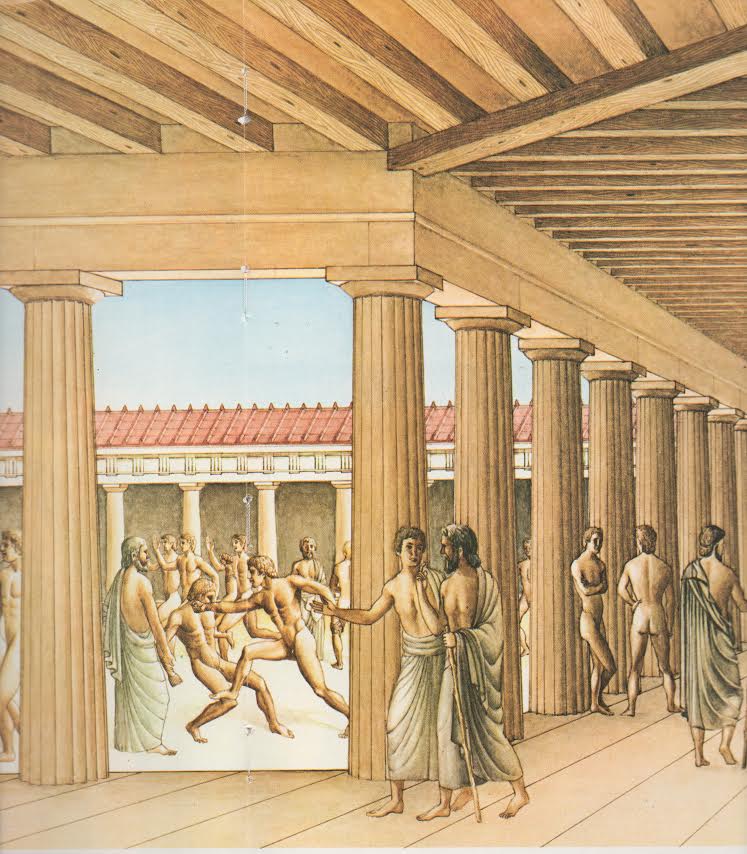
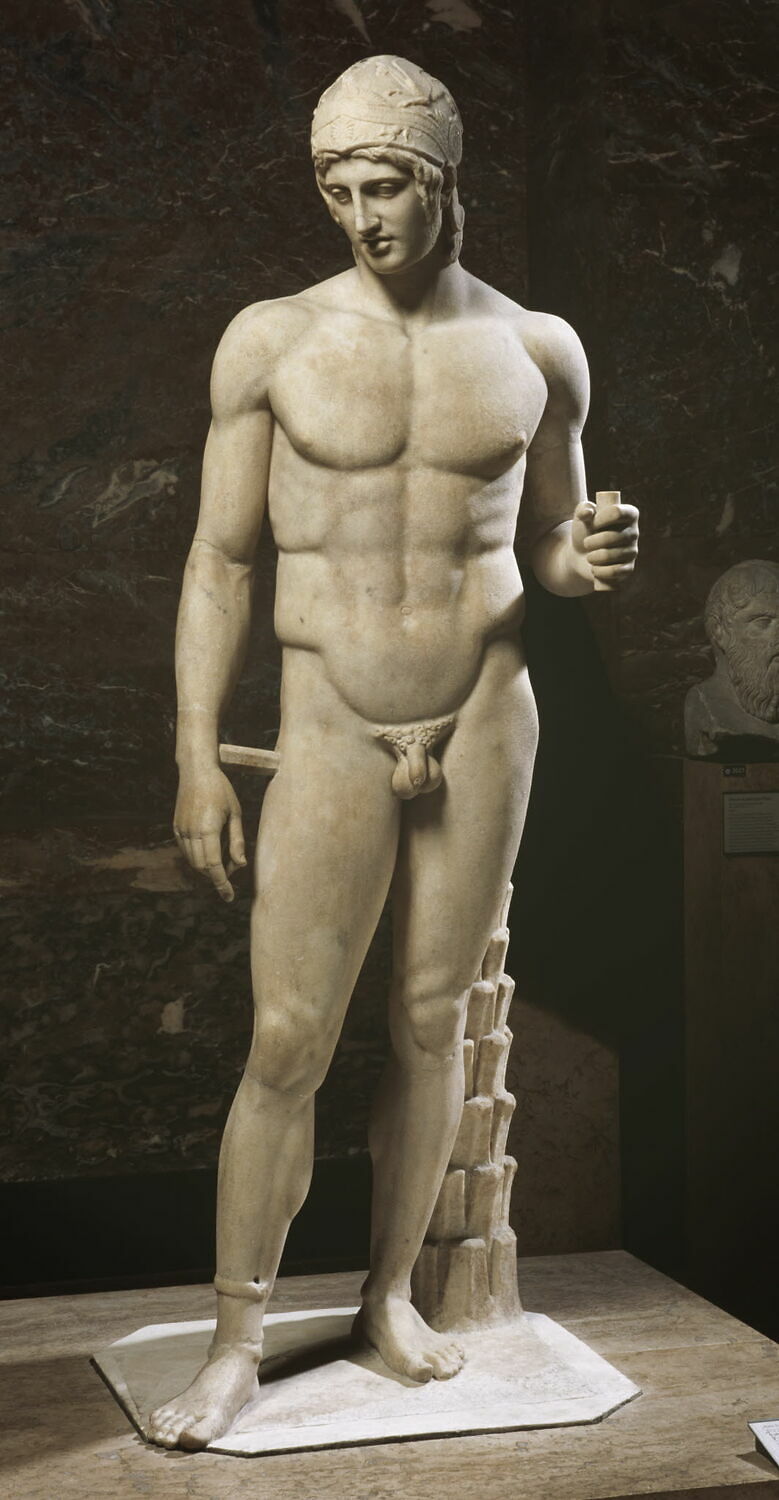





"Strong he is, for strong he deems himself"
~Virgil, referring to a True Warrior
Strong they are, for strong they deem themselves
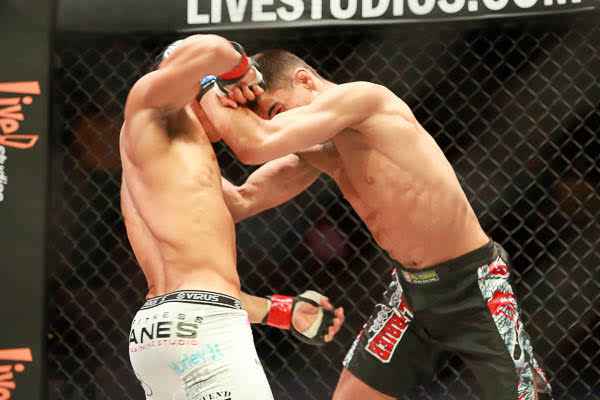


THE TRAINING UP
OF THE YOUTH
FOR WAR
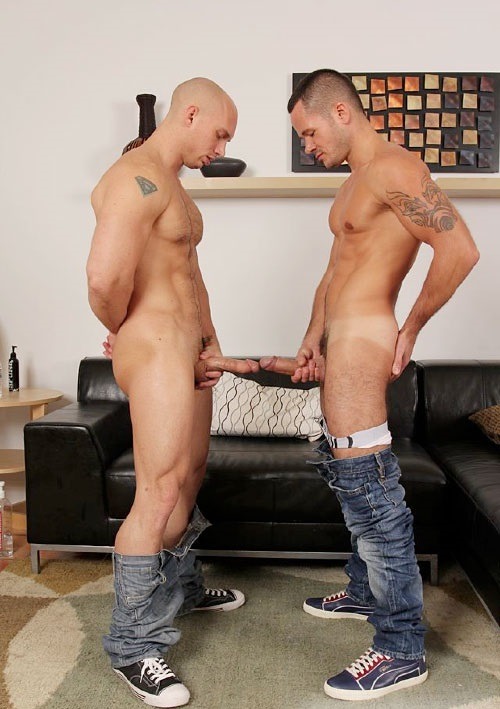
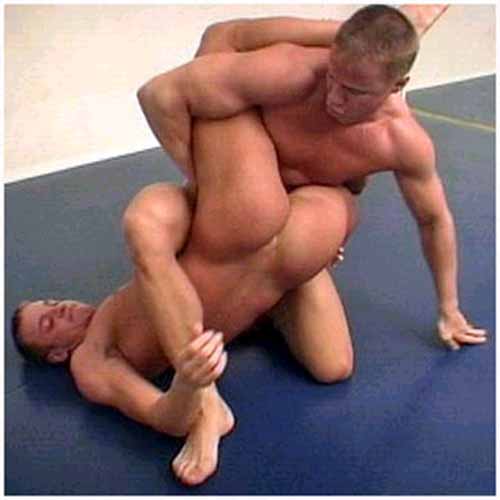
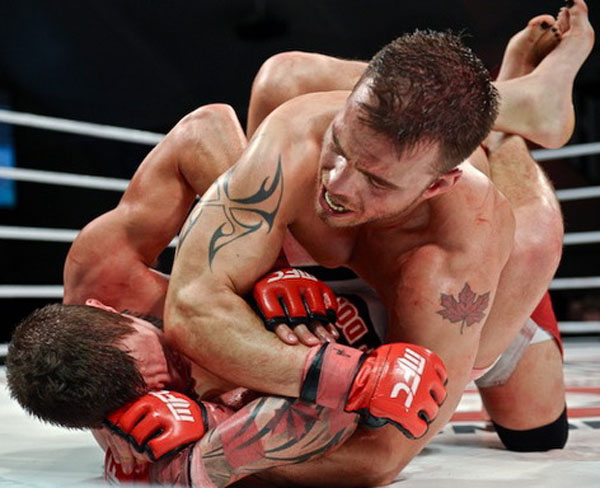
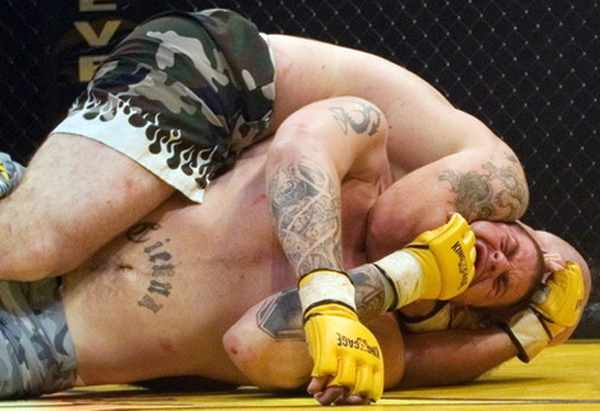
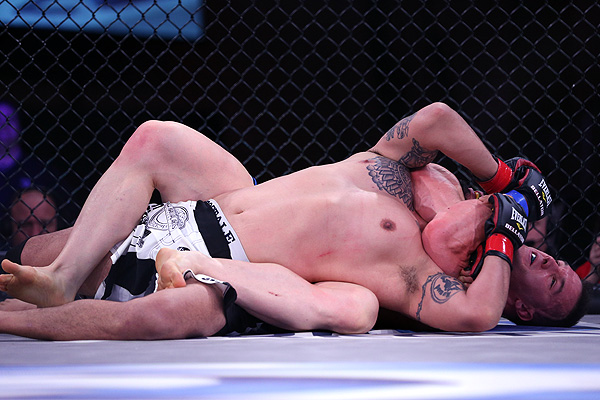
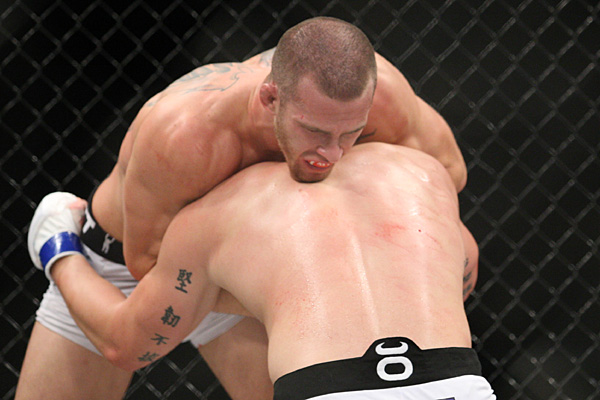
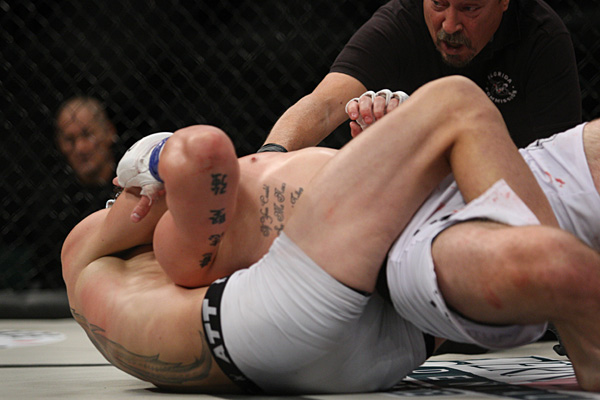
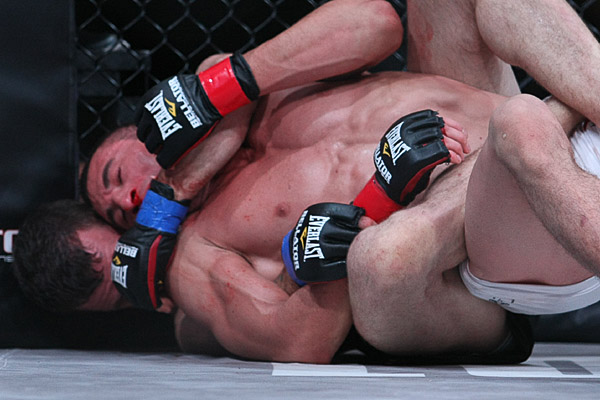
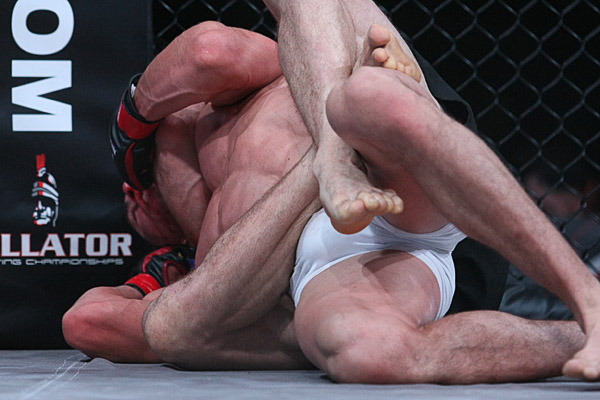
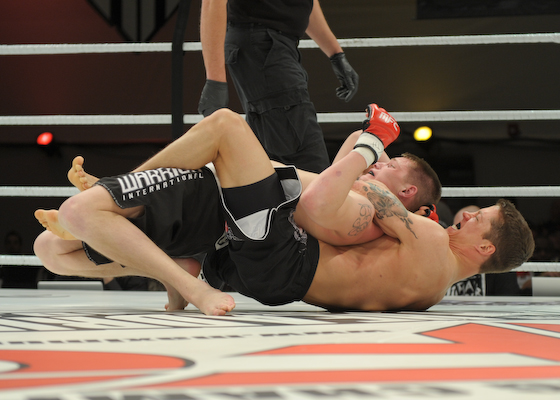
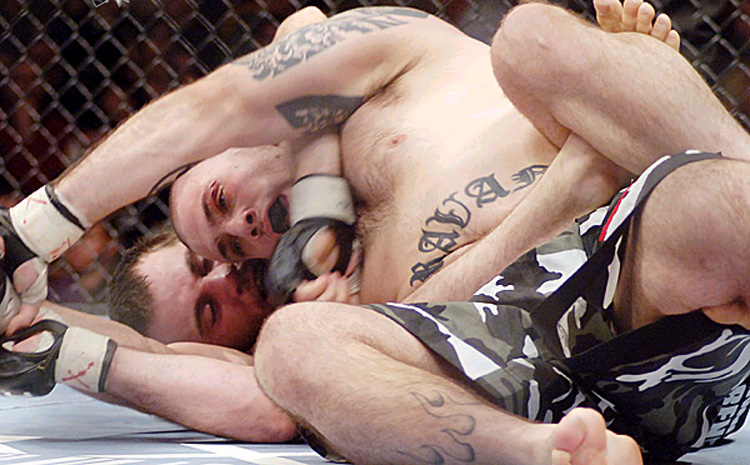


























PALAESTRA

Classrooms grouped around Fight Pits
other Boys Excercising and Fighting Nude
The Ephebeion in the Palaistra at Priene
and military exercises, but so were those of most other ephebic systems.
time of Homer, military preparedness was required of all ephebes everywhere
because they formed the military reserve force for their cities.





the Warrior Kosmos.
which are then experienced by us in the Warrior World of Becoming,
the Combatant Cosmos.
all of which mean the Willingness and Abiilty to Fight :

Fight is core to Man, as can be seen in the images of these young Fighting Men,
who personify another attribute of the Form Man -- Manly Truth.


Manly Truth is Truth which is Willing and Able to Fight




in Chastity : The First Grace of Manhood.
PHYSICAL VIOLENCE AND BLOODY BRUTALITY OF
MAN AGAINST MAN
FIGHT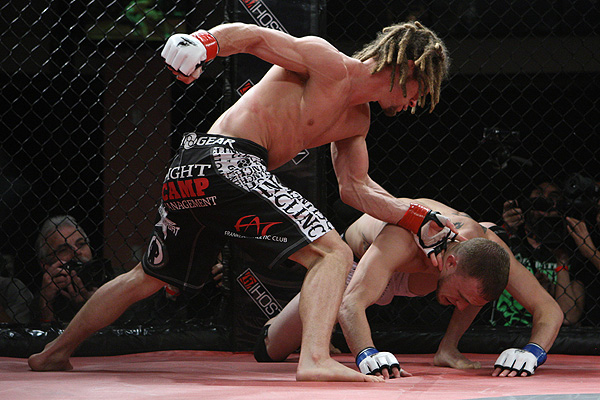
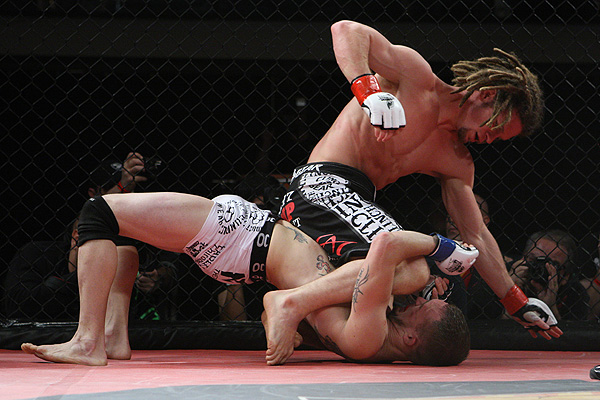
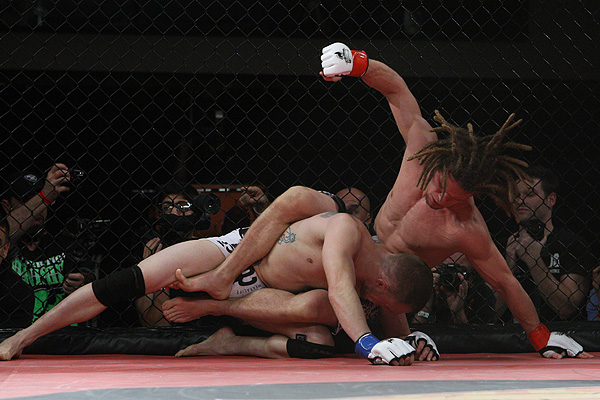




The Ultimate Vindication of Honour lies in Fighting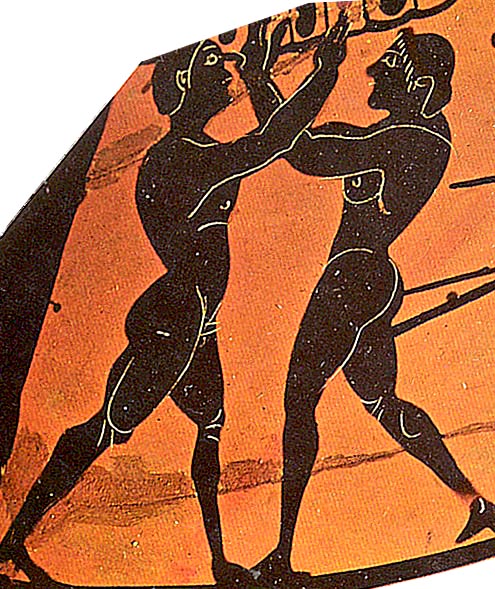
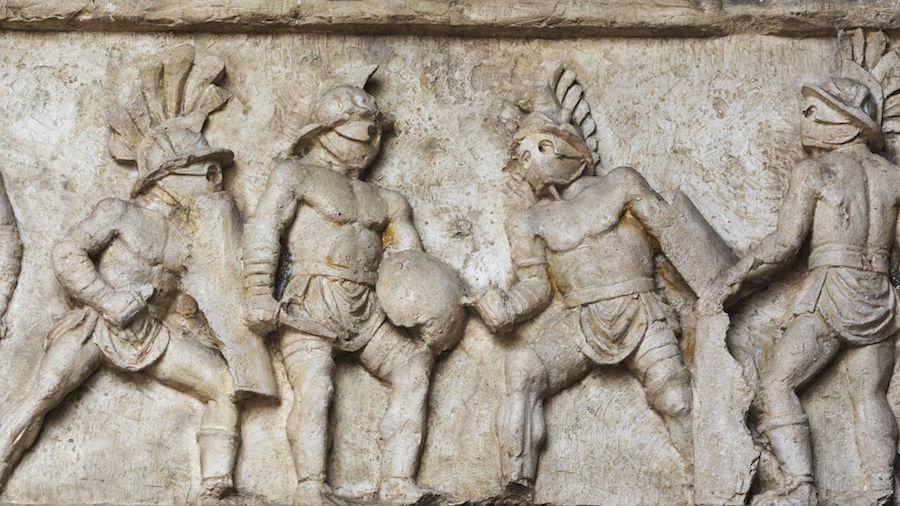













Bronze Statue of the Emperor Hadrian
Wearing a Breastplate Decorated with
Scenes of Nude Gladiators Fighting
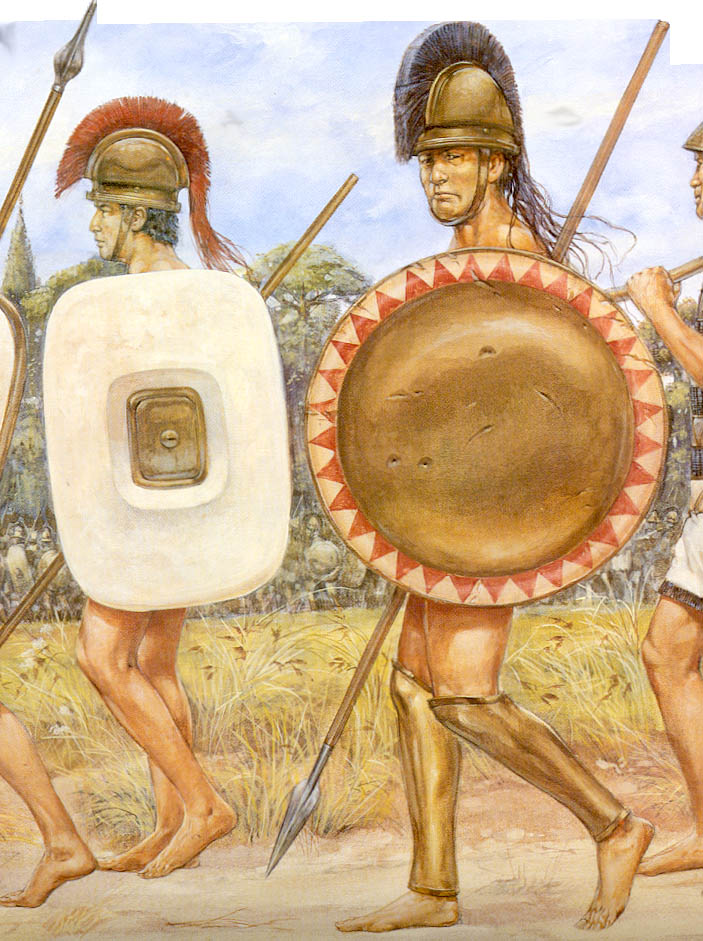
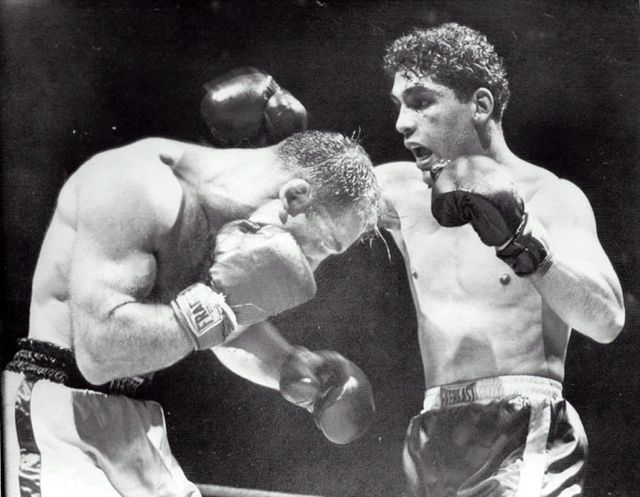
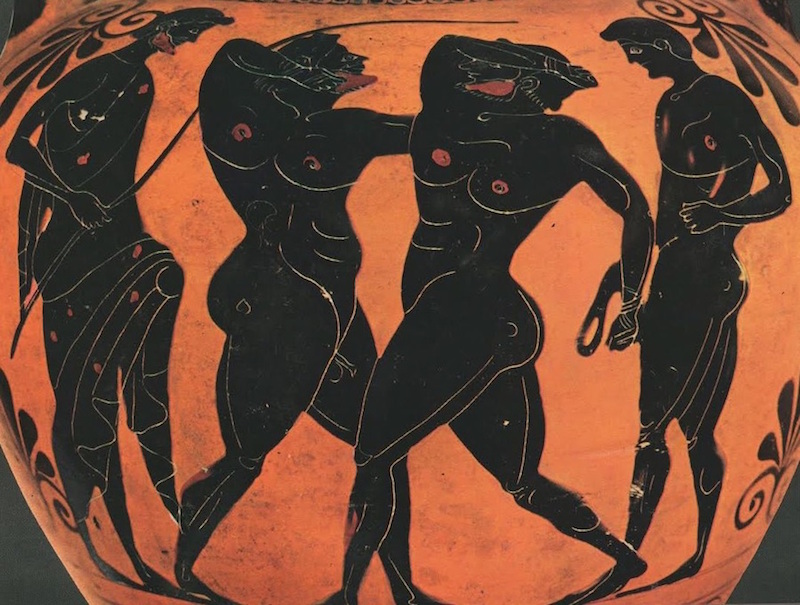































 >
>
in the chaos of embodiment and re-birth into the World of Becoming, the Combatant Cosmos.
through a disciplined course of AN-amnesis, UN-forgetting.
this ordered UN-forgetting :












This image of Lord Ares,
the Greek God of Battle-Fight-War,
was sculpted by Alkamenes in 425 BC,
and is today known as
the Borghesi Ares

Deinomachus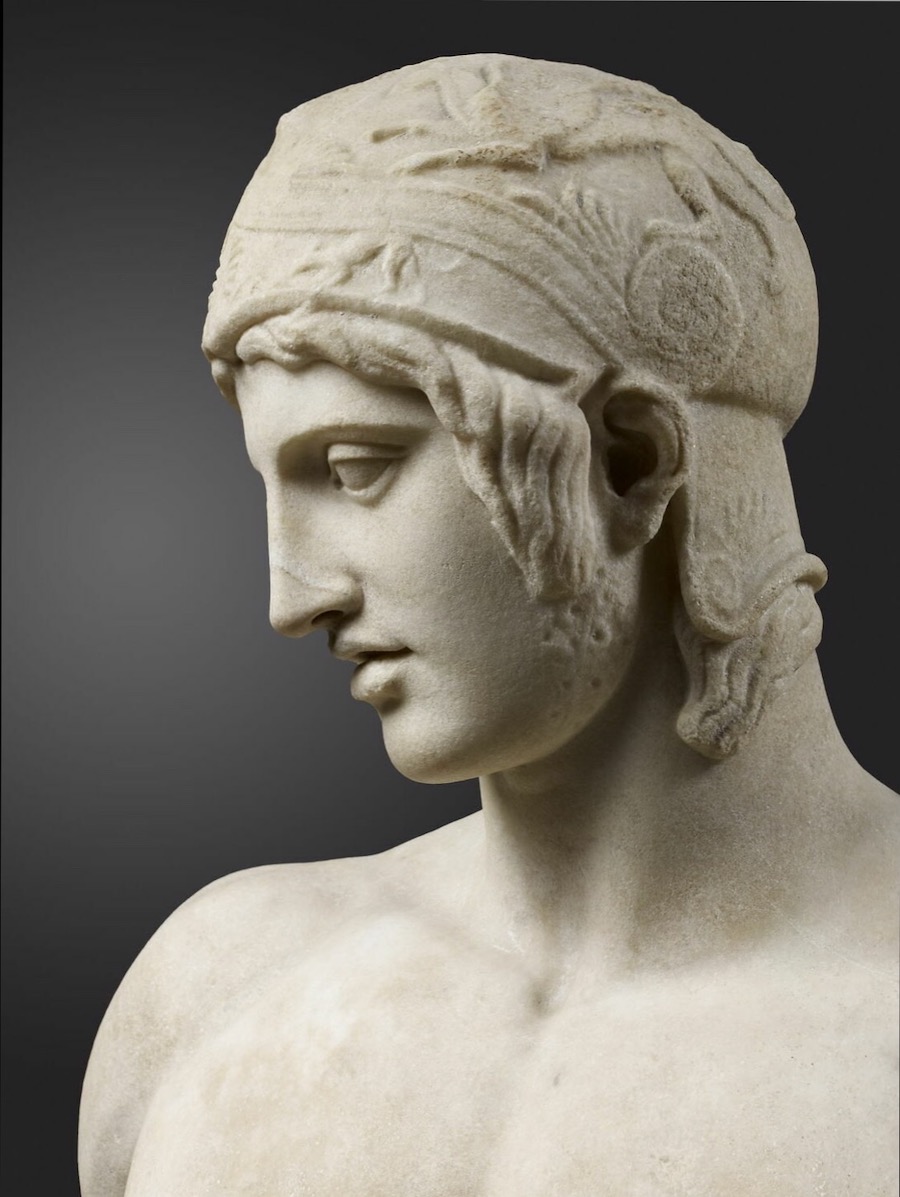
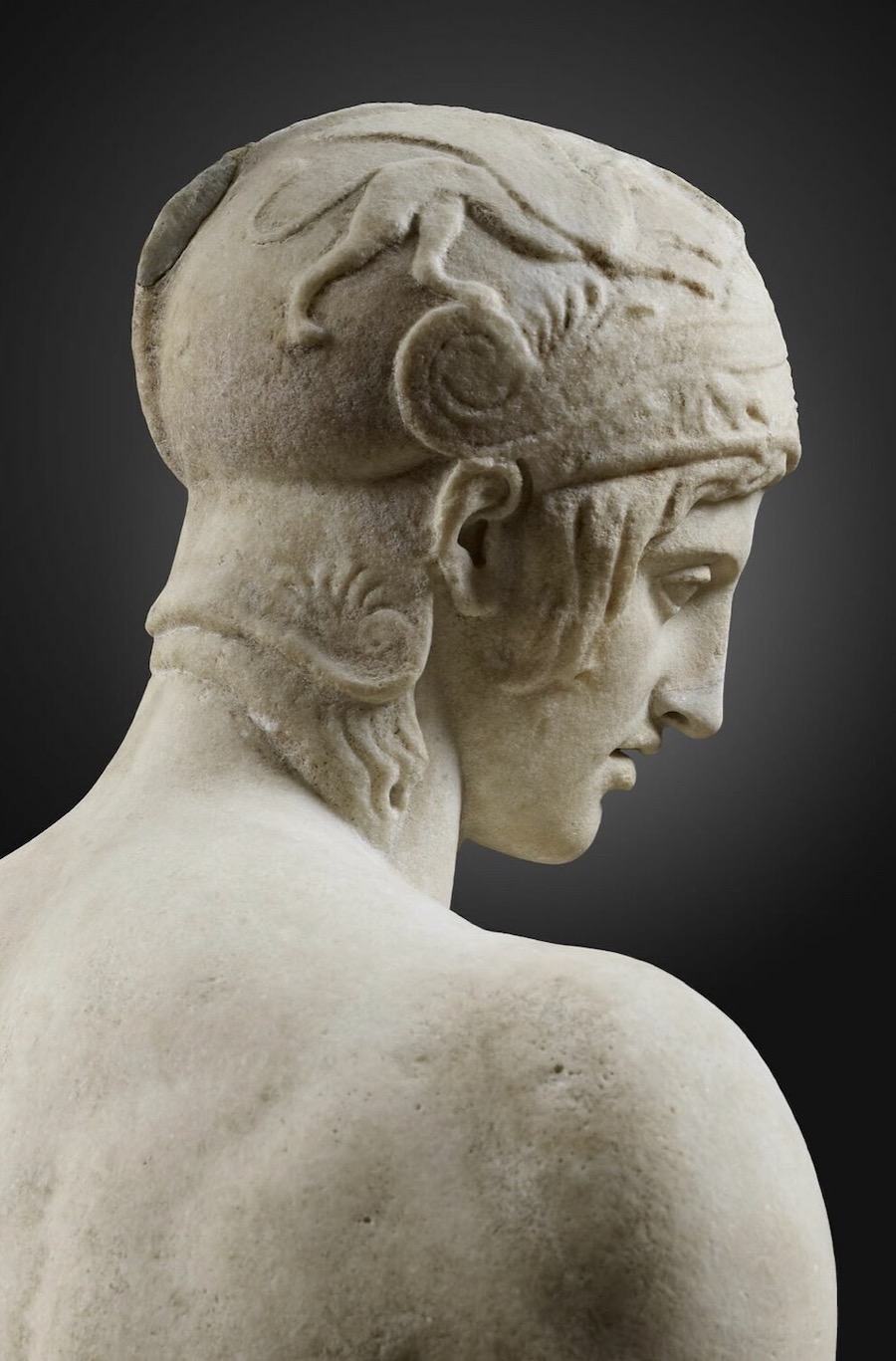


Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD
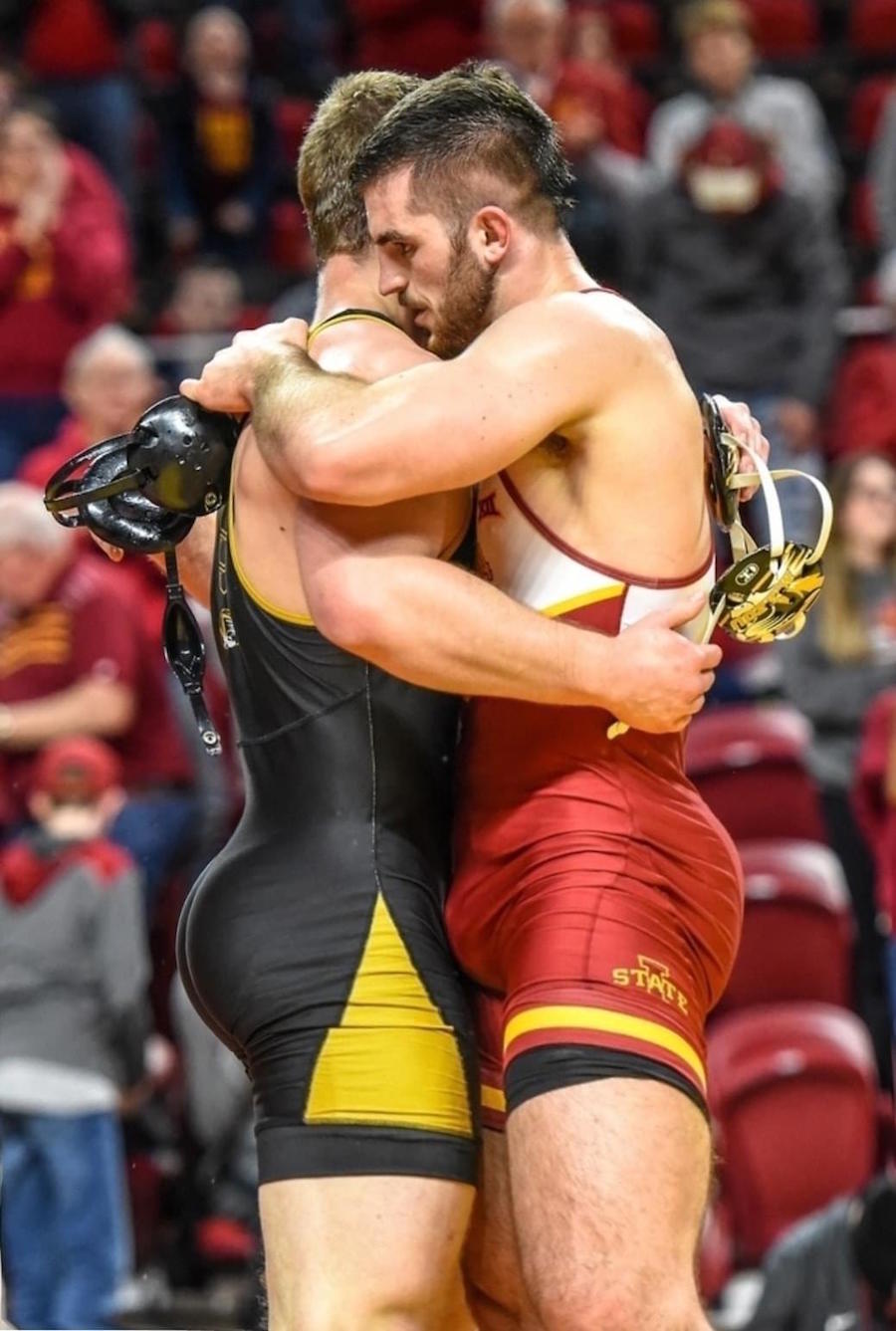






Again :
Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD
is formed and shaped by Greek paideia
and its gymnastic, palaistraean, ideal --
the Wrestling School.
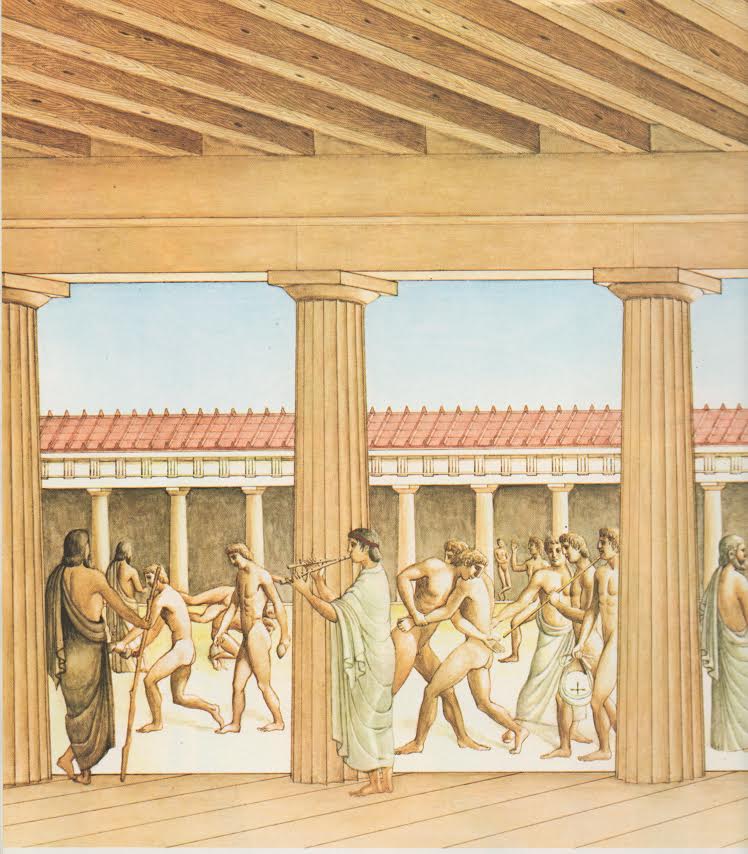


PERFECT SYMMETRY

Lucian :
We [Greeks] have thought up different kinds of athletics and have appointed coaches for each type. We teach one how to box, another how to compete in the pankration, so that they can become used to hard work, to stand up to blows face to face, and not to yield through fear of injury.
Lucian : Our troops have skin of high color, darkened by the sun, and faces like real men; they display great vigor, fire, and virility. They glow with good health, and are neither shriveled skeletons nor excessively heavy, but they have been carved to perfect symmetry ; they have used up and sweated off useless and excess flesh, and that which is left is strong, supple, and free, and they vigorously keep this healthy condition.
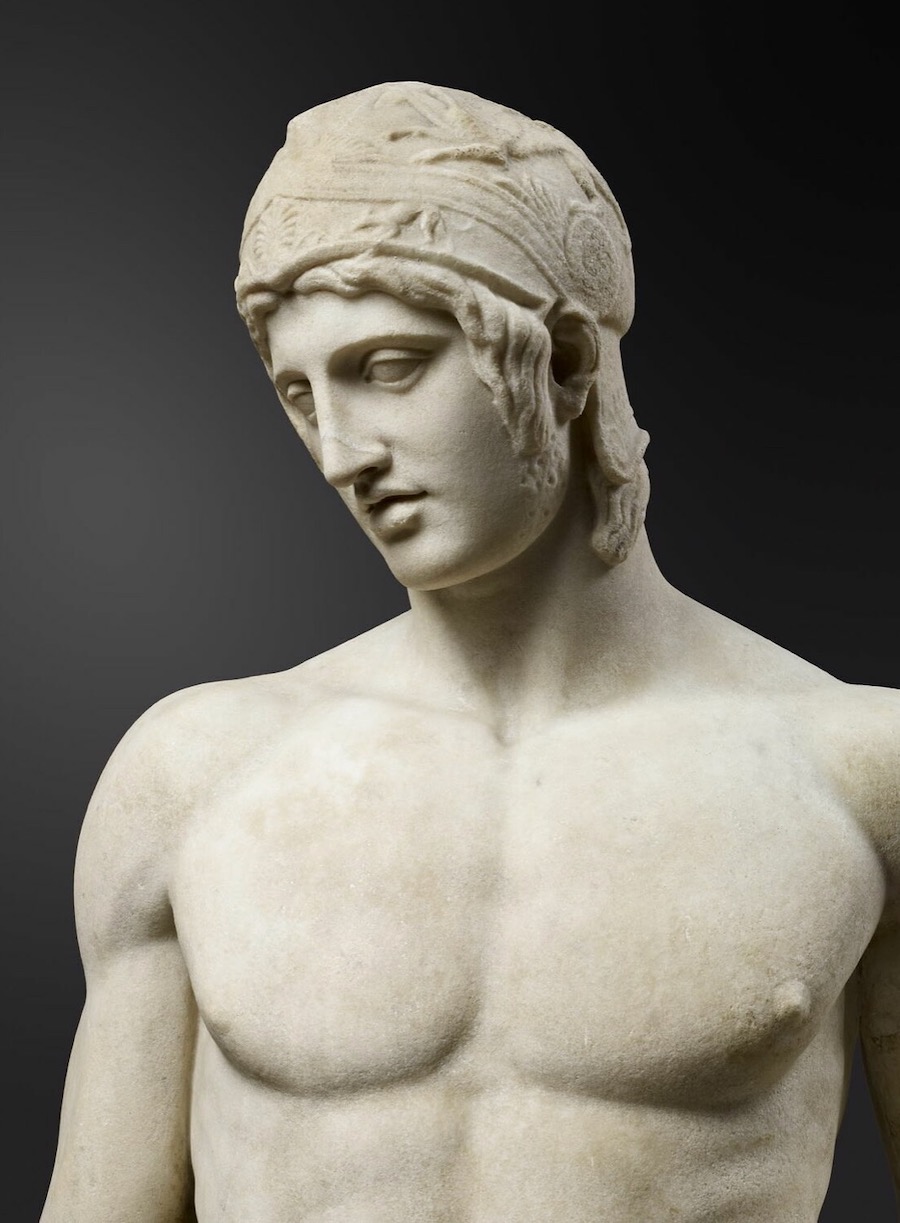


The Youth is primed both to Reproduce -- and to Kill.

Ares and Aphrodite
with their son Eros
at Pompeii
EROS
To the Greeks,
Eros was a muscular adolescent ;
To the Romans,
he was Cupid, a pudgy little boy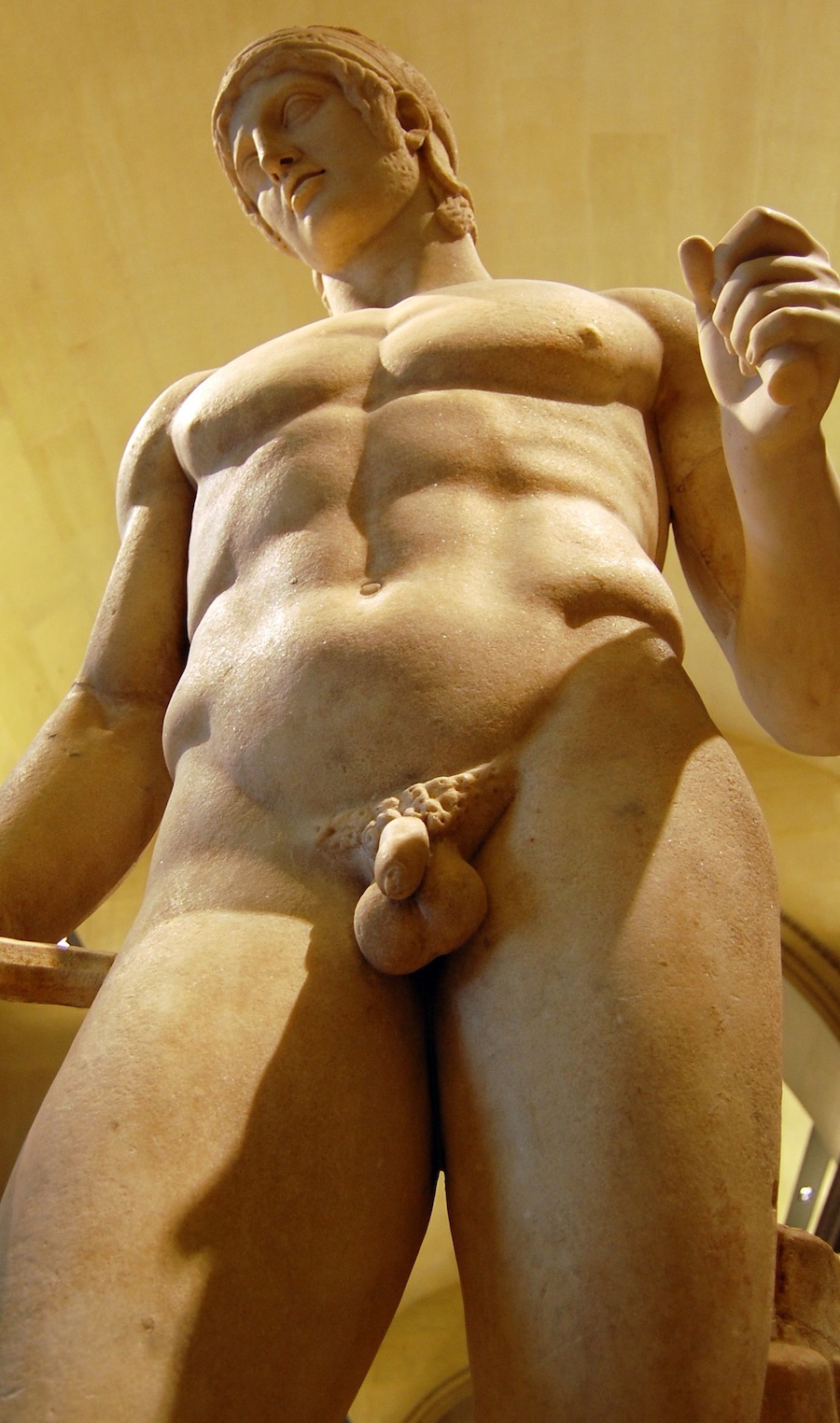
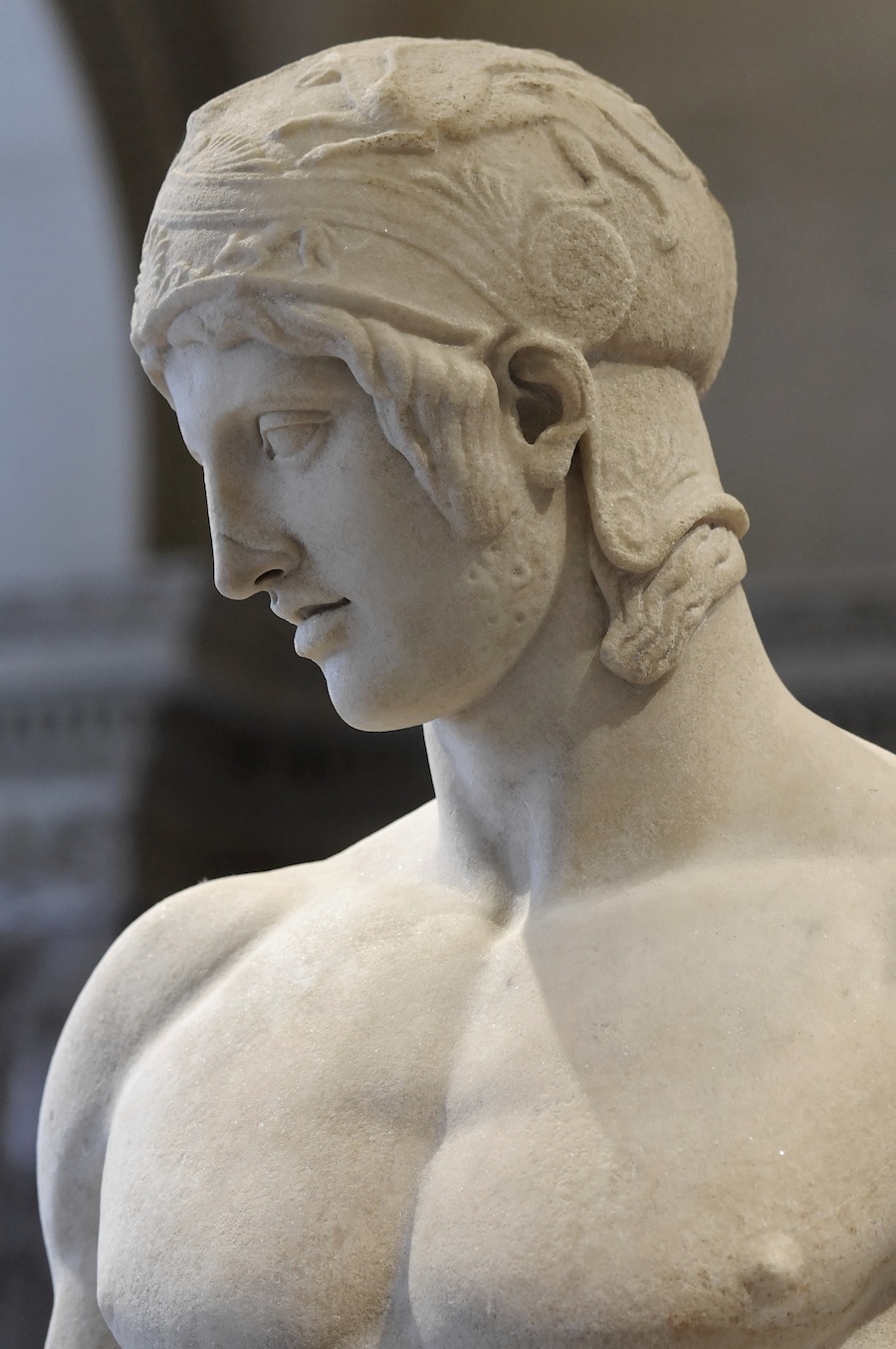
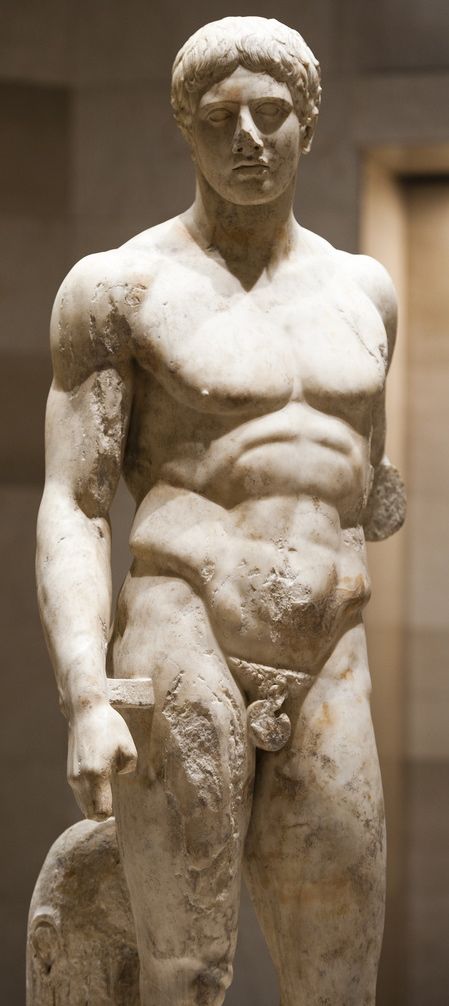
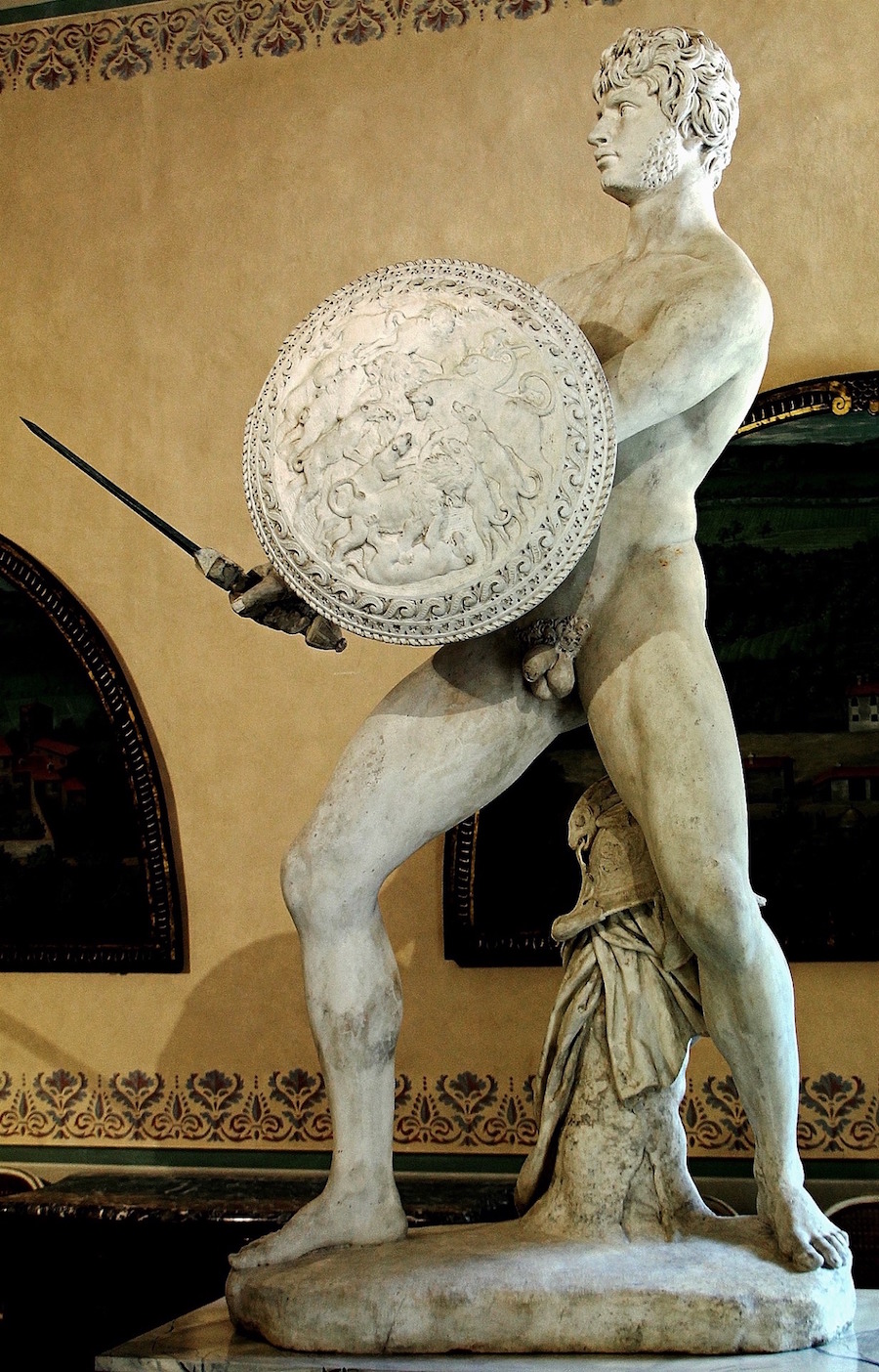

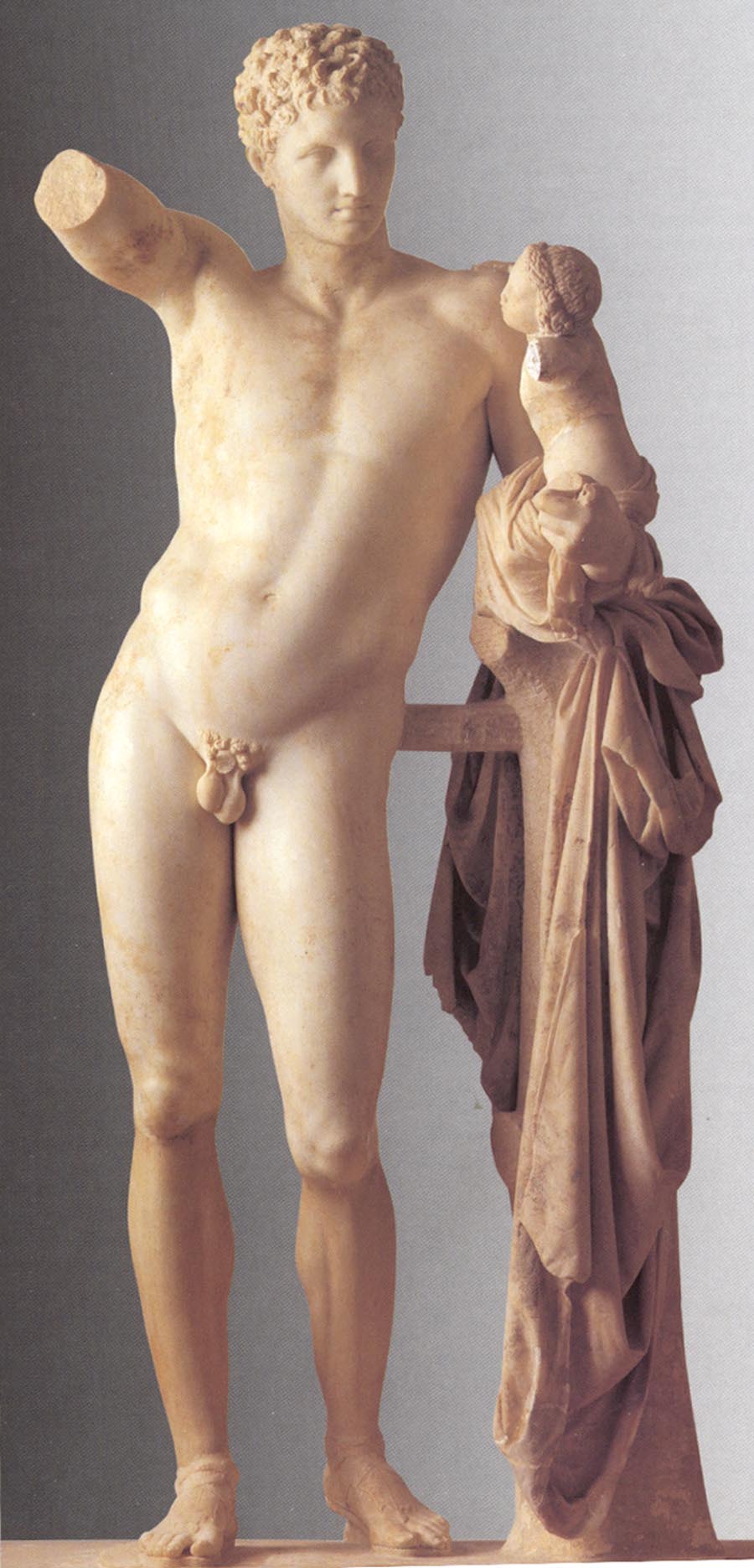







"Strong he is, for strong he deems himself"
~Virgil, referring to a True Warrior
Strong they are, for strong they deem themselves


THE TRAINING UP
OF THE YOUTH
FOR WAR
FIT VIA VIS
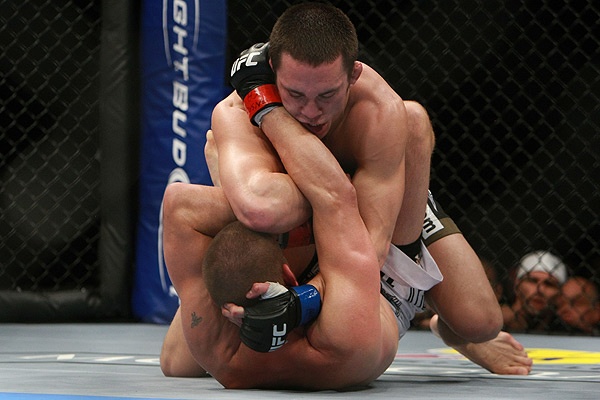



FIT VIA VIS


























PALAESTRA

Classrooms grouped around Fight Pits
other Boys Excercising and Fighting Nude
The Ephebeion in the Palaistra at Priene
and military exercises, but so were those of most other ephebic systems.
time of Homer, military preparedness was required of all ephebes everywhere
because they formed the military reserve force for their cities.
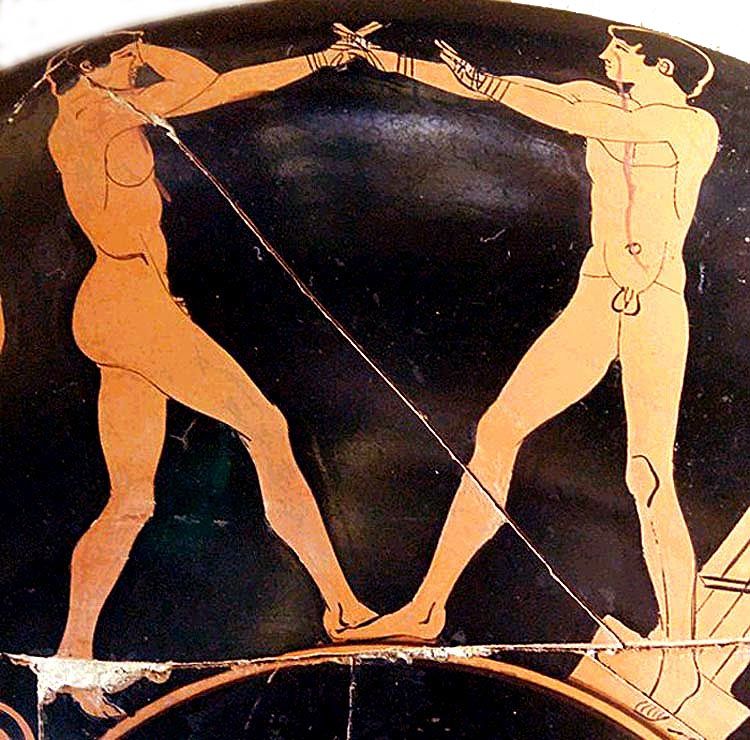
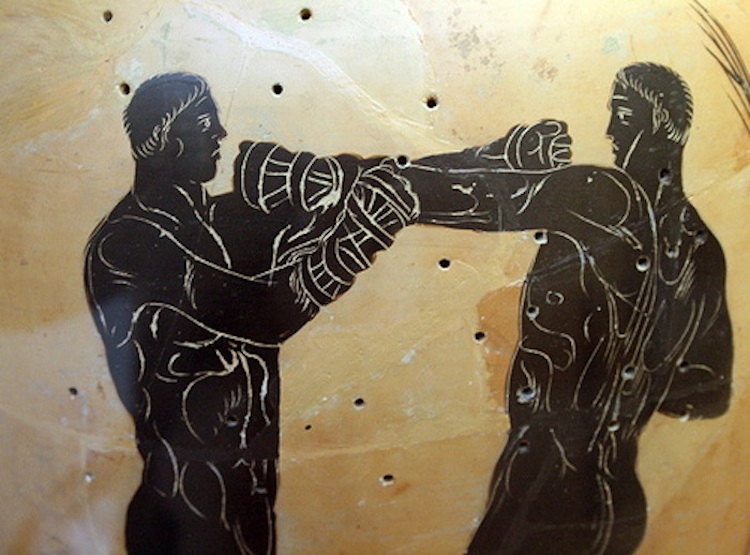
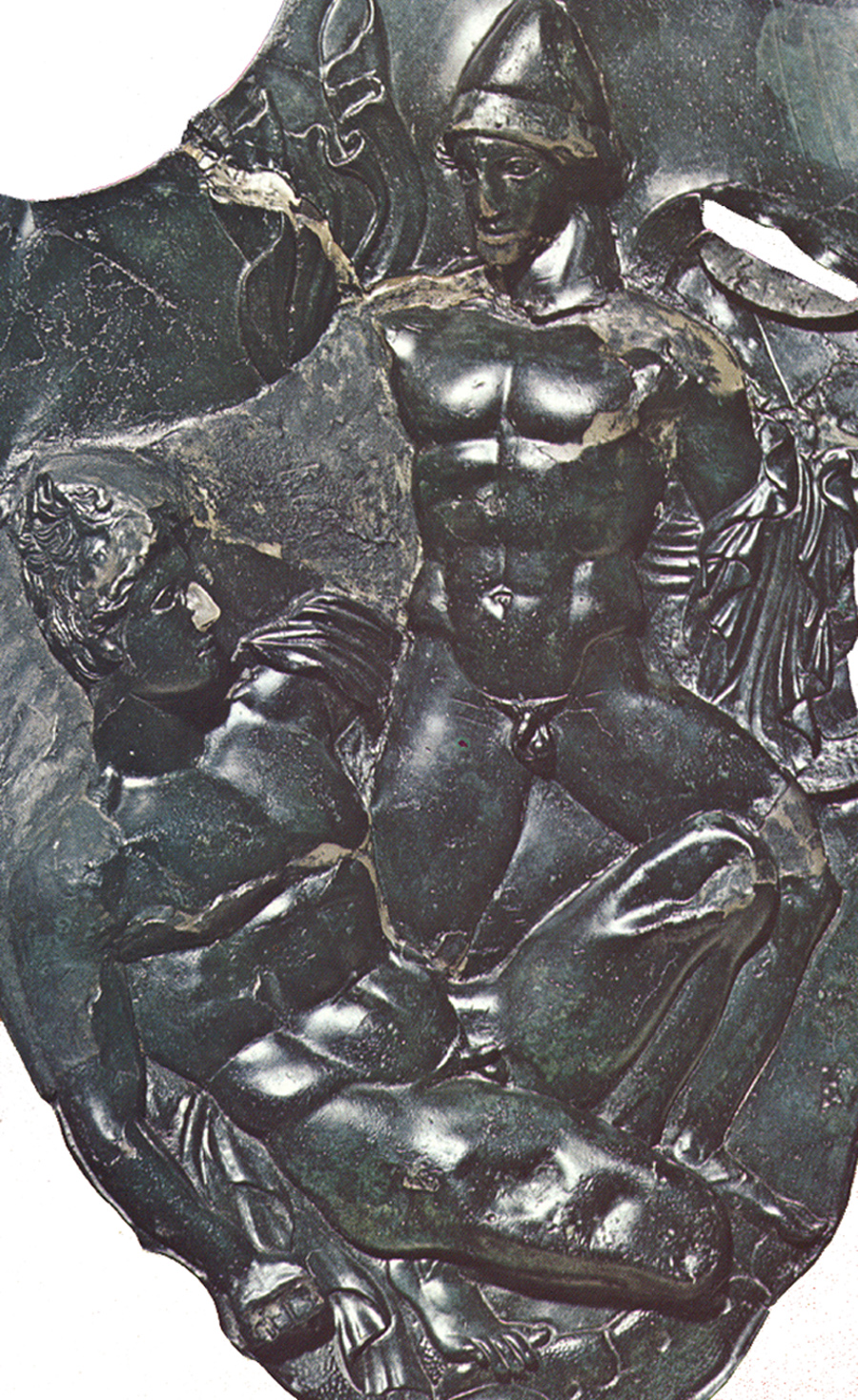







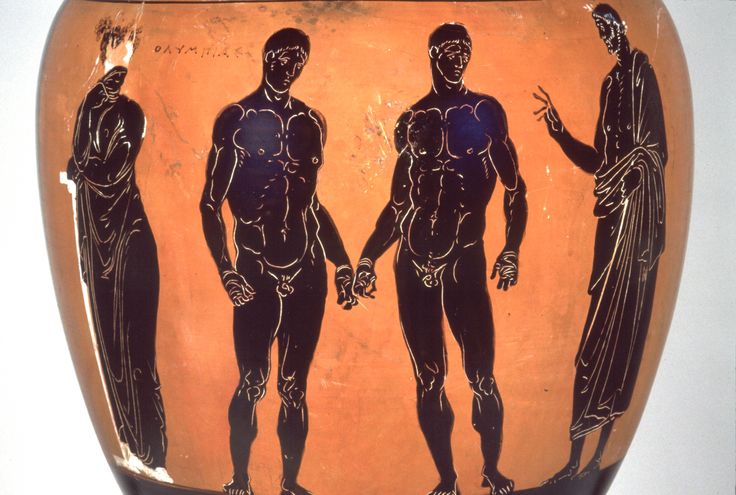







GLUTES
AND THE



Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD






Is this the body of a Pankratiast ?
and requiring on the part of the contestants unusual physique and condition"
"Muscles in your legs help power the rotation that occurs when you throw a punch.
Your glute muscles are not only the biggest muscles in your body,
but they're the largest muscles in your hip." -- FightCamp.com

The muscles in Deinomachos' left buttock are tensed because he's holding,
with his left hand and arm, a hoplon, a hoplite shield, which is very heavy.
The strength in Deinomachos' glutes and hams enables him
to kick and punch with explosive and violent bodily force.
While the muscles in his right buttock are tensed because he's taking a step forward with his right leg :

Alkamenes' portrait of Deinomachus, who would become the God Ares, is,
anatomically and in every other way, painstakingly correct.
A Fighter, a Fighting Man
Deinomachos' pecs, delts, bi's, tri's, and forearms are beefy --
but not over-developed.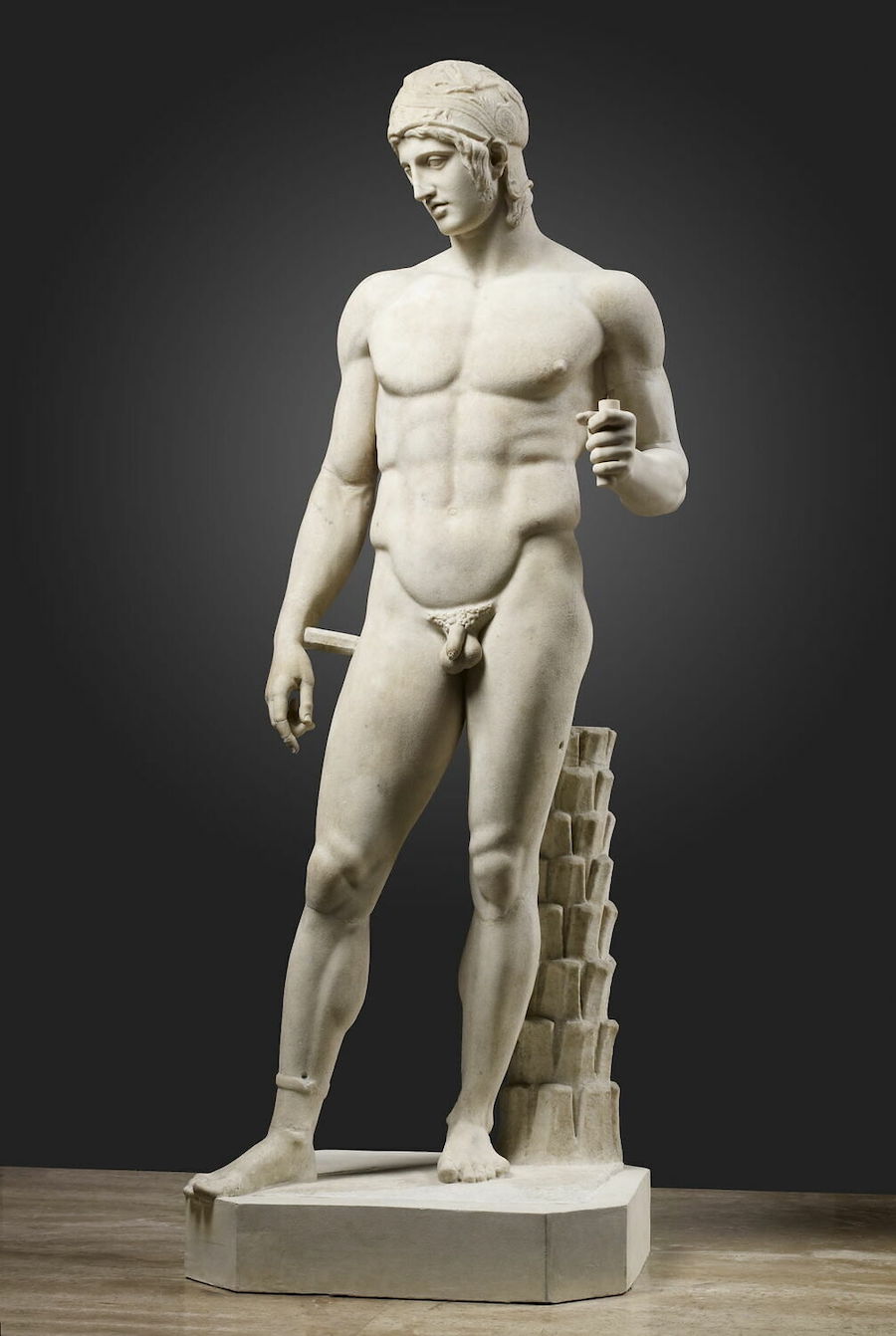
The muscles on the left side of Deinomachos' body
are tensed so he can hold the hoplon.
Deinomachos has the body of a Pankratiastes
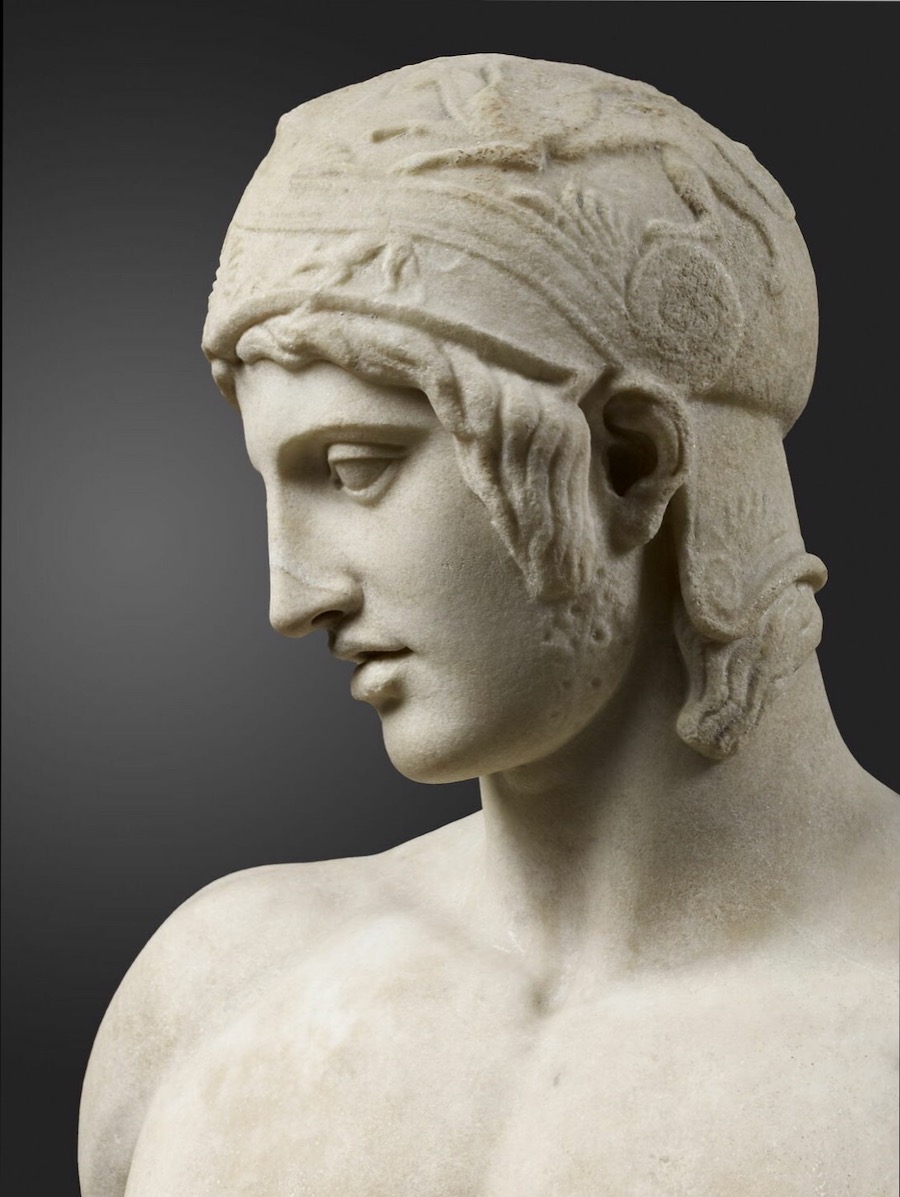

A 19-year-old Pankratiastes,
with abundant head hair growing under his helmet,
and facial hair beginning to appear on his lower jaw.
At 19, Deinomachos is in the last year of his Ephebate.
And the musculature on his adolescent combatant body is spectacular.
We can see this particularly in the development of his massive gluteus muscles.
Wrestlers naturally develop good glutes for pushing, shoving, throwing and picking up an opponent for a toss.



Deinomachos' glutes are larger -- the result of ephebic training in multiple fight skills --
and of a pre-industrial-revolution technological environment
which required walking, running, and fighting
in the hilly and mountainous terrain of ancient Greece ;
often while holding or wearing the heavy weapons and armor of the hoplite panoply.


Lord Ares too
holds and wears
hoplite equipment.


running stairs prepares the glutes, quads, and calves
for the explosive violence of Fight



Notice the two "arrows" at the base of Deinommachos' spine,
visible only on the bodies of exceptionally ripped athletes.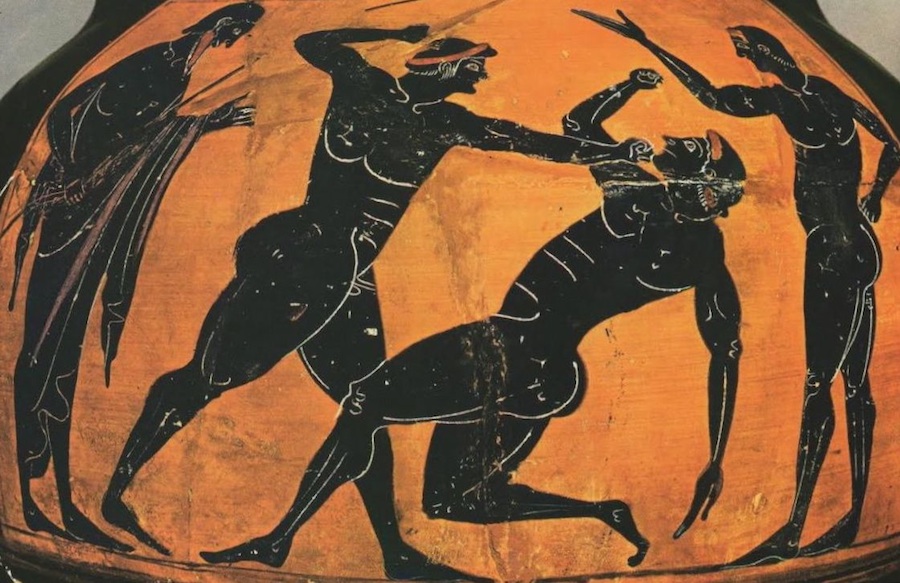
The bodies of ancient Greek athletai were exceptionally well prepared to Fight --
Particularly in the lower body, the Glutes and Hams
Broad Chests and strong Glutes and Hams --
Contributed to the explosive bodily force needed by Pankratiasts





IRREDUCIBLE
MALENESS
OF HIS BODY
IRREDUCIBLE
MALENESS
OF HIS SPIRIT
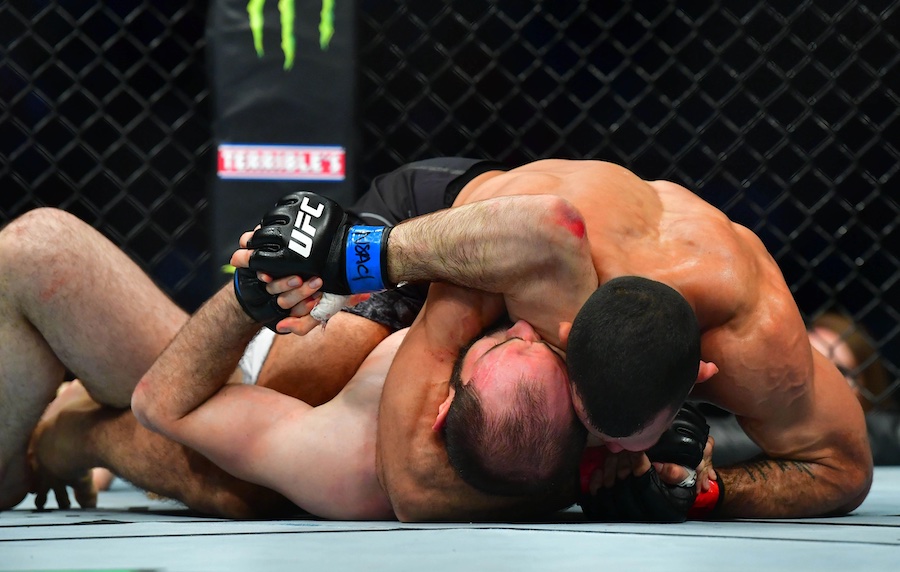


Lord Ares and his Son Eros
Are also the Gods of How
Manly Men Make Love
~NW
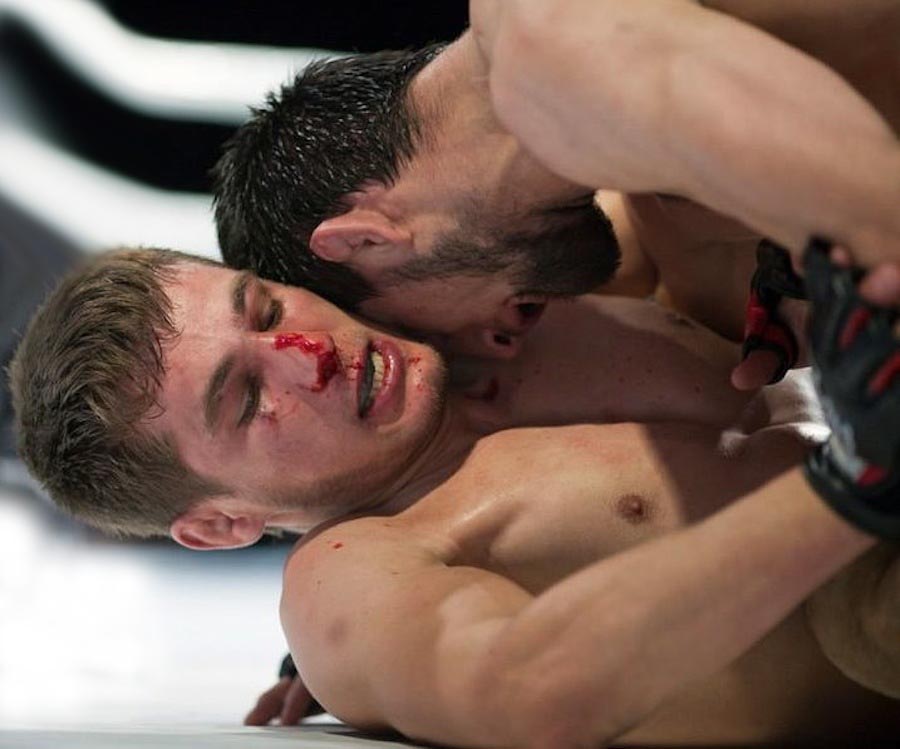
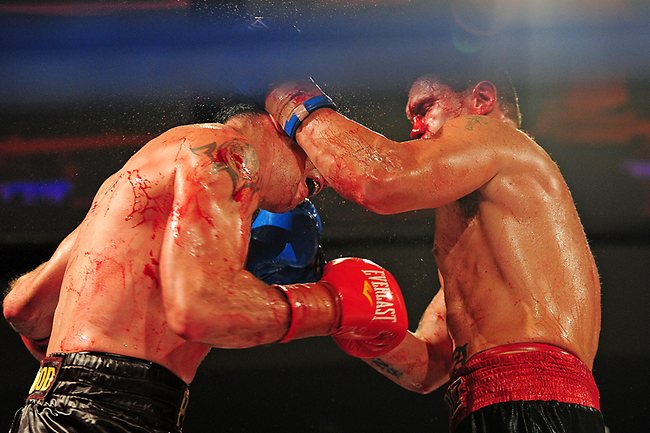
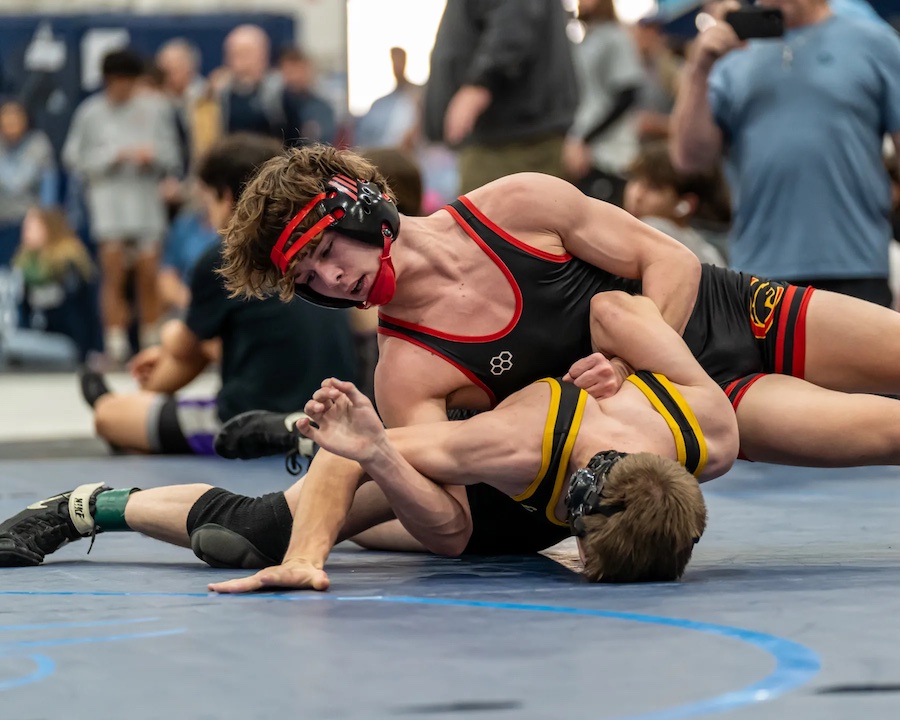
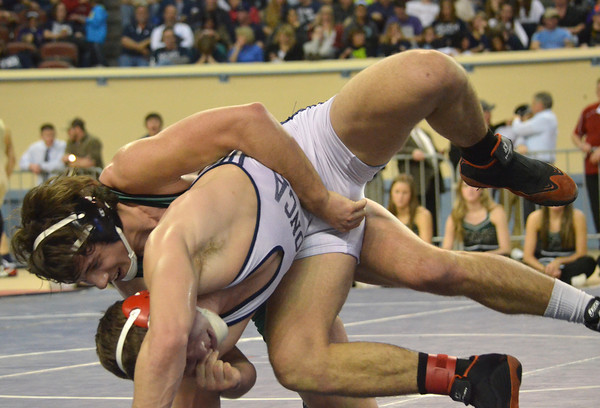



















Deinomachus' powerful glutes of 425 BC remain
stronger, fuller, bigger, than those of
the athletes of 2024 AD
"Strong he is, for strong he deems himself"
~Virgil, who was raised among such Men
for his mother the price tags on various items of merchandise : $6.95, 11.95, 7.95, etc.
but always by the willingness and ability to fight.

Man Flex
In Flexing, the Fighter affirms his own Strength
while challenging and intimidating his opponentPOSSUNT, QUIA POSSE VIDENTUR

Is this the body of a Pankratiast ?
"a severe athletic contest involving a combination of boxing and wrestling,
and requiring on the part of the contestants unusual physique and condition"
"Muscles in your legs help power the rotation that occurs when you throw a punch.
Your glute muscles are not only the biggest muscles in your body,
but they're the largest muscles in your hip." -- FightCamp.com

The muscles in Deinomachos' left buttock are tensed because he's holding,
with his left hand and arm, a hoplon, a hoplite shield, which is very heavy.
The strength in Deinomachos' glutes and hams enables him
to kick and punch with explosive and violent bodily force.
While the muscles in his right buttock are tensed because he's taking a step forward with his right leg :

Alkamenes' portrait of Deinomachus, who would become the God Ares, is,
anatomically and in every other way, painstakingly correct.
A Fighter, a Fighting Man
Deinomachos' pecs, delts, bi's, tri's, and forearms are beefy --
but not over-developed.
The muscles on the left side of Deinomachos' body
are tensed so he can hold the hoplon.
Is this the body of a Pankratiastes ?

This youth or boy victor holds a jar of olive oil, probably a prize in the Panathenaic Games
His nudity strongly suggests that he won in a combatant gymnikos agon --
boxing, wrestling, pankration










In this and the painting above,
the Glutes are particularly pronounced.




ADOLESCENT
EROS
Breadth of Chest
Strength of Lower Body
A Boy Victor
Broad Chest
Strong Glutes and Hams










IRREDUCIBLE
MALENESS
OF HIS BODY















This is a so-called transsexual, a "trans" :
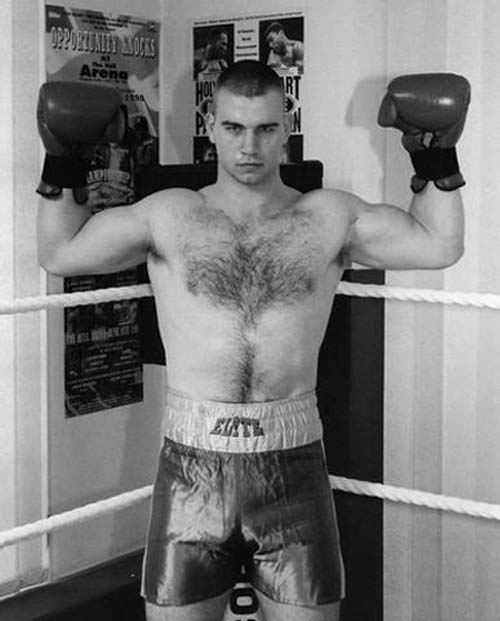


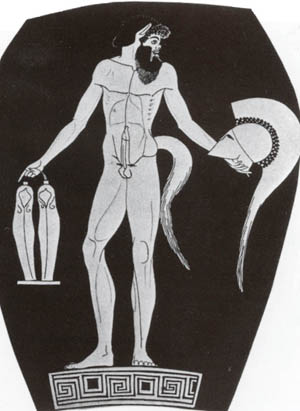






ARES
God of Fight and of Fighting Manhood
The Overwhelming Eagerness and Ardor to Fight of Young Men,
Youths in the Full and Fresh Bloom of Their Young Manhood,
Their Fighting Manhood
Than The Primal Love of Fight of Young Fighting Men

The Brutality and Blood-Soaked Violence of Fight

The Pride, the Valour, and above-all Beautiful and Essential Goodness of Men who Fight, and of Fight Itself
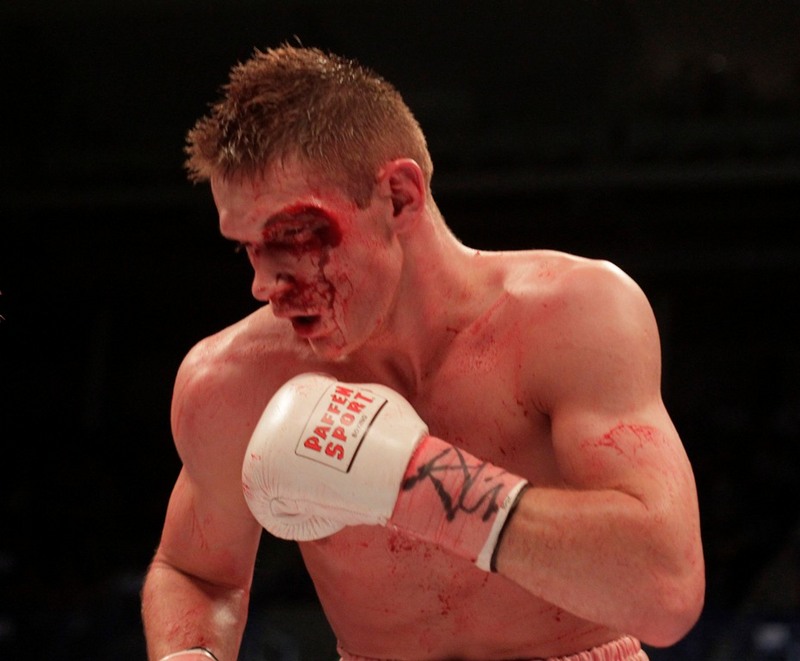

Pugnator InvictusIndomitable Fighter
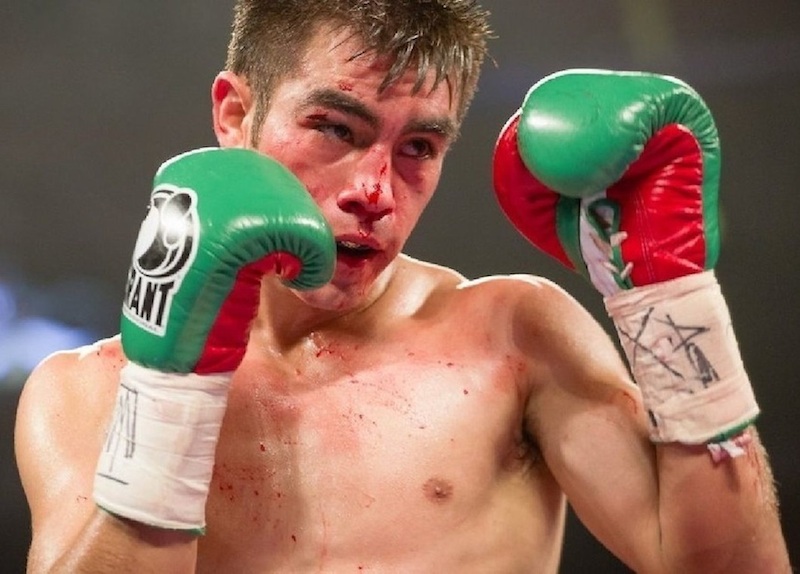

The Youth's Unwavering Trust in the Power of His Young Manhood
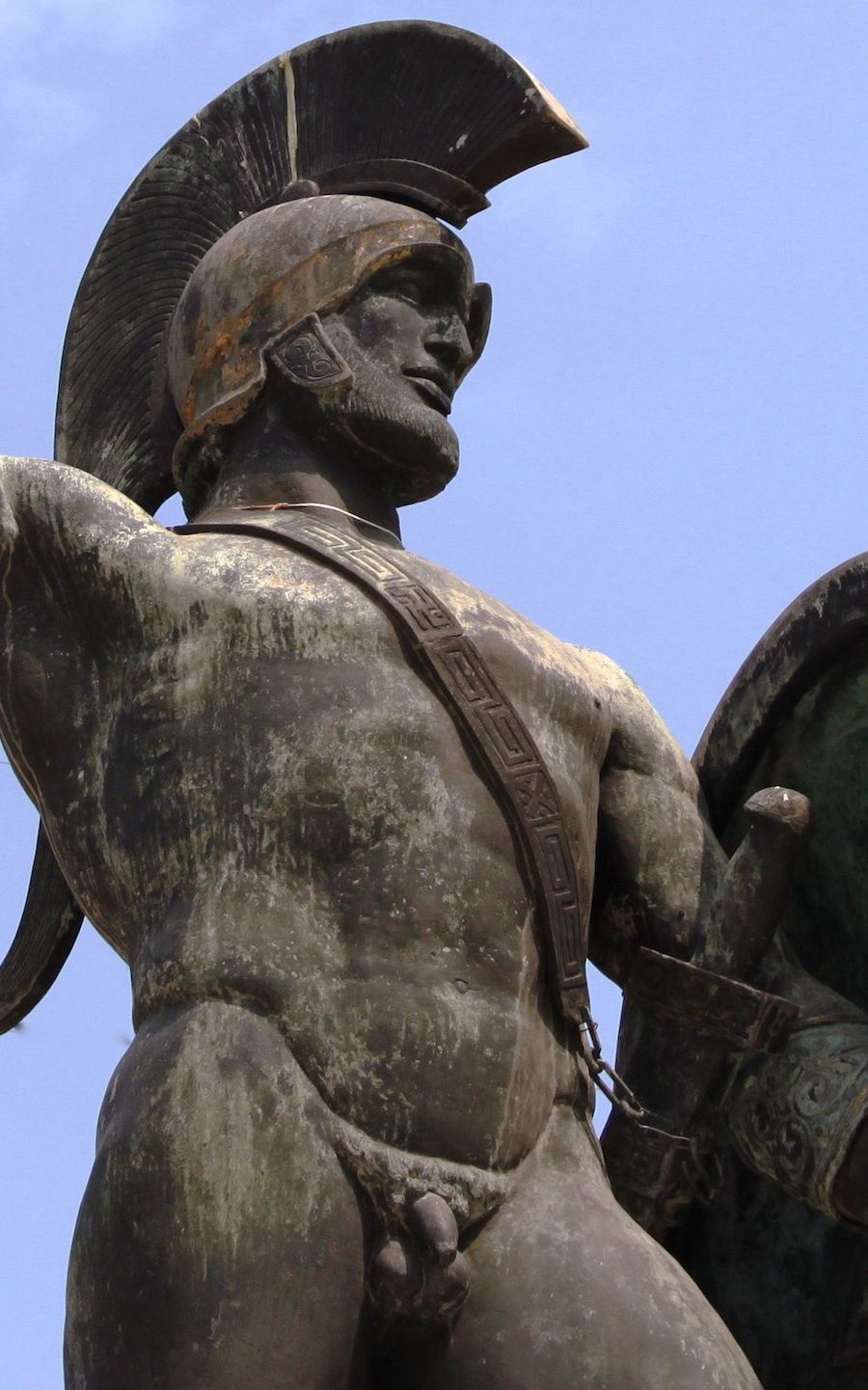

Leonidas of Sparta, of whom Aristotle says
Honour is the Prize of Manhood
and
The Tribute We Pay to the Manly
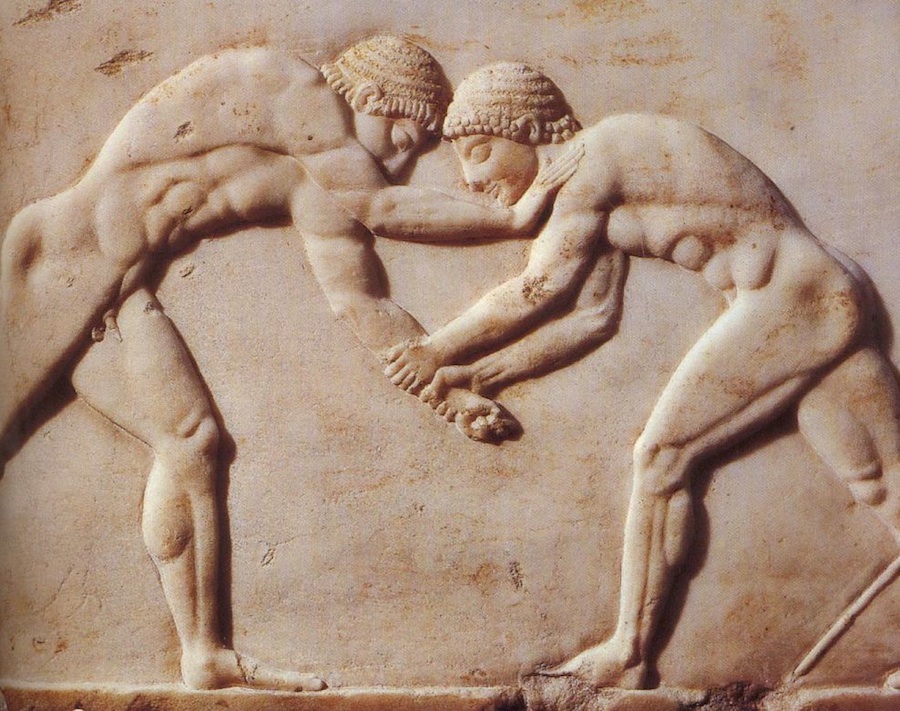
This bas-relief -- ca 525 BC -- of Combatant Youths locked in a Wrestling Tie-Up -- their eyes on each other's naked groins
-- epitomizes the mix of Muscular Athleticism and Martial Homoeroticism which was the Manly, and Romantic, Love of ancient Greece.


The Yearning for Manfight is the Yearning for Manhood
For the Manly Virtue of Manhood can only be conferred through Manfight
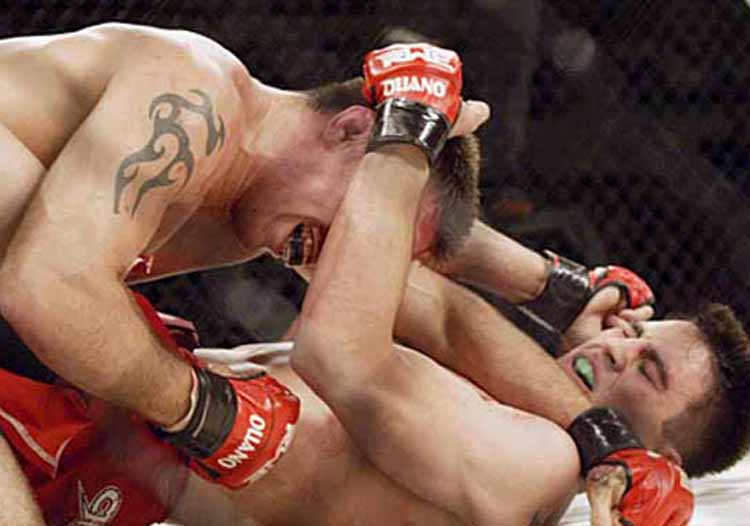


TWO MEN STRENUOUSLY STRUGGLING TO PERFECT THEIR MANHOOD IN VICTORY
THERE IS NO VIRTUE WITHOUT FIGHT, AND THERE IS NO FIGHT WITHOUT VIRTUE





















αγαπη
Discussion :
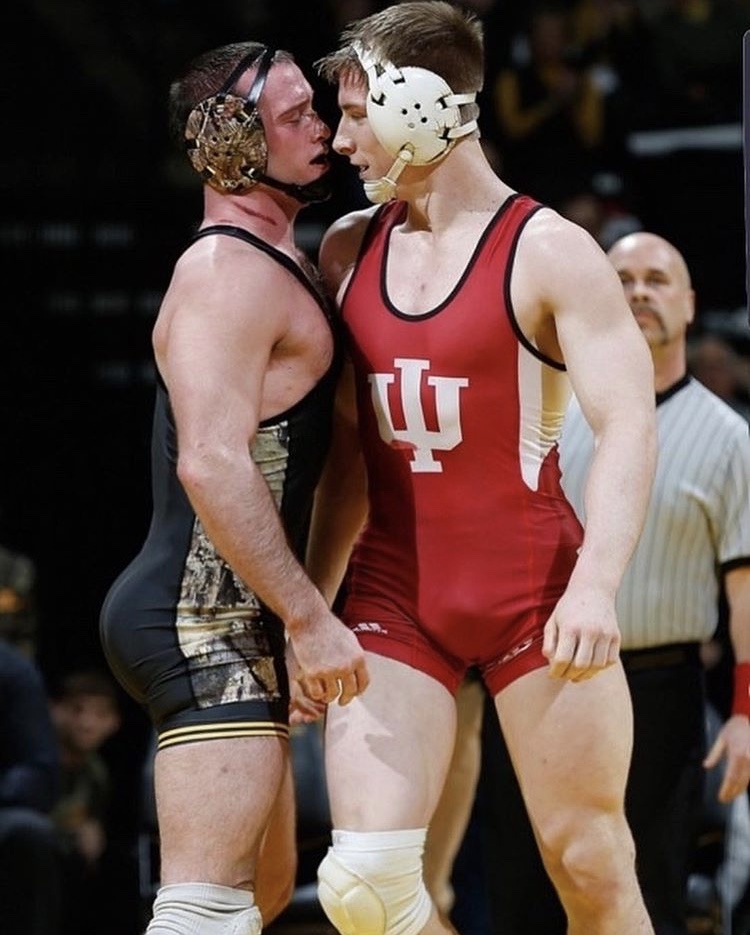
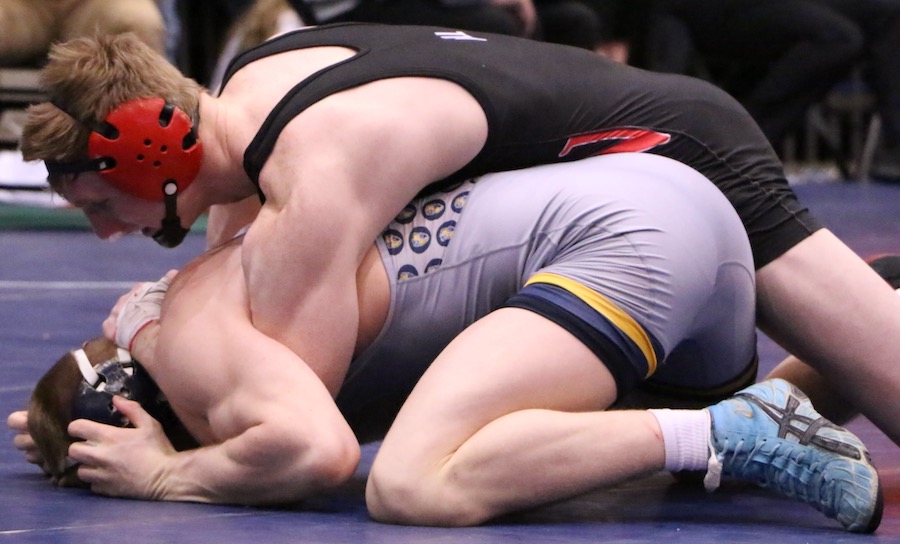



[I]f an eye [ophthalmos] is to see [eidon] itself [autos] it must look at an eye, and at that region [topos] of the eye in which the areté [excellence] of an eye is found to occur ; and this, I presume, is sight [opsis -- eyesight, vision].
[I]f, again, you asked me, "What becomes present in a better [ameinon -- irr. comp. of agathos, which is the adjectival form of Areté -- thus, more excellent] condition of the eyes?" -- I should answer in just the same way, "Sight [opsis] becomes present, and blindness [tuphlotes] absent." So, in the case of the ears [ous], deafness [kophotes] is caused to be absent [apo-gignomai], and hearing [akoe] to
be present [para-gignomai], when they are improved [beltio-o] and getting better treatment.
[Areté is] goodness, excellence, of any kind, esp. of manly qualities, manhood, valour, prowess (like Lat. virtus, from vir)
From the same root [ARES] come areté, ari-, areion [better -- stronger, braver, more Manly], aristos [best -- strongest, bravest, most Manly], the first notion of goodness being that of manhood, bravery in war; cf. Lat. virtus.
Vigor, strength, might, power, potency ; Valour, gallantry, fortitude ; Virtue, goodness, moral perfection, high character ; Value, merit, worth.
Manliness, Manhood : Vigor, strength, might, power, potency ; Valour, gallantry, fortitude ; Virtue, goodness, moral perfection, high character ; Value, merit, worth.



[Areté is] goodness, excellence, of any kind, esp. of manly qualities, manhood, valour, prowess (like Lat. virtus, from vir)
From the same root [ARES] come areté, ari-, areion [better -- more Manly], aristos [best -- most Manly], the first notion of goodness being that of manhood, bravery in war; cf. Lat. virtus.

Cheiron and Achilles


The Kynegetikos is full of Xenophon's zest for hunting, his pietism [devotion to the Gods], his insistence that before you try to do a thing you must understand how to do it, and, above all, his belief in the efficacy of diligence and toil [ponos].
Give the hounds short names, so as to be able to call to them easily. The following are the right sort: Psyche [Spirit], Thymus [Fighting Spirit], Porpax [Shield Handle], Styrax [Spike], Lonche [Lance], Lochus [Ambush], Phrura [Look-Out], Phylax [Guardian], Taxis [Battle Array], Xiphon [Sword], Phonax [Eager for Blood], Phlegon [Blaze], Alke [Valour], Teuchon [Implement of War], Hyleus, Medas, Porthon [Destroyer], Sperchon [Hasty], Orge [Wrath], Bremon [Growler or Howler], Hybris [Wanton Violence], Thallon [Bloomer], Rhome [Might], Antheus [Blossom], Hebe [Youthful Strength, Vigour], Getheus [Joy], Chara [Delight], Leusson [Stoner], Augo [Shine], Poleus [Translator's note : Rover], Bia [Strength, Force, Violent Force], Stichon [Row of Soldiers], Spoude [Speedy], Bryas [Swell], Oenas [Ace], Sterrus [Rugged], Krauge [Howler], Kainon [Killer], Tyrbas [Brawler], Sthenon [Strong], Aither [Sky], Aktis [Sunbeam], Aichme [Spear-point], Noes [Translator's note : Counsellor], Gnome [Judgement], Stibon [Tracker], Horme [Attacker].
an anticipation of the future areté -- the future Manly Excellence -- of its bearer ; it set, as it were, the ideal pattern for his whole life.
an anticipation of the future areté -- the future canine excellence -- of its bearer ; it sets the ideal pattern for his whole life.
Fighting Spirit, Shield, Spike, Lance, Ambush, Look-Out, Guardian, Battle Array, Sword, Eager for Blood, Blaze, Valour, Implement of War, Destroyer, Wrath, Growler, Violent, Might, Youthful Strength, Vigour, Strength, Violent Force, Row of Soldiers, Speedy, Swell, Ace, Rugged, Howler, Killer, Brawler, Strong, Spear-point, Judgement, Tracker, Attacker.
[12.1] With the practical side of hunting I have finished. But the advantages that those who have been attracted by this pursuit will gain are many. For it makes the body [soma] healthy [hygieia], improves the sight and hearing, and keeps men from growing old ; and it affords the best training [paideuo] for war [polemos].
It was because they knew that they owed their successes against the enemy to such qualities that our ancestors [progonoi] looked after [epimeleia] the young men [neoi]. . . . In fact they saw that this is the only one among the pleasures [hedone] of the younger men that produces a rich crop of blessings [agathoi -- Manly Goods].
[hunting] is the only one among the pleasures [hedonai] of the younger men that produces a rich crop of agathoi -- Manly Goods.
Bill Weintraub:
[hunting] is the only one among the pleasures [hedonai] of the younger men that produces a rich crop of agathoi -- of Manly Goods.
(and they -- the progonoi -- the ancestors -- perceived that to these Men -- that is, to Morally Ordered Men -- they owed their success in war, as in other matters) ; and it does not rob them of any other Honourable and Morally Beautiful occupation they wish to follow, as do other and evil pleasures that they ought not to learn. Of such Men, therefore, are Manly, that is, Willing and Able to Fight, citizen-soldiers and citizen-generals made.
In many details, the ethical doctrines of Plato and Aristotle were founded on the aristocratic morality of early Greece . . . . The class limitations of the old ideals were removed when they were sublimated and universalised by philosophy : while their permanent truth and their indestructible ideality were confirmed and strengthened by that process.






].








They must keep themselves physically fit too, since their rivalry actually makes them come to blows when they meet.
At Hom. Il. 3.181, Lattimore translates κυνωπις as slut -- which of course is right : a slut is a woman who is shamelessly promiscuous.
Xenophon's analysis of honour as a method of ruling is more extended and profound than that of any later author.
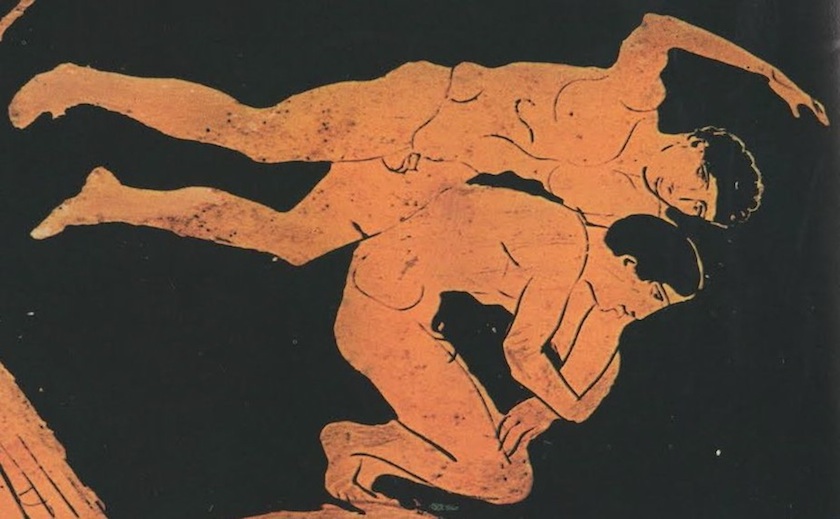

Pleis derives from Pleistos = most ; and Sthenes from Sthenos = strength, might, of all kinds, moral as well as physical :
Plei-sthenes -- the most strength, the most might -- the name spells out the Warrior's Moral Strength and Physical Power.
(While A-sthenes means wanting strength, weak, feeble -- think of an a-sth-matic.)
It is a fact that men desert their fellow tribesmen and relatives and even (God knows) their parents and children ; but lover and beloved, when their God is present [entheos -- when they're in-Godded, filled with their God, have their God within], no enemy has ever encountered and forced his way through.
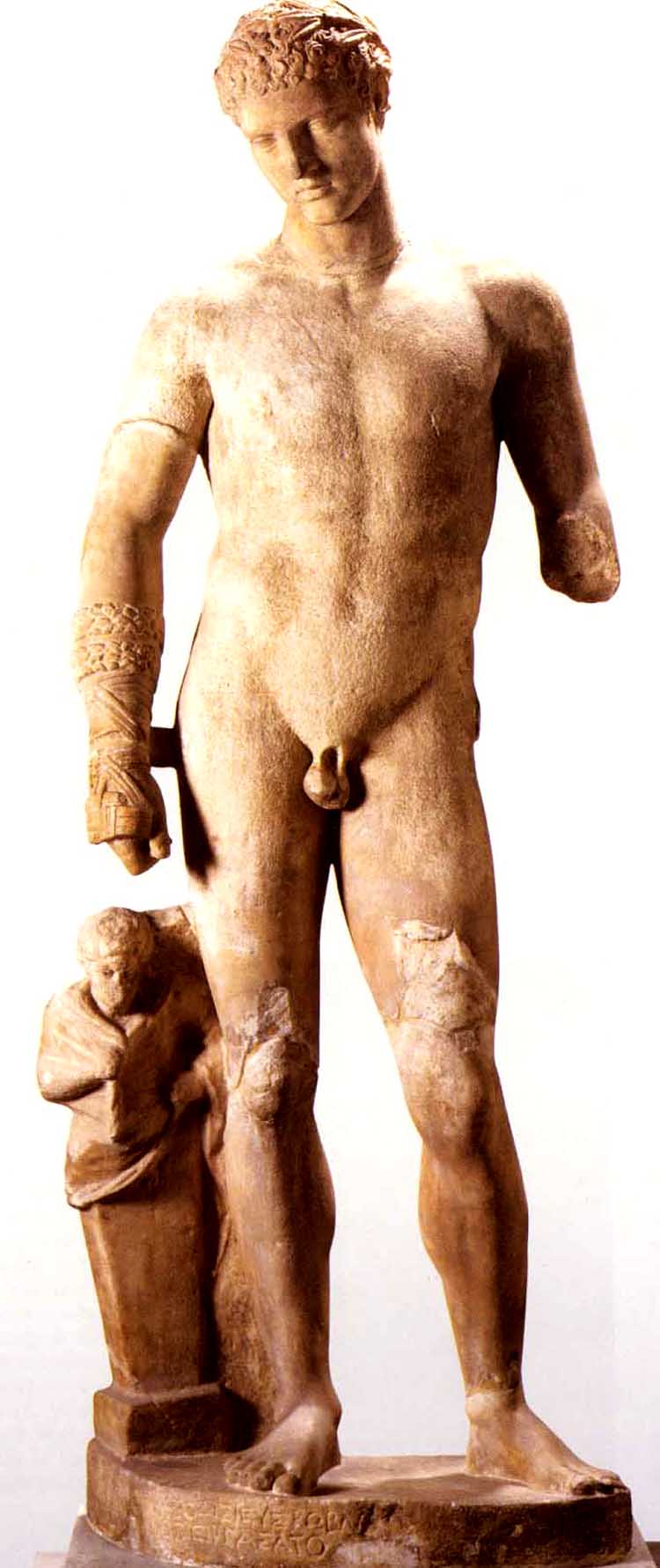
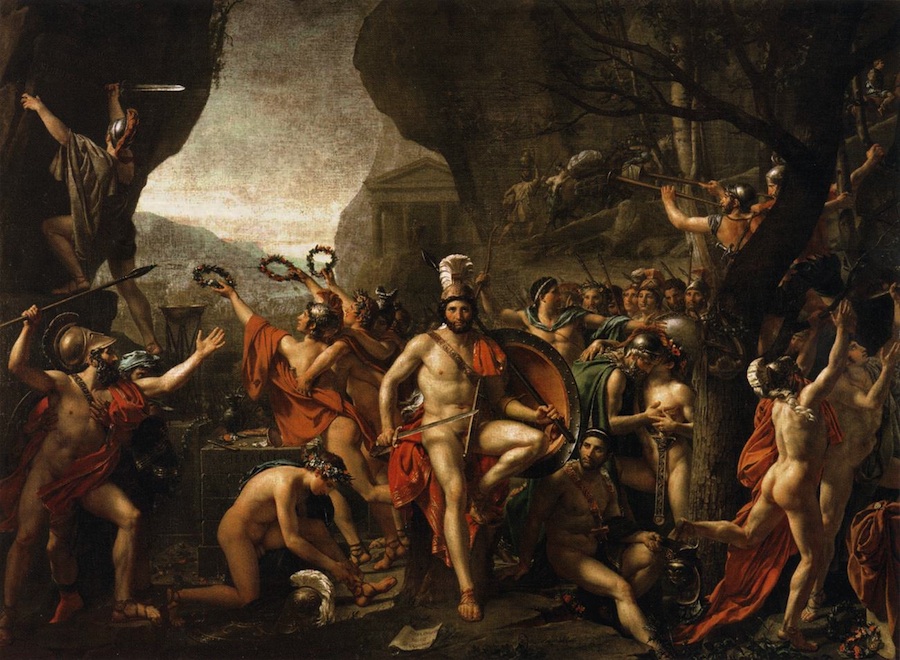











All rights reserved.

Special Warfare Operator First Class Daniel Swift :



All rights reserved.